Ancient Egypt
... 7. During what period did ancient Egypt reach its maximum size? The New Kingdom 8. Do you think historical maps are a good way to show past events? Why or why not? Answers will vary, but could include that it is sometimes easier to have a visual display of information. Summary and Review Ideas to Re ...
... 7. During what period did ancient Egypt reach its maximum size? The New Kingdom 8. Do you think historical maps are a good way to show past events? Why or why not? Answers will vary, but could include that it is sometimes easier to have a visual display of information. Summary and Review Ideas to Re ...
Egypt
... • First centralized government ▫ Easy to govern because of the geography of Egypt, most people lived along the Nile ▫ Pharaoh still seen as a god – people obeyed ...
... • First centralized government ▫ Easy to govern because of the geography of Egypt, most people lived along the Nile ▫ Pharaoh still seen as a god – people obeyed ...
Unit 3 Digging Deeper
... - Egypt was called the gift of the Nile because the Nile River gave life to the desert. - Civilization developed along the Nile after people began farming in this region - Strong kings unified all of Egypt. Directions: Read the False statements below. Replace each underlined word with one from the w ...
... - Egypt was called the gift of the Nile because the Nile River gave life to the desert. - Civilization developed along the Nile after people began farming in this region - Strong kings unified all of Egypt. Directions: Read the False statements below. Replace each underlined word with one from the w ...
File - Ancient History does not have to be a MYSTERY!
... systems explained a decree or an official announcement issued by the pharaoh Ptolomy V sometime in 196 BC. The decree is actually very unimportant, but the fact that the three writing systems were "saying the same thing" made it possible for Champollion to determine the meaning of the Egyptian hiero ...
... systems explained a decree or an official announcement issued by the pharaoh Ptolomy V sometime in 196 BC. The decree is actually very unimportant, but the fact that the three writing systems were "saying the same thing" made it possible for Champollion to determine the meaning of the Egyptian hiero ...
Notes- Daily Life in Egypt Name Period ______ Daily Life in Ancient
... Children of _____________ __________________ began working at the age of ...
... Children of _____________ __________________ began working at the age of ...
Section Summary Key Terms and People
... Around 3100 BC Menes (MEE-neez), the king of Upper Egypt, invaded Lower Egypt. He married a princess there in order to unite the two kingdoms under his rule. Menes was the first pharaoh, which literally means ruler of a “great house.” He also started the first Egyptian dynasty, or series of rulers f ...
... Around 3100 BC Menes (MEE-neez), the king of Upper Egypt, invaded Lower Egypt. He married a princess there in order to unite the two kingdoms under his rule. Menes was the first pharaoh, which literally means ruler of a “great house.” He also started the first Egyptian dynasty, or series of rulers f ...
The Rise of Civilization in Egypt
... to produce food for themselves and their animals. ______________________________________________ ...
... to produce food for themselves and their animals. ______________________________________________ ...
Egypt
... about 1720 BC they had grown strong enough, at the expense of the Middle Kingdom kings, to gain control of Avaris in the north eastern Delta. This site eventually became the capital of the Hyksos kings, yet within 50 years they had also managed to take control of the important Egyptian city of Memph ...
... about 1720 BC they had grown strong enough, at the expense of the Middle Kingdom kings, to gain control of Avaris in the north eastern Delta. This site eventually became the capital of the Hyksos kings, yet within 50 years they had also managed to take control of the important Egyptian city of Memph ...
Egyptian Vocabulary Worksheet
... the ___________ rope within which two of the king's names (his birth name and his throne name) were written. Slide #8 Khnum: A god who controlled the flood_____________ of the Nile who was pictured as a ram-headed _________________. He was also seen as a creator-god who molded people on a potter’s w ...
... the ___________ rope within which two of the king's names (his birth name and his throne name) were written. Slide #8 Khnum: A god who controlled the flood_____________ of the Nile who was pictured as a ram-headed _________________. He was also seen as a creator-god who molded people on a potter’s w ...
