is used as a conjunction to show contrast. The original
... 85. B – ‘when they died’ is a relative clause modifying ‘the day’. If ‘which’ were used, a preposition ‘on’ should be used because we should say ‘on the day’. 86. B – A non-defining clause should be used because ‘four-letter-word’ is a specific noun. Note that ‘that’ should not be used after a comma ...
... 85. B – ‘when they died’ is a relative clause modifying ‘the day’. If ‘which’ were used, a preposition ‘on’ should be used because we should say ‘on the day’. 86. B – A non-defining clause should be used because ‘four-letter-word’ is a specific noun. Note that ‘that’ should not be used after a comma ...
Some tips for improving Spanish-to
... Correcting the first translation makes it evident that we have a “false friend” problem in the translation of the second statement. The use of the Spanish verb ejecutar refers to the implementation of the contract, or the carrying out of the actions that will be taken to fulfill the purpose or oblig ...
... Correcting the first translation makes it evident that we have a “false friend” problem in the translation of the second statement. The use of the Spanish verb ejecutar refers to the implementation of the contract, or the carrying out of the actions that will be taken to fulfill the purpose or oblig ...
Month 10 - Shri Chitrapur Math
... AiSm or a Ah< ¢Nw< pQaim Aasm! , There is no need for exercises with this lesson. When we are through with our study of participles, we can go over all of it at one go and translate an entire story to see how they are all used. Please do go over the last three lessons again though. Then do write to ...
... AiSm or a Ah< ¢Nw< pQaim Aasm! , There is no need for exercises with this lesson. When we are through with our study of participles, we can go over all of it at one go and translate an entire story to see how they are all used. Please do go over the last three lessons again though. Then do write to ...
Document
... Irish appears to be essentially an SVO language, like French. Verbs and auxiliaries raise past the subject to yield VSO. We can analyze the Irish pattern as being minimally different from our existing analysis of French— just one difference, which we hypothesize is another parametric difference betw ...
... Irish appears to be essentially an SVO language, like French. Verbs and auxiliaries raise past the subject to yield VSO. We can analyze the Irish pattern as being minimally different from our existing analysis of French— just one difference, which we hypothesize is another parametric difference betw ...
Correct Answer: D
... 2. These who dream of striking it rich can still 3. This who dream of striking it rich can still 4. Those who dream of striking it rich can still 5. Them who dream of striking it rich can still Correct Answer: D Explanation: This sentence has an error by using a conjunction (that) in the place of a ...
... 2. These who dream of striking it rich can still 3. This who dream of striking it rich can still 4. Those who dream of striking it rich can still 5. Them who dream of striking it rich can still Correct Answer: D Explanation: This sentence has an error by using a conjunction (that) in the place of a ...
On past participles and their external arguments
... care of by Voice (see e.g. Kratzer, 1996, and many others) and that Voice can take a verbal participial complement. If the external argument of the participle appears as a DP in the specifier of Voice, as in active constructions, the result is an active past participle. If it instead takes the form ...
... care of by Voice (see e.g. Kratzer, 1996, and many others) and that Voice can take a verbal participial complement. If the external argument of the participle appears as a DP in the specifier of Voice, as in active constructions, the result is an active past participle. If it instead takes the form ...
Participle - WordPress.com
... c. Present Participle as Taking Relative Pronoun a. Present Participle as Attribute Has a function in front of a noun as a substitute adjective. ...
... c. Present Participle as Taking Relative Pronoun a. Present Participle as Attribute Has a function in front of a noun as a substitute adjective. ...
Formal Commands - Villanova University
... Informal, or familiar, speech is used among friends, coworkers, ...
... Informal, or familiar, speech is used among friends, coworkers, ...
A Comparative Study of Imperative Sentences in English and
... used to emphasize the fact to which we are referring to, it precedes the verb in the imperative mood. As the English language has a fixed word order, in some cases the use of the subject is important to clarify the meaning. The subject is compulsory in this case. Let sentences with pronouns used in ...
... used to emphasize the fact to which we are referring to, it precedes the verb in the imperative mood. As the English language has a fixed word order, in some cases the use of the subject is important to clarify the meaning. The subject is compulsory in this case. Let sentences with pronouns used in ...
