The Gravitational Radius of a Black Hole
... Thus, an error in the determination of the gravitational radius of a black hole according to formula (1), which does not take into account the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation, is 108 times (based upon calculations using the gravitational radius of our Sun), but the astronomers do not kno ...
... Thus, an error in the determination of the gravitational radius of a black hole according to formula (1), which does not take into account the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation, is 108 times (based upon calculations using the gravitational radius of our Sun), but the astronomers do not kno ...
ppt
... If not, disc is thick, non—Keplerian, and does not cool efficiently. Pressure is important: disc ~ rapidly rotating `star’. Progress in calculating structure slow: e.g. flow timescales far shorter at inner edge than further out. One possibility: matter flows inwards without radiating, and can accret ...
... If not, disc is thick, non—Keplerian, and does not cool efficiently. Pressure is important: disc ~ rapidly rotating `star’. Progress in calculating structure slow: e.g. flow timescales far shorter at inner edge than further out. One possibility: matter flows inwards without radiating, and can accret ...
Slide 1
... more stars in a region only 30 light years across, which suggests that all the stars were born in a single episode of star formation. Based on optical properties such as brightness and color some of the normal stars in the cluster are known to have masses of about 40 suns. ...
... more stars in a region only 30 light years across, which suggests that all the stars were born in a single episode of star formation. Based on optical properties such as brightness and color some of the normal stars in the cluster are known to have masses of about 40 suns. ...
The Known Unknowns: predicting the landscape of LISA black hole
... KHB, Khan, Li 2015 Li, KHB, Khan, 2015 Khan, KHB, et al 2013 ...
... KHB, Khan, Li 2015 Li, KHB, Khan, 2015 Khan, KHB, et al 2013 ...
Shockingly Bright Pulsar - Astronomical Society of the Pacific
... •ULXs were previously all suspected to be “intermediate mass” black holes—black holes up to a few hundred solar masses--accreting matter that heated and emitted Xrays in large quantities. •Now, astronomers have to explain how a stellar-mass pulsar can act as extremely as a black hole. ...
... •ULXs were previously all suspected to be “intermediate mass” black holes—black holes up to a few hundred solar masses--accreting matter that heated and emitted Xrays in large quantities. •Now, astronomers have to explain how a stellar-mass pulsar can act as extremely as a black hole. ...
PDF format
... b) Observing a massive star supernova reveals the mass of the stellar remnant, and if it exceeds 3 solar masses it must be a black hole. c) Observing the orbital motion of a star around a stellar remnant reveals the mass of the stellar remnant, and if it exceeds 3 solar masses it must be a black h ...
... b) Observing a massive star supernova reveals the mass of the stellar remnant, and if it exceeds 3 solar masses it must be a black hole. c) Observing the orbital motion of a star around a stellar remnant reveals the mass of the stellar remnant, and if it exceeds 3 solar masses it must be a black h ...
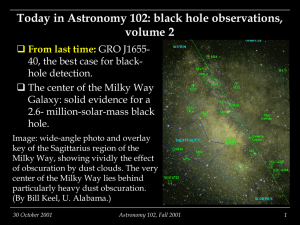
Today in Astronomy 102: black hole observations, v.2
... We expect it to spin, but now we can demonstrate this: A 7 M black hole has a horizon circumference 130 km, and if it doesn’t spin its innermost stable orbit circumference is 390 km. Material in this orbit will circle the black hole 314 times per second. However, one often sees the X-ray brightne ...
... We expect it to spin, but now we can demonstrate this: A 7 M black hole has a horizon circumference 130 km, and if it doesn’t spin its innermost stable orbit circumference is 390 km. Material in this orbit will circle the black hole 314 times per second. However, one often sees the X-ray brightne ...
13 Black-body radiation and Planck`s formula
... An electron rotating about the nucleus has centripetal acceleration. According to Maxwell’s electromagnetic theory, any accelerating charged particle must emit radiation. Therefore, a rotating electron would constantly emit radiation and hence lose energy, so that eventually it would fall into the n ...
