Phase Transformations
... In contrast to metals silicates, borates and phosphates tend to form glasses Due to high cation-cation repulsion these materials have open structures In silicates the difference in total bond energy between periodic and aperiodic array is small (bond energy is primarily determined by the firs ...
... In contrast to metals silicates, borates and phosphates tend to form glasses Due to high cation-cation repulsion these materials have open structures In silicates the difference in total bond energy between periodic and aperiodic array is small (bond energy is primarily determined by the firs ...
Is Bigger Better for Control Valves?
... friction losses of the components within the piping circuit, including the coil, valving, pipe and fittings. Without getting in too much detail, this typically amounts to 30 percent to 50 percent of the total system pressure drop at design conditions. To a certain extent, the temperature control sys ...
... friction losses of the components within the piping circuit, including the coil, valving, pipe and fittings. Without getting in too much detail, this typically amounts to 30 percent to 50 percent of the total system pressure drop at design conditions. To a certain extent, the temperature control sys ...
Size Controlled Nanometer Phase Structure and Thickness Films of
... 2), we approach it in a physical method that is suitable for many kind polymers or other materials. As we know, the dispersion modes of different phases in a mixture of molten polymers depend on the blend compositions, molecular weight, temperature, miscibility, chain mobility and interfacial tensio ...
... 2), we approach it in a physical method that is suitable for many kind polymers or other materials. As we know, the dispersion modes of different phases in a mixture of molten polymers depend on the blend compositions, molecular weight, temperature, miscibility, chain mobility and interfacial tensio ...
Thermal Conductivity of Insulating Materials by
... plays an important role. Although the thermal conductivity is not a function of thickness as a material property, this only applies if the proportions of the heat transfer mechanisms in the material involved do not change. If, however, compression occurs, there is an increase in heat transfer due to ...
... plays an important role. Although the thermal conductivity is not a function of thickness as a material property, this only applies if the proportions of the heat transfer mechanisms in the material involved do not change. If, however, compression occurs, there is an increase in heat transfer due to ...
Flow “Fine” Synthesis: High Yielding and Selective
... Department of Chemistry, School of Science, The University of Tokyo, Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 1130033 (Japan) shu_kobayashi@chem.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp The concept of flow “fine” synthesis, that is high yielding and selective organic synthesis by flow methods, will be presented. Flow methods have several ad ...
... Department of Chemistry, School of Science, The University of Tokyo, Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 1130033 (Japan) shu_kobayashi@chem.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp The concept of flow “fine” synthesis, that is high yielding and selective organic synthesis by flow methods, will be presented. Flow methods have several ad ...
Physics 1A, Section 7
... Bernoulli’s Equation (energy conservation) ½ rv2 + rgz + p = constant along streamline r is the density v is the fluid velocity g is the acceleration due to gravity z is the vertical height p is the pressure Applies ...
... Bernoulli’s Equation (energy conservation) ½ rv2 + rgz + p = constant along streamline r is the density v is the fluid velocity g is the acceleration due to gravity z is the vertical height p is the pressure Applies ...
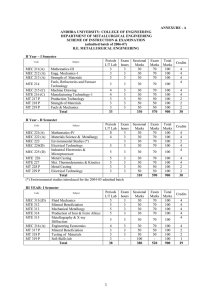
ANDHRA UNIVERSITY : COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
... Space lattice and unit cells, crystal systems. Indices for planes and directions. Structures of common metallic materials. Crystal defects: point, Line and surface defects. Binary phase diagrams. Gibbs rule. Lever rule. Invariant reactions. Iron-Iron carbide phase diagram. Heat treatment of steel. I ...
... Space lattice and unit cells, crystal systems. Indices for planes and directions. Structures of common metallic materials. Crystal defects: point, Line and surface defects. Binary phase diagrams. Gibbs rule. Lever rule. Invariant reactions. Iron-Iron carbide phase diagram. Heat treatment of steel. I ...
1 ATOMIZATION OF HIGHLY VISCOUS FLUIDS Nasser Ashgriz
... to produce powders of the same. They have high viscosity and low surface tension. These liquids have to be atomized rapidly before they cool and solidify. Rapid cooling may result in ligaments and fibers rather than spherical particles. Increasing the melt temperature to prevent rapid ...
... to produce powders of the same. They have high viscosity and low surface tension. These liquids have to be atomized rapidly before they cool and solidify. Rapid cooling may result in ligaments and fibers rather than spherical particles. Increasing the melt temperature to prevent rapid ...
0739.PDF
... causes elastic deformations and at a specified value of stress causes inelastic deformations to evolve. This point on the Hugoniot curve is denoted as the HEL and for the case of metals it is related to the yield stress and to the onset of plastic deformations. The HEL in the compressive phase curve ...
... causes elastic deformations and at a specified value of stress causes inelastic deformations to evolve. This point on the Hugoniot curve is denoted as the HEL and for the case of metals it is related to the yield stress and to the onset of plastic deformations. The HEL in the compressive phase curve ...
Silicone Elastomers UV-Cure Silicone Rubber
... (2C) injection molding processes using this material have been established in a number of applications in the automotive, consumer goods, medical and industrial industries. The technology, which uses heat to cure the silicone, requires a high temperature (120°C and higher) for short and efficient cy ...
... (2C) injection molding processes using this material have been established in a number of applications in the automotive, consumer goods, medical and industrial industries. The technology, which uses heat to cure the silicone, requires a high temperature (120°C and higher) for short and efficient cy ...
ent153_tutorial1
... Problem 4: Member AC shown in Fig. 4 (a) is subjected to a vertical force of 3 kN. Determine the position x of this force so that the average compressive stress at the smooth support C is equal to the average tensile stress in the tie rod AB. The rod has a cross-sectional area of 400 mm2 and the co ...
... Problem 4: Member AC shown in Fig. 4 (a) is subjected to a vertical force of 3 kN. Determine the position x of this force so that the average compressive stress at the smooth support C is equal to the average tensile stress in the tie rod AB. The rod has a cross-sectional area of 400 mm2 and the co ...
p181B 01 09 2006 zhang
... consideration, when τ m / Ym ≥ 1 / 3 , the metal film will deform plastically under the shear stress alone without the aid of the temperature change. In the other limit, when τ m = 0, the metal film undergoes cyclic plastic deformation if the temperature range is sufficiently large. The regime bound ...
... consideration, when τ m / Ym ≥ 1 / 3 , the metal film will deform plastically under the shear stress alone without the aid of the temperature change. In the other limit, when τ m = 0, the metal film undergoes cyclic plastic deformation if the temperature range is sufficiently large. The regime bound ...
Manual
... sensor to prevent potential damage due to excessive stress on the sensor fittings. The inlet flow is redirected via a nozzle, therefore no inlet or outlet straight piping is required and the sensor can be mounted in any orientation. With horizontal flow, we suggest that the sensor electronics be pos ...
... sensor to prevent potential damage due to excessive stress on the sensor fittings. The inlet flow is redirected via a nozzle, therefore no inlet or outlet straight piping is required and the sensor can be mounted in any orientation. With horizontal flow, we suggest that the sensor electronics be pos ...
Association in Solution III - Engineering Conferences International
... states such as equilibrium cluster phases and cluster glasses can exist. While these investigations have been mainly triggered by attempts to make and exploit analogies between the resulting phase or state diagrams of colloidal suspensions and atomic and molecular systems, phase separation and dynam ...
... states such as equilibrium cluster phases and cluster glasses can exist. While these investigations have been mainly triggered by attempts to make and exploit analogies between the resulting phase or state diagrams of colloidal suspensions and atomic and molecular systems, phase separation and dynam ...