e-Version
... There are three periods in time: present (now), past (yesterday), and future (tomorrow). Now is used with the present tense, yesterday with the past tense (the simple past), and tomorrow with the future tense (the simple future). These are basic tenses for any beginning language learner. These tense ...
... There are three periods in time: present (now), past (yesterday), and future (tomorrow). Now is used with the present tense, yesterday with the past tense (the simple past), and tomorrow with the future tense (the simple future). These are basic tenses for any beginning language learner. These tense ...
Passive Sentences
... 3. Passive voice is often used when the agent is very general such as people or somebody. English is spoken here. The door should be locked. 4. Passive voice is often used when the speaker/writer wants to emphasize a result: Several thousand people were killed by the earthquake. 5. Passive voice is ...
... 3. Passive voice is often used when the agent is very general such as people or somebody. English is spoken here. The door should be locked. 4. Passive voice is often used when the speaker/writer wants to emphasize a result: Several thousand people were killed by the earthquake. 5. Passive voice is ...
active_passive
... 1. The bandits robbed the bank. 2. The soldiers will dig the foxhole. 3. The first sergeant completed the guard rosters. 4. You must reorganize your desk. OR Reorganize your desk. 5. The C Battery officers are evaluating the field exercises. Drop part of the verb. 1. The headquarters is in the valle ...
... 1. The bandits robbed the bank. 2. The soldiers will dig the foxhole. 3. The first sergeant completed the guard rosters. 4. You must reorganize your desk. OR Reorganize your desk. 5. The C Battery officers are evaluating the field exercises. Drop part of the verb. 1. The headquarters is in the valle ...
Ser vs Estar
... These verb infinitives express the action or state of ‘being’ but they don’t tell us who is doing the action of the verb or when the action is happening. Conjugating a verb means manipulating it to reflect who is doing the action or who is in the state and when it is happening. ...
... These verb infinitives express the action or state of ‘being’ but they don’t tell us who is doing the action of the verb or when the action is happening. Conjugating a verb means manipulating it to reflect who is doing the action or who is in the state and when it is happening. ...
Lesson 28
... She wants to walk. He wants to walk. They want to walk. We all want to walk. We tried to hike up to 18,500 feet, but the weather was too harsh. He convinced the Sherpas to stand in his picture with him. Our group travelled far to accomplish our goal. I wanted to eat but I was too nauseous from altit ...
... She wants to walk. He wants to walk. They want to walk. We all want to walk. We tried to hike up to 18,500 feet, but the weather was too harsh. He convinced the Sherpas to stand in his picture with him. Our group travelled far to accomplish our goal. I wanted to eat but I was too nauseous from altit ...
On the processing of regular and irregular forms of verbs and nouns
... a group of patients diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease performed worse with irregularly inflected verbs. A contrasting pattern was reported for one aphasic patient with an anterior lesion and for a group of patients with Parkinson’s disease; they encountered greater problems producing regular as opp ...
... a group of patients diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease performed worse with irregularly inflected verbs. A contrasting pattern was reported for one aphasic patient with an anterior lesion and for a group of patients with Parkinson’s disease; they encountered greater problems producing regular as opp ...
Document
... in contact with animal fur. So he found Goliath, a female iguana. (2) She seemed happy while keeping Duane company. One night, Duane had stopped breathing. (3) With her sharp claws Goliath started scratching hard with the hope of waking Duane. (4) She also began whipping his face with her scaly tail ...
... in contact with animal fur. So he found Goliath, a female iguana. (2) She seemed happy while keeping Duane company. One night, Duane had stopped breathing. (3) With her sharp claws Goliath started scratching hard with the hope of waking Duane. (4) She also began whipping his face with her scaly tail ...
Why No Mere Mortal JOHN J. KIM
... subtypes of verbs (those that share some of the distinguishing semantic features) that would be expected to show similar behavior in past tense formation, just as overlap in phonological features defines clusters of verbs with similar past tense forms. But this consequence turns out to be false. The ...
... subtypes of verbs (those that share some of the distinguishing semantic features) that would be expected to show similar behavior in past tense formation, just as overlap in phonological features defines clusters of verbs with similar past tense forms. But this consequence turns out to be false. The ...
