Week 8 ductile deformation continued
... Ductile deformational processes Crystal Plasticity: migration of crystal dislocations causes permanent deformation Dislocation by climb or cross slip, Sometimes glide planes are blocked by point defects. Edge Dislocation: can’t continue on that plane, so dislocation climbs to new glide plane ...
... Ductile deformational processes Crystal Plasticity: migration of crystal dislocations causes permanent deformation Dislocation by climb or cross slip, Sometimes glide planes are blocked by point defects. Edge Dislocation: can’t continue on that plane, so dislocation climbs to new glide plane ...
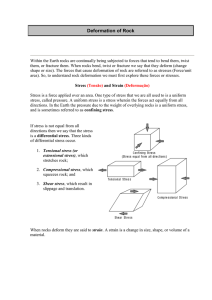
Deformation of Rock
... feldspar which have high strength, particularly at low pressure and temperature. As we go deeper in the Earth the strength of these rocks initially increases. At a depth of about 15 km we reach a point called the brittle-ductile transition zone. Below this point rock strength decreases because fract ...
... feldspar which have high strength, particularly at low pressure and temperature. As we go deeper in the Earth the strength of these rocks initially increases. At a depth of about 15 km we reach a point called the brittle-ductile transition zone. Below this point rock strength decreases because fract ...
technical data - Universal Photonics
... In general, removal of Stacking wax can be accomplished by immersing the blocked assembly in hot water, thereby bringing the wax to its melting temperature and affecting the physical detachment in the blocking media. The temperature of the water will be dictated by the melting point of the particula ...
... In general, removal of Stacking wax can be accomplished by immersing the blocked assembly in hot water, thereby bringing the wax to its melting temperature and affecting the physical detachment in the blocking media. The temperature of the water will be dictated by the melting point of the particula ...
Plane Elasticity Problems
... Semi-inverse method. We next go into the interior of the sheet. We already have obtained a full set of governing equations for linear elasticity problems. No general approach exists to solve partial differential equations analytically. However, numerical methods are now readily available to solve an ...
... Semi-inverse method. We next go into the interior of the sheet. We already have obtained a full set of governing equations for linear elasticity problems. No general approach exists to solve partial differential equations analytically. However, numerical methods are now readily available to solve an ...
View - UK.COM
... and process adjustments, with which the operator needs to be familiar. Logitech are dedicated to complete success and through training at our purpose built laboratories or at client premises, the team ensures that personal training is provided at a level relevant to the clients process requirements. ...
... and process adjustments, with which the operator needs to be familiar. Logitech are dedicated to complete success and through training at our purpose built laboratories or at client premises, the team ensures that personal training is provided at a level relevant to the clients process requirements. ...
Dumitrache_Carabineanu 125
... The fate of the LEV can also be correlated to the heaving efficiency. While the overall efficiency was low, large increases in efficiency occur at the transition from a shed LEV to one that is dissipated. The results are also in accordance with [Gustafson, 1996] in that some of the vorticity contain ...
... The fate of the LEV can also be correlated to the heaving efficiency. While the overall efficiency was low, large increases in efficiency occur at the transition from a shed LEV to one that is dissipated. The results are also in accordance with [Gustafson, 1996] in that some of the vorticity contain ...
... by any elastic attachment to the stationary substratum. Thus, movement, as determined by the properties of a plant or animal’s supporting structure, can potentially affect the total force applied to the organism. Although a few studies have investigated the effects of the mechanical properties of su ...
1 Stress in 3D
... Mechanical stress in a solid generalizes the simpler concept of pressure in a fluid. A fluid in static equilibrium (the so-called hydrostatic equilibrium in the case of a liquid) can support only a pressure state. (In a gas pressure may be tensile or compressive whereas in a liquid it must be compre ...
... Mechanical stress in a solid generalizes the simpler concept of pressure in a fluid. A fluid in static equilibrium (the so-called hydrostatic equilibrium in the case of a liquid) can support only a pressure state. (In a gas pressure may be tensile or compressive whereas in a liquid it must be compre ...
Abstract
... Segmentation is a challenging field of image analysis. In particular, medical image segmentation has become very important with development of complex medical imaging modalities which are capable of producing a large quantity of high-resolution twodimensional (2-D) and three-dimensional (3-D) images ...
