Mid Loddon Sub Catchment Sustainable Soils Group Profile
... research into sustainable practices. The network was formed in 1999 and covers an area of around 95,000ha. A noticeable change in seasonal climate, especially reduced winter/spring rainfall, has meant successive failed seasons and a high risk of wind erosion and soil damage. The group has observed d ...
... research into sustainable practices. The network was formed in 1999 and covers an area of around 95,000ha. A noticeable change in seasonal climate, especially reduced winter/spring rainfall, has meant successive failed seasons and a high risk of wind erosion and soil damage. The group has observed d ...
Summative Assessment Questions on Soils (LCA Ag,Hort Basic Hort
... 1. A good fertile soil provides plants with what? 2. List the constituents of a fertile soil. 3. Name the three main soil types. 4. Soils can have different pH. What does pH mean when referring to soils? 5. Which type of soil is good for crops? 6. Where would you find acid soils? 7. Why is lime adde ...
... 1. A good fertile soil provides plants with what? 2. List the constituents of a fertile soil. 3. Name the three main soil types. 4. Soils can have different pH. What does pH mean when referring to soils? 5. Which type of soil is good for crops? 6. Where would you find acid soils? 7. Why is lime adde ...
Agricultural Soil and Water Conservation Stewardship
... keep livestock out of the streams as well as streambank stabilization with rocks, grass, trees, shrubs, riprap, or gabions. ...
... keep livestock out of the streams as well as streambank stabilization with rocks, grass, trees, shrubs, riprap, or gabions. ...
Abstract: Earthworms are keystone detritivores that can influence
... ecosystems. Impacts vary with soil parent material, land use history, and assemblage of invading earthworm species. Earthworms reduce the thickness of organic layers, increase the bulk density of soils and incorporate litter and humus materials into deeper horizons of the soil profile, thereby affec ...
... ecosystems. Impacts vary with soil parent material, land use history, and assemblage of invading earthworm species. Earthworms reduce the thickness of organic layers, increase the bulk density of soils and incorporate litter and humus materials into deeper horizons of the soil profile, thereby affec ...
Back To Organic Farming
... mutual interdependence) was broken about 5000 years ago, when Man started agriculture by cutting down trees and clearing the forest for growing crops. The soil microbes were deprived of shade and leaves and their activity started going down. As their activity declined, plant nutrition suffered and t ...
... mutual interdependence) was broken about 5000 years ago, when Man started agriculture by cutting down trees and clearing the forest for growing crops. The soil microbes were deprived of shade and leaves and their activity started going down. As their activity declined, plant nutrition suffered and t ...
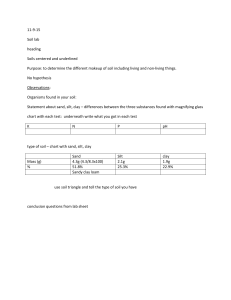
11-9-15 Soils Lab
... Soils centered and underlined Purpose: to determine the different makeup of soil including living and non-living things. No hypothesis Observations: Organisms found in your soil: Statement about sand, silt, clay – differences between the three substances found with magnifying glass chart with each t ...
... Soils centered and underlined Purpose: to determine the different makeup of soil including living and non-living things. No hypothesis Observations: Organisms found in your soil: Statement about sand, silt, clay – differences between the three substances found with magnifying glass chart with each t ...
LECTURE 14 Soil Organisms
... • Utilize water, energy and carbon to make organic molecules and living tissues. ...
... • Utilize water, energy and carbon to make organic molecules and living tissues. ...
soil and weathering
... 4. weathering the breakdown of rock into smaller pieces of the same material without any change to its composition 7. horizon a soil layer with physical and chemical properties that differ from those of the soil layers above or below it 8. the expansion of desert conditions in an area where the natu ...
... 4. weathering the breakdown of rock into smaller pieces of the same material without any change to its composition 7. horizon a soil layer with physical and chemical properties that differ from those of the soil layers above or below it 8. the expansion of desert conditions in an area where the natu ...
Ecological agriculture: essay of weed control management on
... Mancha Province: Lavandula latifolia Medikus and Salvia lavandulifolia Vahl. Weed control with cover management is considered an alternative technique to conventional soil working. All the cover managements were found to reduce the weed in all the tested tillage, although the barley straw cover show ...
... Mancha Province: Lavandula latifolia Medikus and Salvia lavandulifolia Vahl. Weed control with cover management is considered an alternative technique to conventional soil working. All the cover managements were found to reduce the weed in all the tested tillage, although the barley straw cover show ...
CRSC 6 – Introduction to Precision Agriculture
... be used to identify the locations where soil samples are taken. 2. _________________ are used to identify areas of the field which have different levels of nutrients. ...
... be used to identify the locations where soil samples are taken. 2. _________________ are used to identify areas of the field which have different levels of nutrients. ...
Lindsey`s Basic Guide to the Soil Orders of Canada Disclaimer: This
... Lindsey’s Basic Guide to the Soil Orders of Canada Disclaimer: This is an extreme generalization of soil orders of Canada. More information about each order can be found in the Canadian System of Soil Classification and the Soil Management Guide. However, I have found that these resources can be dif ...
... Lindsey’s Basic Guide to the Soil Orders of Canada Disclaimer: This is an extreme generalization of soil orders of Canada. More information about each order can be found in the Canadian System of Soil Classification and the Soil Management Guide. However, I have found that these resources can be dif ...
