Electric Current and Circuits Guided Notes
... Charges (-) flow from _______________ voltage areas to ______________ voltage areas – Voltage is like electrical pressure that ________________________ charges – Voltage Difference: the push/pull that ______________________________________________________ and is measured in volts (V) Circuit: ______ ...
... Charges (-) flow from _______________ voltage areas to ______________ voltage areas – Voltage is like electrical pressure that ________________________ charges – Voltage Difference: the push/pull that ______________________________________________________ and is measured in volts (V) Circuit: ______ ...
Bernoulli`s Equation
... 7. If V2 is greater than V1 then the piezometric head ( ω +Z2) must be less than the P1 piezometric head ( ω +Z1). However if the two points considered lie along the same horizontal plane then Z1 = Z2, in which case the changes in velocity cause corresponding change in pressure. ...
... 7. If V2 is greater than V1 then the piezometric head ( ω +Z2) must be less than the P1 piezometric head ( ω +Z1). However if the two points considered lie along the same horizontal plane then Z1 = Z2, in which case the changes in velocity cause corresponding change in pressure. ...
Phys 784 - WVU Plasma Physics
... to the Coriolis term. The square root of the ratio of the viscous force to the Coriolis force is called the “Ekman number” Ek- write it in terms of the appropriate scales. Thus, for small Ekman number, the effect of viscosity can be ignored relative to the Coriolis force, and vice versa for large Ek ...
... to the Coriolis term. The square root of the ratio of the viscous force to the Coriolis force is called the “Ekman number” Ek- write it in terms of the appropriate scales. Thus, for small Ekman number, the effect of viscosity can be ignored relative to the Coriolis force, and vice versa for large Ek ...
case-study-teaching-material-intro-to
... Therefore, when fluid passes over a stationary body forcing the streamlines to get closer together, the velocity must increase (as the area decreases), and therefore the pressure decreases. This is how an airfoil works, the flow over the top surface is faster than the flow over the bottom surface, t ...
... Therefore, when fluid passes over a stationary body forcing the streamlines to get closer together, the velocity must increase (as the area decreases), and therefore the pressure decreases. This is how an airfoil works, the flow over the top surface is faster than the flow over the bottom surface, t ...
L-14 Fluids [3] - University of Iowa Physics
... • He was born in Switzerland in 1700 • He was one of 5 brothers and came from a large family of mathematicians and scientists. ...
... • He was born in Switzerland in 1700 • He was one of 5 brothers and came from a large family of mathematicians and scientists. ...
Document
... A diagram of a liquid-liquid ejector is shown in the figure below. It is desired to analyze the steady-state mixing of two streams, both of the same fluid, by means of overall balances. At plane 1 the two fluids merge. Stream 1a has a velocity v0 and a cross-sectional area (1/3)A1, and Stream 1b has ...
... A diagram of a liquid-liquid ejector is shown in the figure below. It is desired to analyze the steady-state mixing of two streams, both of the same fluid, by means of overall balances. At plane 1 the two fluids merge. Stream 1a has a velocity v0 and a cross-sectional area (1/3)A1, and Stream 1b has ...
Min-218 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow
... Imagine a circular cross-section of pipe containing a fluid such as water. For flow to occur without slippage, the various layers must move at different velocities. The fluid layer adjacent to the pipe wall is virtually stationary, while the layers further out move at increasingly higher velocities ...
... Imagine a circular cross-section of pipe containing a fluid such as water. For flow to occur without slippage, the various layers must move at different velocities. The fluid layer adjacent to the pipe wall is virtually stationary, while the layers further out move at increasingly higher velocities ...
Electricity Vocabulary
... circuit in which all the lights or resistors are connected in sequence, or one after the other, forming a single path Through which the electricity can flow. Batteries in a flashlight and small, portable radios are frequently connected in series. ...
... circuit in which all the lights or resistors are connected in sequence, or one after the other, forming a single path Through which the electricity can flow. Batteries in a flashlight and small, portable radios are frequently connected in series. ...
CHAPTER 3 HYDRAULICS OF SEWERS
... time characterizes the flow in two categories, steady and unsteady flow. If the flow parameters, such as velocity, pressure, density and discharge do not vary with time or are independent of time then the flow is steady. If the flow parameters vary with time then the flow is categorized as unsteady ...
... time characterizes the flow in two categories, steady and unsteady flow. If the flow parameters, such as velocity, pressure, density and discharge do not vary with time or are independent of time then the flow is steady. If the flow parameters vary with time then the flow is categorized as unsteady ...
Xyloglucan : Its Structure and Function Xyloglucan : Its Structure and
... Xyloglucan is a major structural polysaccharide in the primary cell wall of higher plants. Cell growth and enlargement are controlled by the looseness of a thin net of microfibrils made of cellulose. Xyloglucan cross-links these cellulose microfibrils and provides the flexibility necessary for the m ...
