1 - inetTeacher
... 18. Sesostris III super forts can or cannot be visited? 19. Egyptian obelisks were moved by roads or during the yearly floods of the Nile? 20. How did ancient Egyptians move obelisks? We don’t know for sure or ...
... 18. Sesostris III super forts can or cannot be visited? 19. Egyptian obelisks were moved by roads or during the yearly floods of the Nile? 20. How did ancient Egyptians move obelisks? We don’t know for sure or ...
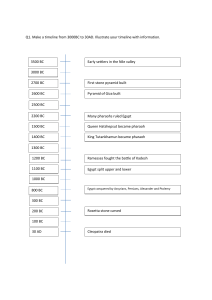
Q1. Make a timeline from 3000BC to 30AD. Illustrate your timeline
... plant known as papyrus. They cut the plant and made strips of them and then they put a cloth over it. They wrote with reed pens. Egyptians wore cotton clothes and liked wearing necklaces, gold and other jewellery. They used to make pottery on a wheel and baked it till it was very hard. They built ho ...
... plant known as papyrus. They cut the plant and made strips of them and then they put a cloth over it. They wrote with reed pens. Egyptians wore cotton clothes and liked wearing necklaces, gold and other jewellery. They used to make pottery on a wheel and baked it till it was very hard. They built ho ...
Bellringer
... • Near the end of the Old Kingdom, governors in the provinces began to challenge the power of the pharaohs • Egypt’s unity crumbled and the dynasties grew weak • Early dynasties of the Middle Kingdom restored order and united the kingdom • Pharaohs spent money on irrigation projects and built a cana ...
... • Near the end of the Old Kingdom, governors in the provinces began to challenge the power of the pharaohs • Egypt’s unity crumbled and the dynasties grew weak • Early dynasties of the Middle Kingdom restored order and united the kingdom • Pharaohs spent money on irrigation projects and built a cana ...
Egypt`s Empire
... territories. B. The military took over _________ in the south as well as present-day Syria. C. Pharaohs required __________, forced payments, in order to increase farming and build a canal to increase trade. III. Art and Architecture A. With the riches from trading, money was spent on the __________ ...
... territories. B. The military took over _________ in the south as well as present-day Syria. C. Pharaohs required __________, forced payments, in order to increase farming and build a canal to increase trade. III. Art and Architecture A. With the riches from trading, money was spent on the __________ ...
homework_10-3 - WordPress.com
... Isis. Egyptians believed that the gods controlled the universe. Therefore, it was important to keep them happy. They could make the Nile overflow, cause famine (a period with no rain and thus crops cannot grow), or even bring death. (1) The Egyptians also elevated some human beings to gods. Their le ...
... Isis. Egyptians believed that the gods controlled the universe. Therefore, it was important to keep them happy. They could make the Nile overflow, cause famine (a period with no rain and thus crops cannot grow), or even bring death. (1) The Egyptians also elevated some human beings to gods. Their le ...
2.1 Why was Ancient Egypt such a successful civilization?
... land that is known as the delta. This gives the river the shape like the lotus flower that is so often seen in ancient Egyptian art. The ancient Greeks spoke with envy when they referred to Egypt as “the Gift of the Nile.” Thanks to the Nile, these ancient people had fresh water for drinking and bat ...
... land that is known as the delta. This gives the river the shape like the lotus flower that is so often seen in ancient Egyptian art. The ancient Greeks spoke with envy when they referred to Egypt as “the Gift of the Nile.” Thanks to the Nile, these ancient people had fresh water for drinking and bat ...
Daily Life in Ancient Egypt
... Men supported the family and trained their sons to take on their line of work. Women raised the children. Upper class women had servants or slaves. – Egyptian women had more rights that in other societies. They could: ask for divorces, represent themselves in legal matters, upper and middle class wo ...
... Men supported the family and trained their sons to take on their line of work. Women raised the children. Upper class women had servants or slaves. – Egyptian women had more rights that in other societies. They could: ask for divorces, represent themselves in legal matters, upper and middle class wo ...
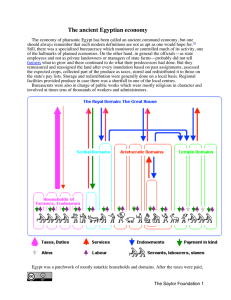
The Ancient Egyptian Economy
... minority and the stone quarried for temples and tombs served the same class of people and profitted only the craftsmen involved in building. Natron needed for the embalming process, was mined in the Wadi Natrun. Embalming was too expensive for all but a few. Commerce and banking Egypt, Retenu and Nu ...
... minority and the stone quarried for temples and tombs served the same class of people and profitted only the craftsmen involved in building. Natron needed for the embalming process, was mined in the Wadi Natrun. Embalming was too expensive for all but a few. Commerce and banking Egypt, Retenu and Nu ...
Egypt-The Gift of the Nile
... The New Kingdom is also called the Empire Age, due to the vast land that was conquered Conquered people paid taxes so the kingdom also became very wealthy With the money they built temples, palaces, and statues ...
... The New Kingdom is also called the Empire Age, due to the vast land that was conquered Conquered people paid taxes so the kingdom also became very wealthy With the money they built temples, palaces, and statues ...
Egypt and the Nile River Valley System
... – At the bottom was Greek (which the archaeologists could read) – In the middle was Demotic-a later Egyptian writing (which could ...
... – At the bottom was Greek (which the archaeologists could read) – In the middle was Demotic-a later Egyptian writing (which could ...
egypt and nile river power point
... – At the bottom was Greek (which the archaeologists could read) – In the middle was Demotic-a later Egyptian writing (which could ...
... – At the bottom was Greek (which the archaeologists could read) – In the middle was Demotic-a later Egyptian writing (which could ...