1-20-15 About 2 inches of soil across the earth Soil
... organisms, water, gases, nutrients, and micro organisms. About 38% of earth's surface (land) is used for agriculture. Forestry Soil cycles nutrients Flow of energy Medications can come from soils. Soil formation is affected by: 1. Climate - long term. Soils form faster in warm, moist climates 2. Org ...
... organisms, water, gases, nutrients, and micro organisms. About 38% of earth's surface (land) is used for agriculture. Forestry Soil cycles nutrients Flow of energy Medications can come from soils. Soil formation is affected by: 1. Climate - long term. Soils form faster in warm, moist climates 2. Org ...
Chapter 2-section 3 geology notes
... Everything that lives on land, including humans, depends directly or indirectly on soil. Fertile soil is valuable because there is a limited supply. Less than 1/8 of the land on Earth have soils suitable for farming. ...
... Everything that lives on land, including humans, depends directly or indirectly on soil. Fertile soil is valuable because there is a limited supply. Less than 1/8 of the land on Earth have soils suitable for farming. ...
Organic matter and biological activity
... fraction is strongly influenced by weather conditions, moisture status of the soil, growth stage of the vegetation, addition of organic residues, and cultural practices, like tillage. ...
... fraction is strongly influenced by weather conditions, moisture status of the soil, growth stage of the vegetation, addition of organic residues, and cultural practices, like tillage. ...
Organic matter and biological activity
... fraction is strongly influenced by weather conditions, moisture status of the soil, growth stage of the vegetation, addition of organic residues, and cultural practices, like tillage. ...
... fraction is strongly influenced by weather conditions, moisture status of the soil, growth stage of the vegetation, addition of organic residues, and cultural practices, like tillage. ...
Figure 18.1
... Relatively high amounts of mineralization of available nutrients is produced by a combination of rapid decomposition plus previously accumulated POM or a high amount of added residues. Rapid decomposition is stimulated by intensive tillage, good soil drainage, coarse texture, and alternating wet and ...
... Relatively high amounts of mineralization of available nutrients is produced by a combination of rapid decomposition plus previously accumulated POM or a high amount of added residues. Rapid decomposition is stimulated by intensive tillage, good soil drainage, coarse texture, and alternating wet and ...
THE EFFECT OF AGRICULTURE
... surrounding the fields for large-scale farming lead to soil erosion easily due to the removal of the wind break, mechanical ploughing loosens soil and speed up erosion ...
... surrounding the fields for large-scale farming lead to soil erosion easily due to the removal of the wind break, mechanical ploughing loosens soil and speed up erosion ...
New soil test - Washtenaw County
... Cost: Mailers for landscapes, vegetable & flower gardens are available at your local MSU Extension office for $25.00. Sampling: for garden soils, sample 6 inches to 8 inches deep. For lawns, lift the sod and sample 3 inches deep. Take 15 or 20 sub samples in the area you are testing and mix them tho ...
... Cost: Mailers for landscapes, vegetable & flower gardens are available at your local MSU Extension office for $25.00. Sampling: for garden soils, sample 6 inches to 8 inches deep. For lawns, lift the sod and sample 3 inches deep. Take 15 or 20 sub samples in the area you are testing and mix them tho ...
Teaching soil ecology in one lab session
... formation, profile, and components. • Talk about variation among ecosystems, as well as within ecosystems. • Have students generate hypotheses about how soils might differ within their campus ecosystem (based on plant cover, management, etc.) ...
... formation, profile, and components. • Talk about variation among ecosystems, as well as within ecosystems. • Have students generate hypotheses about how soils might differ within their campus ecosystem (based on plant cover, management, etc.) ...
Tillage

Tillage is the agricultural preparation of soil by mechanical agitation of various types, such as digging, stirring, and overturning. Examples of human-powered tilling methods using hand tools include shovelling, picking, mattock work, hoeing, and raking. Examples of draft-animal-powered or mechanized work include ploughing (overturning with moldboards or chiseling with chisel shanks), rototilling, rolling with cultipackers or other rollers, harrowing, and cultivating with cultivator shanks (teeth). Small-scale gardening and farming, for household food production or small business production, tends to use the smaller-scale methods above, whereas medium- to large-scale farming tends to use the larger-scale methods. There is a fluid continuum, however. Any type of gardening or farming, but especially larger-scale commercial types, may also use low-till or no-till methods as well.Tillage is often classified into two types, primary and secondary. There is no strict boundary between them so much as a loose distinction between tillage that is deeper and more thorough (primary) and tillage that is shallower and sometimes more selective of location (secondary). Primary tillage such as ploughing tends to produce a rough surface finish, whereas secondary tillage tends to produce a smoother surface finish, such as that required to make a good seedbed for many crops. Harrowing and rototilling often combine primary and secondary tillage into one operation.""Tillage"" can also mean the land that is tilled. The word ""cultivation"" has several senses that overlap substantially with those of ""tillage"". In a general context, both can refer to agriculture. Within agriculture, both can refer to any of the kinds of soil agitation described above. Additionally, ""cultivation"" or ""cultivating"" may refer to an even narrower sense of shallow, selective secondary tillage of row crop fields that kills weeds while sparing the crop plants.