... An electron rotating about the nucleus has centripetal acceleration. According to Maxwell’s electromagnetic theory, any accelerating charged particle must emit radiation. Therefore, a rotating electron would constantly emit radiation and hence lose energy, so that eventually it would fall into the n ...
Document
... • Goal is to measure the detailed properties and rate of the events to probe accretion physics, the mass of the black hole, and evolution of the tidal disruption rate. • The next generation of optical synoptic surveys such as Pan-STARRs and LSST have the potential to detect hundreds of events. • Wit ...
... • Goal is to measure the detailed properties and rate of the events to probe accretion physics, the mass of the black hole, and evolution of the tidal disruption rate. • The next generation of optical synoptic surveys such as Pan-STARRs and LSST have the potential to detect hundreds of events. • Wit ...
Black Holes
... The puzzle of supermassive black holes While the formation of stellar-mass black holes is fairly well understood, it is not clear how black holes as massive as a million to a billion times the mass of the Sun could have formed and have already been in place at a time when the Universe was less than ...
... The puzzle of supermassive black holes While the formation of stellar-mass black holes is fairly well understood, it is not clear how black holes as massive as a million to a billion times the mass of the Sun could have formed and have already been in place at a time when the Universe was less than ...
Mass Estimate of Black Hole Candidates GRS 1758
... Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics Seminar May 23, 2006 ...
... Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics Seminar May 23, 2006 ...
Gauss-Bonnet black holes at the LHC: beyond the
... fall within an hadronic jet, making them impossible to distinguish from the background of decay products. Furthermore, the background from standard model Z(ee)+jets and γ+jets remains much lower than the expected signal. The value of the Planck scale is assumed to be known as a clear threshold effec ...
... fall within an hadronic jet, making them impossible to distinguish from the background of decay products. Furthermore, the background from standard model Z(ee)+jets and γ+jets remains much lower than the expected signal. The value of the Planck scale is assumed to be known as a clear threshold effec ...
JUL 12 ARCHNES LIBRARIES
... building computer simulations that could handle complex calculations. But they were theorists, playing with theoretical objects. Black holes looked nice on paper, but were they real? To be more than a physicist's daydream, black holes had to prove themselves astronomically. For stellar-mass black ho ...
... building computer simulations that could handle complex calculations. But they were theorists, playing with theoretical objects. Black holes looked nice on paper, but were they real? To be more than a physicist's daydream, black holes had to prove themselves astronomically. For stellar-mass black ho ...
Xiao Yang Xia
... (1) The optical emission of both infrared and optically selected QSOs and NLS1s is mainly from the central AGN, the infrared excess, especially farinfrared excess of IR QSOs should come from starbursts. (2) Star formation rate and accretion rate onto the central BH in IR QSOs at low redshift follow ...
... (1) The optical emission of both infrared and optically selected QSOs and NLS1s is mainly from the central AGN, the infrared excess, especially farinfrared excess of IR QSOs should come from starbursts. (2) Star formation rate and accretion rate onto the central BH in IR QSOs at low redshift follow ...
DIETER LÃST (LMU, MPI) - Stony Brook University
... • We found evidence for classicalization and black hole production (black hole N-portrait) in field theory. • We found an interesting trans-Planckian transition between field theory and string theory: string black hole correspondence. Next steps: ...
... • We found evidence for classicalization and black hole production (black hole N-portrait) in field theory. • We found an interesting trans-Planckian transition between field theory and string theory: string black hole correspondence. Next steps: ...
Quantum Criticality and Black Holes
... The quantum theory of a black hole in a 3+1dimensional negatively curved AdS universe is holographically represented by a CFT (the theory of a quantum critical point) in 2+1 dimensions 3+1 dimensional AdS space ...