... Xyloglucan is a major structural polysaccharide in the primary cell wall of higher plants. Cell growth and enlargement are controlled by the looseness of a thin net of microfibrils made of cellulose. Xyloglucan cross-links these cellulose microfibrils and provides the flexibility necessary for the m ...
Chapter-9 The Behavior of Fluids
... body that was submerged. This observation is now known as Archimedes' Principle and gave him the means to solve the problem. He was so excited that he ran naked through the streets of Syracuse shouting "Eureka! eureka!" (I have found it!). The fraudulent goldsmith was brought to justice. ...
... body that was submerged. This observation is now known as Archimedes' Principle and gave him the means to solve the problem. He was so excited that he ran naked through the streets of Syracuse shouting "Eureka! eureka!" (I have found it!). The fraudulent goldsmith was brought to justice. ...
Fluid Dynamics
... Fluid Dynamics: The Momentum and Bernoulli Equations 45 2. Steady non-uniform flow. Conditions change from point to point in the stream but do not change with time. An example is flow in a tapering pipe with constant velocity at the inlet - velocity will change as you move along the length of the pi ...
... Fluid Dynamics: The Momentum and Bernoulli Equations 45 2. Steady non-uniform flow. Conditions change from point to point in the stream but do not change with time. An example is flow in a tapering pipe with constant velocity at the inlet - velocity will change as you move along the length of the pi ...
Control surface Control Volume
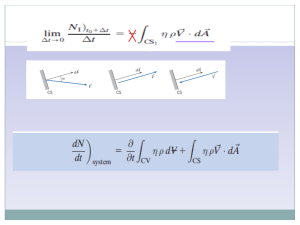
... EXP1)The balloon is being filled through section 1, where the area is A1, velocity is V1,and fluid density is ρ1. The average density within the balloon is ρb(t). Find an expression for the rate of change of system mass within the balloon at this ...
... EXP1)The balloon is being filled through section 1, where the area is A1, velocity is V1,and fluid density is ρ1. The average density within the balloon is ρb(t). Find an expression for the rate of change of system mass within the balloon at this ...
Mechanical Engineering Department
... is interested in mechanics of stretchable and flexible electronics, and mechanically guided deterministic 3D assembly. He has published 2 books and more than 500 journal papers, including multi-disciplinary journals Science (2006, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015) and Nature (2008, 201 ...
... is interested in mechanics of stretchable and flexible electronics, and mechanically guided deterministic 3D assembly. He has published 2 books and more than 500 journal papers, including multi-disciplinary journals Science (2006, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015) and Nature (2008, 201 ...
History and Current Status of the Plastics Industry
... • Strength: Amount of force per unit area that a material can support without breaking. • Stiffness: A material’s resistance to deformation under load ...
... • Strength: Amount of force per unit area that a material can support without breaking. • Stiffness: A material’s resistance to deformation under load ...
chapter14 - People Server at UNCW
... The pressure P exerted by a fluid is defined as the magnitude F of the force acting perpendicular to a surface divided by the area A over which the force acts: ...
... The pressure P exerted by a fluid is defined as the magnitude F of the force acting perpendicular to a surface divided by the area A over which the force acts: ...
akdeniz university faculty of engineering 2013
... solution methods in nonlinear structure analysis. Binding materials: gypsum, lime, pozzolanic materials, cements, Aggregates: properties and experiments, Concrete: Parameters affecting strength, fresh concrete properties, mixture design, hardened concrete properties, quality control, durability, con ...
... solution methods in nonlinear structure analysis. Binding materials: gypsum, lime, pozzolanic materials, cements, Aggregates: properties and experiments, Concrete: Parameters affecting strength, fresh concrete properties, mixture design, hardened concrete properties, quality control, durability, con ...
Fluid Mechanics Concepts
... less by the magnitude of the buoyant force. In our particular example, the buoyant force, B, on the object is about half the magnitude of the weight of the object, W. Can you estimate the specific gravity of the substance ...
... less by the magnitude of the buoyant force. In our particular example, the buoyant force, B, on the object is about half the magnitude of the weight of the object, W. Can you estimate the specific gravity of the substance ...
Diapositiva 1
... are short with small flows Mediterranean Sea because there is little rainfall. The rivers which flow into The rivers which flow into thethe Atlantic Cantabrian are short and steep. Ocean have large flows. However, the River Ebro is Sea Spanish rivers are generally short with the longest river in Spa ...
... are short with small flows Mediterranean Sea because there is little rainfall. The rivers which flow into The rivers which flow into thethe Atlantic Cantabrian are short and steep. Ocean have large flows. However, the River Ebro is Sea Spanish rivers are generally short with the longest river in Spa ...





![L-14 Fluids [3] - University of Iowa Physics](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015391226_1-fdc5124b593c632cc9a0ec2ed3f4cea6-300x300.png)