The Verbal Group: Finites and Non- Finites
... In a functioning flowering plant, both photosynthesis and respiration occur. When we look at the generalised equations, they appear to be the reverse of each other. However, this is a serious misunderstanding. Each process is a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions and the sequence in one is not the ...
... In a functioning flowering plant, both photosynthesis and respiration occur. When we look at the generalised equations, they appear to be the reverse of each other. However, this is a serious misunderstanding. Each process is a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions and the sequence in one is not the ...
Caesar Selections - Online Grammatical Appendix - 04-09
... a. When a single consonant appears between two vowels, it is pronounced with the vowel that follows it; as in fe-rō, a-gō, mo-nē. b. Some consonants can be pronounced indefi nitely. They “flow,” and are thus called “liquids.” Other consonants fall silent immediately after they are pronounced. Such c ...
... a. When a single consonant appears between two vowels, it is pronounced with the vowel that follows it; as in fe-rō, a-gō, mo-nē. b. Some consonants can be pronounced indefi nitely. They “flow,” and are thus called “liquids.” Other consonants fall silent immediately after they are pronounced. Such c ...
THE INTERPRETATION OF TENSE AND ASPECT IN ENGLISH
... and progressive reference points for sentences with progressive aspect. Thus, the interpretation of each sentence involves a number of relevant times: the beginning and end of the event described by the main verb for all sentences, the perfect time if it has perfect aspect, and the progressive time ...
... and progressive reference points for sentences with progressive aspect. Thus, the interpretation of each sentence involves a number of relevant times: the beginning and end of the event described by the main verb for all sentences, the perfect time if it has perfect aspect, and the progressive time ...
How to Find Serial Verbs in English
... separating the two verbs. The serial verbs belong to a single intonation contour, with no pause separating them. The entire SVC refers to a single (possibly complex) event. A true SVC may contain only one specification for tense, aspect, modality, negation, etc., though these features are sometimes ...
... separating the two verbs. The serial verbs belong to a single intonation contour, with no pause separating them. The entire SVC refers to a single (possibly complex) event. A true SVC may contain only one specification for tense, aspect, modality, negation, etc., though these features are sometimes ...
Front Matter - Assets - Cambridge
... A tense used to refer to completed actions in the future, e.g. E. I will have done it by next week, D. ik zal het gedaan hebben. A tense used usually to refer to future time, e.g. E. I will do it soon, D. ik zal het doen, or to express an assumption, e.g. E. he will be th ...
... A tense used to refer to completed actions in the future, e.g. E. I will have done it by next week, D. ik zal het gedaan hebben. A tense used usually to refer to future time, e.g. E. I will do it soon, D. ik zal het doen, or to express an assumption, e.g. E. he will be th ...
French III - Neshaminy School District
... Be able to use all verbs studied in present, past, imperfect and future Emphasize what each tense sounds like Discuss main ideas from all Notes culturelles (Chap. 1-8) Review main vocabulary groups ...
... Be able to use all verbs studied in present, past, imperfect and future Emphasize what each tense sounds like Discuss main ideas from all Notes culturelles (Chap. 1-8) Review main vocabulary groups ...
Chapter XII: The Reflexive Pronoun & Adjective
... The words causā and grātiā take the gerund in the genitive to express purpose. In this construction, the gerund is always placed before causā and grātiā. causā and grātiā are both translated as “for the sake of” ...
... The words causā and grātiā take the gerund in the genitive to express purpose. In this construction, the gerund is always placed before causā and grātiā. causā and grātiā are both translated as “for the sake of” ...
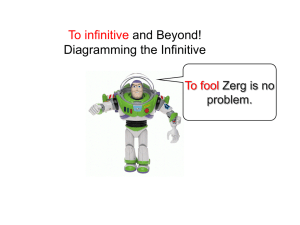
Diagramming the Infinitive as a Predicate
... Mr. Kullman’s goal is to help his students. (infinitive has its own direct object) Mr. Kullman wanted to travel to Paris, but his students wanted to work on grammar problems. (infinitives with adverbial phrases) When Tianne started to clean the garage, Perry decided to watch from a distance. (Infini ...
... Mr. Kullman’s goal is to help his students. (infinitive has its own direct object) Mr. Kullman wanted to travel to Paris, but his students wanted to work on grammar problems. (infinitives with adverbial phrases) When Tianne started to clean the garage, Perry decided to watch from a distance. (Infini ...