Chapter Three – Art of Ancient Egypt
... By 8000 BCE the Egyptian valley was inhabited and was considered to be Neolithic by 5000 BCE. By 3500 BCE several large states or chiefdoms would appear in the lower Nile. Prehistoric Egypt was divided into 2 kingdoms: Northern delta Lower Egypt and the swampy southern delta- Upper Egypt. The pre - ...
... By 8000 BCE the Egyptian valley was inhabited and was considered to be Neolithic by 5000 BCE. By 3500 BCE several large states or chiefdoms would appear in the lower Nile. Prehistoric Egypt was divided into 2 kingdoms: Northern delta Lower Egypt and the swampy southern delta- Upper Egypt. The pre - ...
WHICh2Egypt-Sec1_2-2016 - Alabama School of Fine Arts
... while the skull is cleared of the rest by rinsing with drugs; next they make a cut along the flank with a sharp Ethiopian stone, and take out the whole contents of the abdomen, which they then cleanse, washing it thoroughly with palm wine, and again frequently with an infusion of pounded aromatics. ...
... while the skull is cleared of the rest by rinsing with drugs; next they make a cut along the flank with a sharp Ethiopian stone, and take out the whole contents of the abdomen, which they then cleanse, washing it thoroughly with palm wine, and again frequently with an infusion of pounded aromatics. ...
Ancient Egypt Big Bird Sentences
... 7. The Egyptians planted crops along the __________________________. 8. The Egyptians ___________________________ the Nile for irrigation. 9. _______________ were used on the Nile. 10. The Nile River flooded every ____________________________. 11. Egypt is very _____________________. 12. There were ...
... 7. The Egyptians planted crops along the __________________________. 8. The Egyptians ___________________________ the Nile for irrigation. 9. _______________ were used on the Nile. 10. The Nile River flooded every ____________________________. 11. Egypt is very _____________________. 12. There were ...
The Nile through ancient Egypt - pauledwards
... The process took two or three months Carefully workers removed the organs The body was then filled with natural salt and stored for at least 42 days The body completely dried out When dry the body was cleaned and bathed in spices Then it was wrapped with long linen bandages Arms and legs were bandag ...
... The process took two or three months Carefully workers removed the organs The body was then filled with natural salt and stored for at least 42 days The body completely dried out When dry the body was cleaned and bathed in spices Then it was wrapped with long linen bandages Arms and legs were bandag ...
Document
... • The Nile was the source of life and path to immortality • Egyptians lived on Eastern side but buried on Western side – River was symbol of passage of one life to next ...
... • The Nile was the source of life and path to immortality • Egyptians lived on Eastern side but buried on Western side – River was symbol of passage of one life to next ...
Egyptian Daily Life
... objects such as furniture, jewelry, and pottery • They learned their trade from their fathers and, in turn, taught their sons. • They used simple techniques and tools to make all sorts of useful things. • The Pharaoh, government or temples often employed them. • Egypt traded grain, gold, copper, lin ...
... objects such as furniture, jewelry, and pottery • They learned their trade from their fathers and, in turn, taught their sons. • They used simple techniques and tools to make all sorts of useful things. • The Pharaoh, government or temples often employed them. • Egypt traded grain, gold, copper, lin ...
Egypt and the Nile River Valley System
... • Make sure you know: – what the 3 kingdoms are – The role of the pharaoh in each kingdom – Major contributions to Egyptian life from each kingdom ...
... • Make sure you know: – what the 3 kingdoms are – The role of the pharaoh in each kingdom – Major contributions to Egyptian life from each kingdom ...
egypt and nile river power point
... • Make sure you know: – what the 3 kingdoms are – The role of the pharaoh in each kingdom – Major contributions to Egyptian life from each kingdom ...
... • Make sure you know: – what the 3 kingdoms are – The role of the pharaoh in each kingdom – Major contributions to Egyptian life from each kingdom ...
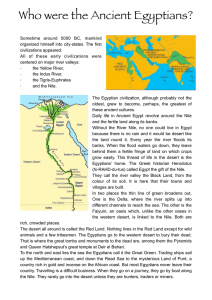
Who were the Ancient Egyptians?