Commands in Deni (Arawá)
... Deni verbal morphology is a highly synthetic and predominantly composed by suffixes. Whereas syntactically verbs are the head of predicate, semantically they typically express actions, states and natural phenomena. There are a plenty of morphemes which may be attached to the verb root in Deni. Every ...
... Deni verbal morphology is a highly synthetic and predominantly composed by suffixes. Whereas syntactically verbs are the head of predicate, semantically they typically express actions, states and natural phenomena. There are a plenty of morphemes which may be attached to the verb root in Deni. Every ...
gerúndio - CLUL - Universidade de Lisboa
... The structure of the paper is as follows: in section 2, we present a brief review of the basic syntactic and semantic facts about the Portuguese «gerúndio»; in sections 3 and 4, we focus on the different preferences exhibited by EP and BP with respect to the periphrastic and the adverbial «gerúndio» ...
... The structure of the paper is as follows: in section 2, we present a brief review of the basic syntactic and semantic facts about the Portuguese «gerúndio»; in sections 3 and 4, we focus on the different preferences exhibited by EP and BP with respect to the periphrastic and the adverbial «gerúndio» ...
grammar - BS Publication
... 4 . The lions of Africa are fiercer than those of India. 5 . He is a fatherly figure, so we must respect him as such. 3 . INDEFINITE PRONOUN : An indefinite pronoun is a pronoun that refers to a person or thing in a general and indefinite way, but not in a specific or particular way. The main indefi ...
... 4 . The lions of Africa are fiercer than those of India. 5 . He is a fatherly figure, so we must respect him as such. 3 . INDEFINITE PRONOUN : An indefinite pronoun is a pronoun that refers to a person or thing in a general and indefinite way, but not in a specific or particular way. The main indefi ...
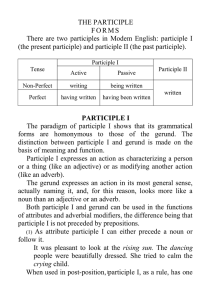
The participle
... sight for the villagers. 4. The (terrify) villagers ran for their lives. 5. I found myself in an (embarrass) situation last night. 6. A kid accidentally threw a ball at one of the school windows. Someone needs to repair the (break) window. 7. A (damage) earthquake occurred recently. 8. People are st ...
... sight for the villagers. 4. The (terrify) villagers ran for their lives. 5. I found myself in an (embarrass) situation last night. 6. A kid accidentally threw a ball at one of the school windows. Someone needs to repair the (break) window. 7. A (damage) earthquake occurred recently. 8. People are st ...
The Use of the Infinitive in Latvian and Norwegian
... by the sentence. The deep structure of a definite sentence is called a proposition with the abstract semantic or thematic roles (e.g., agent, experiencer, patient, recipient) filled by definite lexical items (Saeed, 2000:14-15). One of the most characteristic features of infinitive constructions is ...
... by the sentence. The deep structure of a definite sentence is called a proposition with the abstract semantic or thematic roles (e.g., agent, experiencer, patient, recipient) filled by definite lexical items (Saeed, 2000:14-15). One of the most characteristic features of infinitive constructions is ...
Restructuring Involving Purpose/ Gerundive Clause in Japanese*
... which in turn allows the instrumental adjunct zitensya-de to modify the verb.) In contrast, kowas(u) in (10) is suffixed by -te, which has a [-Tense] feature. Since this feature sanctions an event argument, the gerund kowasi-te is modifiable. So in (10), this gerund, which heads a GC, is modified by ...
... which in turn allows the instrumental adjunct zitensya-de to modify the verb.) In contrast, kowas(u) in (10) is suffixed by -te, which has a [-Tense] feature. Since this feature sanctions an event argument, the gerund kowasi-te is modifiable. So in (10), this gerund, which heads a GC, is modified by ...