File
... • Egyptians celebrated the 3 stages: • Inundation (flooding which usually lasted 4 months) • Emergence (planting & growing) • Harvest (collecting the food) ...
... • Egyptians celebrated the 3 stages: • Inundation (flooding which usually lasted 4 months) • Emergence (planting & growing) • Harvest (collecting the food) ...
Egypt Old Kingdom notes
... • Ordinary tombs were seen as unsuitable for Pharaohs. • Egyptian decided to build pyramids (huge stone tomb) for their pharaohs resting spot. • Pyramids were built to protect the bodies of Pharaohs from flood, animals, and grave robbers. • Items that maybe needed for the after world, such as clothi ...
... • Ordinary tombs were seen as unsuitable for Pharaohs. • Egyptian decided to build pyramids (huge stone tomb) for their pharaohs resting spot. • Pyramids were built to protect the bodies of Pharaohs from flood, animals, and grave robbers. • Items that maybe needed for the after world, such as clothi ...
Egypt – An Ancient Civilisation
... what was stored could perhaps explain why writing was invented. At first the Egyptians began using small pictures for words, i. e. depicting* objects in the real world. This was enough for very simple messages, but to express more abstract ideas, such as colours or references to time, was difficult. ...
... what was stored could perhaps explain why writing was invented. At first the Egyptians began using small pictures for words, i. e. depicting* objects in the real world. This was enough for very simple messages, but to express more abstract ideas, such as colours or references to time, was difficult. ...
Ancient Egypt
... what was stored could perhaps explain why writing was invented. At first the Egyptians began using small pictures for words, i. e. depicting* objects in the real world. This was enough for very simple messages, but to express more abstract ideas, such as colours or references to time, was difficult. ...
... what was stored could perhaps explain why writing was invented. At first the Egyptians began using small pictures for words, i. e. depicting* objects in the real world. This was enough for very simple messages, but to express more abstract ideas, such as colours or references to time, was difficult. ...
Chapter Two Egyptian Overview Powerpoint
... wealth = full granaries, plenty of wildlife and fish, and thriving herds were the signs of prosperity. These were the images used in the tombs of the Pharaohs to illustrate the wealth of their reigns Economy ...
... wealth = full granaries, plenty of wildlife and fish, and thriving herds were the signs of prosperity. These were the images used in the tombs of the Pharaohs to illustrate the wealth of their reigns Economy ...
Egypt_Flocabulary
... can get with. "Am I a dimwit? I can’t believe it, I can’t read it, Looks like symbols to me," naw, it’s simple you see: The ______________ let us know how to decipher the code, So now we study the old words that were written in stone. They believed in an afterlife, They’d get strips of cloth and the ...
... can get with. "Am I a dimwit? I can’t believe it, I can’t read it, Looks like symbols to me," naw, it’s simple you see: The ______________ let us know how to decipher the code, So now we study the old words that were written in stone. They believed in an afterlife, They’d get strips of cloth and the ...
Chapter 2, Section 3 The Egyptian Empire
... • Sculptors made large statues of pharaohs—showing them as ordinary people rather than gods. • Poets wrote loves songs and tributes to pharaohs. • Instead of building more pyramids, pharaohs had tombs cut into cliffs west of Nile River. • Area became known as the ___________________________. ...
... • Sculptors made large statues of pharaohs—showing them as ordinary people rather than gods. • Poets wrote loves songs and tributes to pharaohs. • Instead of building more pyramids, pharaohs had tombs cut into cliffs west of Nile River. • Area became known as the ___________________________. ...
EGYPT
... There were divorces, with compensation for the wife People married young and had arranged marriages Pharaohs often married their sisters to keep the royal blood pure Many upper class people shaved their heads and wore wigs, for both fashion and sun protection ...
... There were divorces, with compensation for the wife People married young and had arranged marriages Pharaohs often married their sisters to keep the royal blood pure Many upper class people shaved their heads and wore wigs, for both fashion and sun protection ...
The success of ancient Egyptian civilization came partly
... pharaoh. The history of ancient Egypt occurred in a series of stable Kingdoms, separated by periods of relative instability known as Intermediate Periods. The success of ancient Egyptian civilization came partly from its ability to adapt to the conditions of the Nile River Valley. The predictable fl ...
... pharaoh. The history of ancient Egypt occurred in a series of stable Kingdoms, separated by periods of relative instability known as Intermediate Periods. The success of ancient Egyptian civilization came partly from its ability to adapt to the conditions of the Nile River Valley. The predictable fl ...
Ancient Egypt Storybook
... Nubians provided gold, ivory, granite, and cattle in trades with Egypt. Trade on the Nile was easy! While the Nile flows north, the winds in Egypt mainly blow south. This makes the Nile perfect for boats and trade. All this trade led to cultural diffusion! For example, the Egyptians probably did not ...
... Nubians provided gold, ivory, granite, and cattle in trades with Egypt. Trade on the Nile was easy! While the Nile flows north, the winds in Egypt mainly blow south. This makes the Nile perfect for boats and trade. All this trade led to cultural diffusion! For example, the Egyptians probably did not ...
Ancient Egypt Storybook
... Nubians provided gold, ivory, granite, and cattle in trades with Egypt. Trade on the Nile was easy! While the Nile flows north, the winds in Egypt mainly blow south. This makes the Nile perfect for boats and trade. All this trade led to cultural diffusion! For example, the Egyptians probably did not ...
... Nubians provided gold, ivory, granite, and cattle in trades with Egypt. Trade on the Nile was easy! While the Nile flows north, the winds in Egypt mainly blow south. This makes the Nile perfect for boats and trade. All this trade led to cultural diffusion! For example, the Egyptians probably did not ...