Egypt: The Middle Kingdom
... During this generally peaceful time trade picked up dramatically. Many resources which before had been unused were now being exploited such as the cultivation of crops, mines which produced gold and quarries that were dug for building projects. During the entire Middle Kingdom many building projects ...
... During this generally peaceful time trade picked up dramatically. Many resources which before had been unused were now being exploited such as the cultivation of crops, mines which produced gold and quarries that were dug for building projects. During the entire Middle Kingdom many building projects ...
Egyptians Crossword Name
... Re The Egyptian Sun God was called Atum or this.46 Menes The first king of Egypt (Upper and Lower) around 3100 B.C.47 Dynasty This is a family of rulers whose right to rule is passed on within the family.47 Pharaoh Another name for Egyptian monarchs.47 Absolute Egyptian pharaohs held this type of "u ...
... Re The Egyptian Sun God was called Atum or this.46 Menes The first king of Egypt (Upper and Lower) around 3100 B.C.47 Dynasty This is a family of rulers whose right to rule is passed on within the family.47 Pharaoh Another name for Egyptian monarchs.47 Absolute Egyptian pharaohs held this type of "u ...
September 29, 2008 SWBAT: Discuss the early civilizations of
... • Middle Kingdom was attacked by western Hyksos, why were they able to do this? • Egyptians learned how to use bronze from them, and mastered their military skills • They eventually were able to drive the Hyksos out of Egypt, how do you think? Why is this ironic? ...
... • Middle Kingdom was attacked by western Hyksos, why were they able to do this? • Egyptians learned how to use bronze from them, and mastered their military skills • They eventually were able to drive the Hyksos out of Egypt, how do you think? Why is this ironic? ...
Main Idea 1 - Cloudfront.net
... Growth and Effects of Trade • Conquests brought traders into contact with distant lands, and trade routes, or paths followed by traders, developed. • Queen Hatshepsut encouraged trade and used the profits to support the arts and architecture. • Led by Ramses the Great, Egypt fought invaders for man ...
... Growth and Effects of Trade • Conquests brought traders into contact with distant lands, and trade routes, or paths followed by traders, developed. • Queen Hatshepsut encouraged trade and used the profits to support the arts and architecture. • Led by Ramses the Great, Egypt fought invaders for man ...
Document
... Growth and Effects of Trade • Conquests brought traders into contact with distant lands, and trade routes, or paths followed by traders, developed. • Queen Hatshepsut encouraged trade and used the profits to support the arts and architecture. • Led by Ramses the Great, Egypt fought invaders for man ...
... Growth and Effects of Trade • Conquests brought traders into contact with distant lands, and trade routes, or paths followed by traders, developed. • Queen Hatshepsut encouraged trade and used the profits to support the arts and architecture. • Led by Ramses the Great, Egypt fought invaders for man ...
IV. ANCIENT EGYPT A. Geography 1. The Nile River – the
... to the east and South. Tribute from distant lands increases pharaoh’s income. ii. Invasion of the Hyksos (ca.1780 B.C.) – The origins of the Hyksos are unknown, but they were most likely a nomadic tribe from western Asia. They had horses, chariots and stronger bows than the Egyptians. 6. Second Inte ...
... to the east and South. Tribute from distant lands increases pharaoh’s income. ii. Invasion of the Hyksos (ca.1780 B.C.) – The origins of the Hyksos are unknown, but they were most likely a nomadic tribe from western Asia. They had horses, chariots and stronger bows than the Egyptians. 6. Second Inte ...
The Egyptian Empire The New Kingdom Expanding the Empire
... armies expanded Egypt’s borders north to the Euphrates River in Mesopotamia. His troops also moved south and regained control of _________________, which had broken free from Egypt earlier. Thutmose’s empire grew rich from trade and tribute. In addition to claiming gold, copper, ivory, and other ...
... armies expanded Egypt’s borders north to the Euphrates River in Mesopotamia. His troops also moved south and regained control of _________________, which had broken free from Egypt earlier. Thutmose’s empire grew rich from trade and tribute. In addition to claiming gold, copper, ivory, and other ...
Egypt`s Early Rulers
... • This unified the kingdoms – for the first time, all of Egypt was ruled by one king • He established a new capital at Memphis which is a border city between Upper and Lower Egypt • He governs both parts of Egypt from Memphis causing it to be the center of government and culture along the Nile and a ...