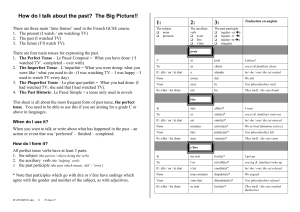
Slide 1
... (guide p44/5 + 62 +84) •Numbers (guide p4) •Time phrases (guide p21 + 54) •Word Order (guide p76) ...
... (guide p44/5 + 62 +84) •Numbers (guide p4) •Time phrases (guide p21 + 54) •Word Order (guide p76) ...
Psychophysical and Physical Causative Emotion Verbs in Finnish
... example in the clause Mattia hävettää kävellä ‘Matti feels ashamed to walk’, both the subject of the infinitive 1 verb kävellä (Matti kävelee ‘Matti walks’) and the object of the matrix verb hävettää (Mattia hävettää ‘Matti feels ashamed’) refer to the same person, to Matti. In this construction the ...
... example in the clause Mattia hävettää kävellä ‘Matti feels ashamed to walk’, both the subject of the infinitive 1 verb kävellä (Matti kävelee ‘Matti walks’) and the object of the matrix verb hävettää (Mattia hävettää ‘Matti feels ashamed’) refer to the same person, to Matti. In this construction the ...
Grammar Packet #1: The Present Participle
... Any daily grades taken from packets will be based on completion for a portion of the credit and correctness for the major part of the grade. Work on the packets (unless specified otherwise) is individual—not group—work. You will have 6 of these packets, one per six weeks. Sometimes a grade will be t ...
... Any daily grades taken from packets will be based on completion for a portion of the credit and correctness for the major part of the grade. Work on the packets (unless specified otherwise) is individual—not group—work. You will have 6 of these packets, one per six weeks. Sometimes a grade will be t ...
Motion events can be segmented into several components
... These studies will be discussed in more detail in Section 2.3. 1.2 Motion typology and narration style SLOBIN (1996, 1997, 2004) finds that satellite-framed languages (S-languages) and verb-framed languages (V-languages) differ from each other in interesting ways with respect to the description of m ...
... These studies will be discussed in more detail in Section 2.3. 1.2 Motion typology and narration style SLOBIN (1996, 1997, 2004) finds that satellite-framed languages (S-languages) and verb-framed languages (V-languages) differ from each other in interesting ways with respect to the description of m ...
Exerceamus 21-30 12-21-08 FINAL
... Directions: Fill in the missing words for the fourth conjugation verb audiō. Use the chart for capiō if you need help. This time we have given you only two forms to get you started. 4th Conjugation Present System ...
... Directions: Fill in the missing words for the fourth conjugation verb audiō. Use the chart for capiō if you need help. This time we have given you only two forms to get you started. 4th Conjugation Present System ...
Get-passives, Raising, and Control
... Note that the morphology here distinguishes only between stative and ‘other’ participles. This means that even for the cases that are morphologically distinguished, we still have to test whether we are looking at an eventive (verbal) participle or a resultative adjectival one. Both of these involve ...
... Note that the morphology here distinguishes only between stative and ‘other’ participles. This means that even for the cases that are morphologically distinguished, we still have to test whether we are looking at an eventive (verbal) participle or a resultative adjectival one. Both of these involve ...
What Does Gustar Mean?
... Clearly, someone likes the car, but who? Just using "Le" doesn't help; it could mean "him," or "her," or even "you" (in the usted form). How do Spanish-speaking people understand each other in these situations? Quite often they will add a few words for clarification: Spanish: ...
... Clearly, someone likes the car, but who? Just using "Le" doesn't help; it could mean "him," or "her," or even "you" (in the usted form). How do Spanish-speaking people understand each other in these situations? Quite often they will add a few words for clarification: Spanish: ...
ÜiÜJ - GAGL
... more morphologically dependent. On the contrary, it changes from what could be called a prefix to an independent auxiliary. The third change I examine involves the progressive construction with on. There is, already in Old English, a 'progressive' form, namely be followed by a Verb in -ing. In Middl ...
... more morphologically dependent. On the contrary, it changes from what could be called a prefix to an independent auxiliary. The third change I examine involves the progressive construction with on. There is, already in Old English, a 'progressive' form, namely be followed by a Verb in -ing. In Middl ...