... The quantum theory of a black hole in a 3+1dimensional negatively curved AdS universe is holographically represented by a CFT (the theory of a quantum critical point) in 2+1 dimensions 3+1 dimensional AdS space ...
Cool horizons for entangled black holes
... Spacetime locality is one of the cornerstones in our present understanding of physics. By locality we mean the impossibility of sending signals faster than the speed of light. Locality appears to be challenged both by quantum mechanics and by general relativity. Quantum mechanics gives rise to Einst ...
... Spacetime locality is one of the cornerstones in our present understanding of physics. By locality we mean the impossibility of sending signals faster than the speed of light. Locality appears to be challenged both by quantum mechanics and by general relativity. Quantum mechanics gives rise to Einst ...
Quasars- The Brightest Black Holes
... recession of 48,000 km/s. This high a redshift was itself not new – it was comparable to that seen in distant faint galaxies at the time – but no-one had considered that the spectrum of an individual star could be explained in this way. The redshift meant that either the star was close, but escaping ...
... recession of 48,000 km/s. This high a redshift was itself not new – it was comparable to that seen in distant faint galaxies at the time – but no-one had considered that the spectrum of an individual star could be explained in this way. The redshift meant that either the star was close, but escaping ...
Black holes - Institute of Physics
... description regards the universe as having three dimensions of space and one of time – spacetime; gravity is thought of as the distortion of spacetime caused by the presence of matter. A Dutch physicist, Johannes Droste, and a German physicist, Karl Schwarzschild, independently found a spherical sol ...
... description regards the universe as having three dimensions of space and one of time – spacetime; gravity is thought of as the distortion of spacetime caused by the presence of matter. A Dutch physicist, Johannes Droste, and a German physicist, Karl Schwarzschild, independently found a spherical sol ...
Lecture9
... Note: A massive star with main sequence mass larger than ~ 25M☉ will become a black hole, because it cannot eject enough mass and the collapsed core will have mass larger than the neutron star maximum mass limit ~ 3M☉ So, if the remnant collapsed mass is larger than ~3M☉, the core keeps collapsing ...
... Note: A massive star with main sequence mass larger than ~ 25M☉ will become a black hole, because it cannot eject enough mass and the collapsed core will have mass larger than the neutron star maximum mass limit ~ 3M☉ So, if the remnant collapsed mass is larger than ~3M☉, the core keeps collapsing ...
... However, after the work of Bekenstein, Hawking found that actually one can speak about the thermodynamics of black holes. In [8] Hawking found that black holes radiate a thermal spectrum of particles, since then called Hawking radiation, at ~κ . However, this result shows that the temperature of a a ...
Hawking radiation

Hawking radiation is black body radiation that is predicted to be released by black holes, due to quantum effects near the event horizon. It is named after the physicist Stephen Hawking, who provided a theoretical argument for its existence in 1974, and sometimes also after Jacob Bekenstein, who predicted that black holes should have a finite, non-zero temperature and entropy.Hawking's work followed his visit to Moscow in 1973 where the Soviet scientists Yakov Zeldovich and Alexei Starobinsky showed him that, according to the quantum mechanical uncertainty principle, rotating black holes should create and emit particles. Hawking radiation reduces the mass and energy of black holes and is therefore also known as black hole evaporation. Because of this, black holes that lose more mass than they gain through other means are expected to shrink and ultimately vanish. Micro black holes are predicted to be larger net emitters of radiation than larger black holes and should shrink and dissipate faster.In September 2010, a signal that is closely related to black hole Hawking radiation (see analog gravity) was claimed to have been observed in a laboratory experiment involving optical light pulses. However, the results remain unverified and debatable. Other projects have been launched to look for this radiation within the framework of analog gravity. In June 2008, NASA launched the Fermi space telescope, which is searching for the terminal gamma-ray flashes expected from evaporating primordial black holes. In the event that speculative large extra dimension theories are correct, CERN's Large Hadron Collider may be able to create micro black holes and observe their evaporation.