... • This unified the kingdoms – for the first time, all of Egypt was ruled by one king • He established a new capital at Memphis which is a border city between Upper and Lower Egypt • He governs both parts of Egypt from Memphis causing it to be the center of government and culture along the Nile and a ...
6th Grade Math Lesson Plans
... the rest of the world? 5. Looking at the resources map, why do you think invading and capturing Nubia was so important in Egyptian history? Nubia is the region south of Egypt (modern day Sudan.) 6. Describe how the Egyptian Empire grew over the years. Why do you think it didn’t expand west, southwes ...
... the rest of the world? 5. Looking at the resources map, why do you think invading and capturing Nubia was so important in Egyptian history? Nubia is the region south of Egypt (modern day Sudan.) 6. Describe how the Egyptian Empire grew over the years. Why do you think it didn’t expand west, southwes ...
I cans modified w vocab
... 6. Analyze the accomplishments of the Middle and New Kingdoms. Essential Vocabulary to be able to do this: kingdom, empire, incense, Thebes, Hyksos, Ahmose, Hatshepsut, Thutmose, Tutankhamen, Ramses 7. Compare the specialization and technology seen in the cultures of ancient Egypt and Kush. Essentia ...
... 6. Analyze the accomplishments of the Middle and New Kingdoms. Essential Vocabulary to be able to do this: kingdom, empire, incense, Thebes, Hyksos, Ahmose, Hatshepsut, Thutmose, Tutankhamen, Ramses 7. Compare the specialization and technology seen in the cultures of ancient Egypt and Kush. Essentia ...
Egypt - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 1. If you didn’t disturb the peace or tick off an embalmer or die in a foreign land you would probably make it to the afterlife, where you took part in activities you enjoyed most while alive. Eternity is a long time for a round of ping-pong (just an observation). 2. Social status had a profound inf ...
... 1. If you didn’t disturb the peace or tick off an embalmer or die in a foreign land you would probably make it to the afterlife, where you took part in activities you enjoyed most while alive. Eternity is a long time for a round of ping-pong (just an observation). 2. Social status had a profound inf ...
The Middle Kingdom - Mr. Scott`s Cyberdesk
... Nile and travelling overland for several days by donkey caravans to the shores of the Red Sea © Keith Wheatley - Fotolia.com ...
... Nile and travelling overland for several days by donkey caravans to the shores of the Red Sea © Keith Wheatley - Fotolia.com ...
Each was A period of ancient Egyptian history that lasted from about
... Each was A period of ancient Egyptian history that lasted from about: Old Kingdom’ 2686 B.C. to 2181 B. C. Middle Kingdom’2055 B.C. to 1650 B. C. The most well known pyramid was built for the pharaohKhufu. It is known as the Great Pyramid. Temples: The ancient Egyptians believed that temples were th ...
... Each was A period of ancient Egyptian history that lasted from about: Old Kingdom’ 2686 B.C. to 2181 B. C. Middle Kingdom’2055 B.C. to 1650 B. C. The most well known pyramid was built for the pharaohKhufu. It is known as the Great Pyramid. Temples: The ancient Egyptians believed that temples were th ...
Seven Wonders of Ancient Egypt
... temples, chapels, pylons, and other buildings; notably the Temple of Amun with the Sacred Lake as part of the magnificent site. It is part of the monumental city of Thebes and is the main place of worship of the 18th Dynasty, Theban Triad with God Amun as its head. It is the largest ancient religiou ...
... temples, chapels, pylons, and other buildings; notably the Temple of Amun with the Sacred Lake as part of the magnificent site. It is part of the monumental city of Thebes and is the main place of worship of the 18th Dynasty, Theban Triad with God Amun as its head. It is the largest ancient religiou ...
Egypt_Flocabulary
... "Am I a dimwit? I can’t believe it, I can’t read it, Looks like symbols to me," naw, it’s simple you see: The ______________ let us know how to decipher the code, So now we study the old words that were written in stone. They believed in an afterlife, They’d get strips of cloth and they’d __________ ...
... "Am I a dimwit? I can’t believe it, I can’t read it, Looks like symbols to me," naw, it’s simple you see: The ______________ let us know how to decipher the code, So now we study the old words that were written in stone. They believed in an afterlife, They’d get strips of cloth and they’d __________ ...
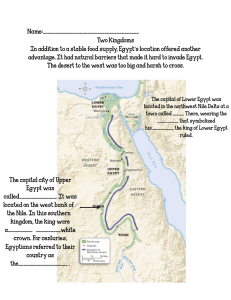
Geography and ancient egypt
... the princess of lower Egypt to strengthen his control He combined the white and red crowns ...