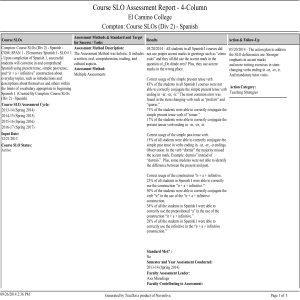
SP14 - El Camino College Compton Center
... the accent mark. Example: durmio” instead of “durmió.” Plus, some students were not able to identify the difference between the present and past. Correct usage of the construction “ir + a + infinitive. 23% of all students in Spanish I were able to correctly use the construction “ir + a + infinitive. ...
... the accent mark. Example: durmio” instead of “durmió.” Plus, some students were not able to identify the difference between the present and past. Correct usage of the construction “ir + a + infinitive. 23% of all students in Spanish I were able to correctly use the construction “ir + a + infinitive. ...
File - Pastor larry dela cruz
... a person knows the form of a word, (for example that a particular verb is present tense, active voice, and indicative mood), then they can have a much better understanding of the original meaning and even subtle feeling that the Holy Spirit was conveying through the New Testament writers. Thus with ...
... a person knows the form of a word, (for example that a particular verb is present tense, active voice, and indicative mood), then they can have a much better understanding of the original meaning and even subtle feeling that the Holy Spirit was conveying through the New Testament writers. Thus with ...
Slide 1
... When infinitive phrases have an “actor,” they may be roughly characterized as the “subject” of the action or state expressed in the infinitive. It is somewhat misleading to use the word subject, though, since an infinitive phrase is not a full clause with a subject and a finite verb. Also remember t ...
... When infinitive phrases have an “actor,” they may be roughly characterized as the “subject” of the action or state expressed in the infinitive. It is somewhat misleading to use the word subject, though, since an infinitive phrase is not a full clause with a subject and a finite verb. Also remember t ...
The Spanish Language Speed Learning Course - Figure B
... dealing with many Spanish speakers in the office or business, or you simply like adding another entry on the “language spoken” part on your résumé, you have chosen the right report to help you learn the language by yourself. With this report, you’ll be learning basic Spanish not within a whole year, ...
... dealing with many Spanish speakers in the office or business, or you simply like adding another entry on the “language spoken” part on your résumé, you have chosen the right report to help you learn the language by yourself. With this report, you’ll be learning basic Spanish not within a whole year, ...
Difference between gerund and participle worksheet
... State whether the –ing forms given in the following sentences are participles or gerunds. In the case of participles, name the noun or pronoun they qualify. In.Aug 22, 2013 . It's tough to know the difference between gerunds and present participles in English just by looking because they both consis ...
... State whether the –ing forms given in the following sentences are participles or gerunds. In the case of participles, name the noun or pronoun they qualify. In.Aug 22, 2013 . It's tough to know the difference between gerunds and present participles in English just by looking because they both consis ...
Greek 1001 Elementary Greek
... Participles always modify their subjects, so a participle modifies whatever noun is its subject. If the subject-noun is not part of a sentence already, however, the problem arises: what case should the noun and participle be? ...
... Participles always modify their subjects, so a participle modifies whatever noun is its subject. If the subject-noun is not part of a sentence already, however, the problem arises: what case should the noun and participle be? ...
Chapter 2
... When used absolutely, with the day of speaking as the reference point, these represent reference to: 1. just have/just about to, 2. same day, 3. hesternal/crastinal, 4. a few days away, and 5. a long time away, respectively. But they can also be used relatively, where the first verb establishes a ti ...
... When used absolutely, with the day of speaking as the reference point, these represent reference to: 1. just have/just about to, 2. same day, 3. hesternal/crastinal, 4. a few days away, and 5. a long time away, respectively. But they can also be used relatively, where the first verb establishes a ti ...
3015 FRENCH MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2010 question paper
... recognisable and acceptable tense. For past tense narrative, please accept (for Communication only) the Imperfect and Pluperfect as well as the Perfect and Past Historic). If a Future is required, please accept the Conditional as well. In the context of Communication, please accept minor spelling er ...
... recognisable and acceptable tense. For past tense narrative, please accept (for Communication only) the Imperfect and Pluperfect as well as the Perfect and Past Historic). If a Future is required, please accept the Conditional as well. In the context of Communication, please accept minor spelling er ...