... Segmentation is a challenging field of image analysis. In particular, medical image segmentation has become very important with development of complex medical imaging modalities which are capable of producing a large quantity of high-resolution twodimensional (2-D) and three-dimensional (3-D) images ...
1 CHAPTER 22 DIMENSIONS 22.1 Mass, Length and Time Any
... could express any mechanical quantity in terms of, say, energy E, speed V and angular momentum J. We might then say that the dimensions of area could be expressed as E −2 V 2 J 2 . (Verify this!) While agreeing that such a system might be possible, you might feel that it would be totally absurd and ...
... could express any mechanical quantity in terms of, say, energy E, speed V and angular momentum J. We might then say that the dimensions of area could be expressed as E −2 V 2 J 2 . (Verify this!) While agreeing that such a system might be possible, you might feel that it would be totally absurd and ...
a.2) After IIT. - Sociedade Brasileira de Metrologia
... additional test force, it was noticed how much this new method was more powerful when one wanted to analyse material properties, mainly the localised measurements and small thickness of the materials, remarkably in the micro and nanometer ranges. Only, in 1997 the technical subcommittee ISO/TC 164/S ...
... additional test force, it was noticed how much this new method was more powerful when one wanted to analyse material properties, mainly the localised measurements and small thickness of the materials, remarkably in the micro and nanometer ranges. Only, in 1997 the technical subcommittee ISO/TC 164/S ...
EIN 3390 Chap 19 Non..
... Involves the use of UV (Ultra-Violet) lightsensitive emulsions, called photoresists Photoresists are applied to the surface of the workpiece and selectively exposed to an intense ray of UV light ICs use semiconductor materials that can be made to be either electrically conducting or insulating ◦ Dop ...
... Involves the use of UV (Ultra-Violet) lightsensitive emulsions, called photoresists Photoresists are applied to the surface of the workpiece and selectively exposed to an intense ray of UV light ICs use semiconductor materials that can be made to be either electrically conducting or insulating ◦ Dop ...
Stress
... In fluids at rest pressure is the only contact force. For solids at rest or in motion, and for viscous fluids in motion, this simple picture is no longer valid. Besides pressure-like forces acting along the normal to a contact surface, there may also be shearing forces acting in any tangential direc ...
... In fluids at rest pressure is the only contact force. For solids at rest or in motion, and for viscous fluids in motion, this simple picture is no longer valid. Besides pressure-like forces acting along the normal to a contact surface, there may also be shearing forces acting in any tangential direc ...
Physics 231 Topic 9: Solids & Fluids Wade Fisher
... Strain: Measure of the degree of deformation Measure of the amount of deformation For small stress, strain and stress are linearly correlated. inelastic regime ...
... Strain: Measure of the degree of deformation Measure of the amount of deformation For small stress, strain and stress are linearly correlated. inelastic regime ...
Managing Stress and Anxiety Chapter 8
... Prolonged or repeated stress can lead to stressful illnesses caused by the changes that take place in your body during these three stages. 1) Sleeplessness, upset stomach, high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. ...
... Prolonged or repeated stress can lead to stressful illnesses caused by the changes that take place in your body during these three stages. 1) Sleeplessness, upset stomach, high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. ...
Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (QCM
... Analysis using modeling Dissipation measurements enable qualitative analysis of the structural properties of adsorbed molecular layers. Different materials can easily be compared and one can ascertain if the Sauerbrey relation will accurately approximate the adsorbed mass or not. Furthermore, the QC ...
... Analysis using modeling Dissipation measurements enable qualitative analysis of the structural properties of adsorbed molecular layers. Different materials can easily be compared and one can ascertain if the Sauerbrey relation will accurately approximate the adsorbed mass or not. Furthermore, the QC ...
Khusnutdinova2009-Kolmogorov.pdf
... “Mathematicians always wish mathematics to be as ‘pure’ as possible, i.e. rigorous, provable. But usually most interesting real problems that are offered to us are inaccessible in this way. And then it is very important for a mathematician to be able to find himself approximate, non-rigorous but eff ...
... “Mathematicians always wish mathematics to be as ‘pure’ as possible, i.e. rigorous, provable. But usually most interesting real problems that are offered to us are inaccessible in this way. And then it is very important for a mathematician to be able to find himself approximate, non-rigorous but eff ...