... the princess of lower Egypt to strengthen his control He combined the white and red crowns ...
Ancient History
... and Egypt? What are the differences between the innovative sites of Sumer and Egypt? ...
... and Egypt? What are the differences between the innovative sites of Sumer and Egypt? ...
Egyptian Class Structure Powerpoint
... their native Canaan, and eventually permanently settled there. The Pharaoh came to see their presence as a threat to his Kingdom, so he enslaved them. The departure from Egypt (led by Moses) is called the Exodus and remains an important event in Jewish history. The Hebrews then found themselves at M ...
... their native Canaan, and eventually permanently settled there. The Pharaoh came to see their presence as a threat to his Kingdom, so he enslaved them. The departure from Egypt (led by Moses) is called the Exodus and remains an important event in Jewish history. The Hebrews then found themselves at M ...
Ancient Egypt Study Guide Vocabulary: cataracts – river rapids
... most people in Ancient Egypt belonged to the lower class, they did most of the work bodies of pharaohs and other wealthy people were given mummification they preserved the bodies for the afterlife pyramids were built for dead rulers Egyptians invented first writing system called hieroglyph ...
... most people in Ancient Egypt belonged to the lower class, they did most of the work bodies of pharaohs and other wealthy people were given mummification they preserved the bodies for the afterlife pyramids were built for dead rulers Egyptians invented first writing system called hieroglyph ...
Chpt. 2 prentice hall world history
... Historians believe Egyptians built the pyramids as a demonstration of the strength and wealth of their society. ...
... Historians believe Egyptians built the pyramids as a demonstration of the strength and wealth of their society. ...
Untitled 3
... also founded Egypt’s first dynasty, or series of rulers from the same family. Menes built a new capital city at the southern tip of the Nile Delta. The city was later named Memphis. For centuries, Memphis was the political and cultural center of Egypt. Many government offices were located there, ...
... also founded Egypt’s first dynasty, or series of rulers from the same family. Menes built a new capital city at the southern tip of the Nile Delta. The city was later named Memphis. For centuries, Memphis was the political and cultural center of Egypt. Many government offices were located there, ...
Egypt, Kush, and Axum - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... The Aksumites were a people formed from the mix of Kushitic speaking people in Ethiopia and Semitic speaking people in southern Arabia who settled the territory across the ...
... The Aksumites were a people formed from the mix of Kushitic speaking people in Ethiopia and Semitic speaking people in southern Arabia who settled the territory across the ...
File
... Ramses II The pharaoh who ruled Egypt from 1279 to 1213 B.C. and created a stable empire. Built the house of Ramses which contained four 66 foot statues of himself ...
... Ramses II The pharaoh who ruled Egypt from 1279 to 1213 B.C. and created a stable empire. Built the house of Ramses which contained four 66 foot statues of himself ...
EGYPT
... Spoke different dialects and had different customs Dynasty = a series of rulers from the same family There were a total of 31 dynasties ...
... Spoke different dialects and had different customs Dynasty = a series of rulers from the same family There were a total of 31 dynasties ...
Nubia

Nubia is a region along the Nile river located in what is today northern Sudan and southern Egypt. One of the earliest civilizations of ancient Northeastern Africa, with a history that can be traced from at least 2000 B.C. onward through Nubian monuments and artifacts as well as written records from Egypt and Rome, it was home to one of the African empires. There were a number of large Nubian kingdoms throughout the Postclassical Era, the last of which collapsed in 1504, when Nubia became divided between Egypt and the Sennar sultanate resulting in the Arabization of much of the Nubian population. Nubia was again united within Ottoman Egypt in the 19th century, and within Anglo-Egyptian Sudan from 1899 to 1956.The name Nubia is derived from that of the Noba people, nomads who settled the area in the 4th century, with the collapse of the kingdom of Meroë. The Noba spoke a Nilo-Saharan language, ancestral to Old Nubian. Old Nubian was mostly used in religious texts dating from the 8th and 15th centuries AD. Before the 4th century, and throughout classical antiquity, Nubia was known as Kush, or, in Classical Greek usage, included under the name Ethiopia (Aithiopia).Historically, the people of Nubia spoke at least two varieties of the Nubian language group, a subfamily which includes Nobiin (the descendant of Old Nubian), Kenuzi-Dongola, Midob and several related varieties in the northern part of the Nuba Mountains in South Kordofan. Until at least 1970, the Birgid language was spoken north of Nyala in Darfur but is now extinct.