... under the pharaoh. They were the most powerful groups in Egypt. Government officials carried out the orders of the pharaoh. Most of them came from noble families. They were powerful and wealthy, and they enjoyed a high quality of life. Priests were also a powerful group, because religion touched eve ...
... under the pharaoh. They were the most powerful groups in Egypt. Government officials carried out the orders of the pharaoh. Most of them came from noble families. They were powerful and wealthy, and they enjoyed a high quality of life. Priests were also a powerful group, because religion touched eve ...
Pharaoh`s Role - Brookville Local Schools
... Ancient Egypt was a monarchy because it was led by a monarch (king) who got power through the family. It was a theocracy because the leader of the government (pharaoh) was a religious leader and considered to be a god. What geographic characteristic allowed Egypt to flourish? Why did they depend on ...
... Ancient Egypt was a monarchy because it was led by a monarch (king) who got power through the family. It was a theocracy because the leader of the government (pharaoh) was a religious leader and considered to be a god. What geographic characteristic allowed Egypt to flourish? Why did they depend on ...
File
... • Make sure you know: – what the 3 kingdoms are – The role of the pharaoh in each kingdom – Major contributions to Egyptian life from each kingdom ...
... • Make sure you know: – what the 3 kingdoms are – The role of the pharaoh in each kingdom – Major contributions to Egyptian life from each kingdom ...
History 110B World History 1500 to the Present
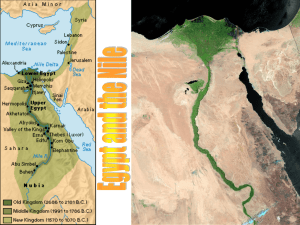
... Ancient Egypt Three Eras: 1) The Old Kingdom 2) The Middle Kingdom 3) The New Kingdom Each period was followed by a break-down in order called the First, Second and Third Intermediate Periods, respectively Terms: Ma’at, Pharaoh ...
... Ancient Egypt Three Eras: 1) The Old Kingdom 2) The Middle Kingdom 3) The New Kingdom Each period was followed by a break-down in order called the First, Second and Third Intermediate Periods, respectively Terms: Ma’at, Pharaoh ...
4 - Images
... 1. On the File menu, select Print 2. In the pop-up menu, select Microsoft PowerPoint If the dialog box does not include this pop-up, continue to step 4 3. In the Print what box, choose the presentation format you want to print: slides, notes, handouts, or outline 4. Click the Print button to print t ...
... 1. On the File menu, select Print 2. In the pop-up menu, select Microsoft PowerPoint If the dialog box does not include this pop-up, continue to step 4 3. In the Print what box, choose the presentation format you want to print: slides, notes, handouts, or outline 4. Click the Print button to print t ...
Nubia

Nubia is a region along the Nile river located in what is today northern Sudan and southern Egypt. One of the earliest civilizations of ancient Northeastern Africa, with a history that can be traced from at least 2000 B.C. onward through Nubian monuments and artifacts as well as written records from Egypt and Rome, it was home to one of the African empires. There were a number of large Nubian kingdoms throughout the Postclassical Era, the last of which collapsed in 1504, when Nubia became divided between Egypt and the Sennar sultanate resulting in the Arabization of much of the Nubian population. Nubia was again united within Ottoman Egypt in the 19th century, and within Anglo-Egyptian Sudan from 1899 to 1956.The name Nubia is derived from that of the Noba people, nomads who settled the area in the 4th century, with the collapse of the kingdom of Meroë. The Noba spoke a Nilo-Saharan language, ancestral to Old Nubian. Old Nubian was mostly used in religious texts dating from the 8th and 15th centuries AD. Before the 4th century, and throughout classical antiquity, Nubia was known as Kush, or, in Classical Greek usage, included under the name Ethiopia (Aithiopia).Historically, the people of Nubia spoke at least two varieties of the Nubian language group, a subfamily which includes Nobiin (the descendant of Old Nubian), Kenuzi-Dongola, Midob and several related varieties in the northern part of the Nuba Mountains in South Kordofan. Until at least 1970, the Birgid language was spoken north of Nyala in Darfur but is now extinct.