Concept Note
... 2. Currently, more than 1 billion people worldwide depend on fish as their primary protein source. The ocean is the key component of the climate system, absorbing solar radiation and exchanging, absorbing, and emitting oxygen and carbon dioxide. However, the intensity of use and technology have reac ...
... 2. Currently, more than 1 billion people worldwide depend on fish as their primary protein source. The ocean is the key component of the climate system, absorbing solar radiation and exchanging, absorbing, and emitting oxygen and carbon dioxide. However, the intensity of use and technology have reac ...
Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global
... Annual clean-up operations, costing millions of pounds sterling, are now organized in many countries and on every continent. Here we document global plastics production and the accumulation of plastic waste. While plastics typically constitute approximately 10 per cent of discarded waste, they repre ...
... Annual clean-up operations, costing millions of pounds sterling, are now organized in many countries and on every continent. Here we document global plastics production and the accumulation of plastic waste. While plastics typically constitute approximately 10 per cent of discarded waste, they repre ...
Oceanography ppt
... • the amount of evaporation that takes place. • If much evaporation occurs, the water is more saline because water is evaporating faster than freshwater is added. Thus, more salts are left over. *Conversely, the more freshwater added to the system, the less the salinity is. Where do the salts come f ...
... • the amount of evaporation that takes place. • If much evaporation occurs, the water is more saline because water is evaporating faster than freshwater is added. Thus, more salts are left over. *Conversely, the more freshwater added to the system, the less the salinity is. Where do the salts come f ...
Report of the Director & CEO Gary G. Borisy
... • Human activities are driving the sixth major extinction in the history of life,-a new era, the Anthropocene. • Species are disappearing at 100 to 1,000 times the natural rate. • At least 21% of mammal, 12% of bird and 29% of amphibian species are now threatened with extinction. ...
... • Human activities are driving the sixth major extinction in the history of life,-a new era, the Anthropocene. • Species are disappearing at 100 to 1,000 times the natural rate. • At least 21% of mammal, 12% of bird and 29% of amphibian species are now threatened with extinction. ...
File
... The climate of the Pacific Ocean is between 29.5˚F~86˚F obviously this where the Northern & Southern parts are going to vary depending on how close they are to the dividing line called the equator. The average temperature of the Pacific is 86˚F. It can also vary in regions because towards the poles ...
... The climate of the Pacific Ocean is between 29.5˚F~86˚F obviously this where the Northern & Southern parts are going to vary depending on how close they are to the dividing line called the equator. The average temperature of the Pacific is 86˚F. It can also vary in regions because towards the poles ...
Protection of the Marine Environment from Sea
... marine pollution originates from land, 10 percent from maritime transportation and another 10 percent from dumping at sea. However, marine pollution from sea-based activities is an “attention grabber” especially when it involves oil spills. Land-based pollution on the other hand is ...
... marine pollution originates from land, 10 percent from maritime transportation and another 10 percent from dumping at sea. However, marine pollution from sea-based activities is an “attention grabber” especially when it involves oil spills. Land-based pollution on the other hand is ...
Environmental, scientific and technological aspects
... While the oceans cover two thirds of the planet, it is estimated that the vast majority thereof are yet to be explored. Access to marine ecosystems beyond areas of national jurisdiction, in particular to benthic and deep pelagic ecosystems, is dependent on highly specialized technology relating to v ...
... While the oceans cover two thirds of the planet, it is estimated that the vast majority thereof are yet to be explored. Access to marine ecosystems beyond areas of national jurisdiction, in particular to benthic and deep pelagic ecosystems, is dependent on highly specialized technology relating to v ...
Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Sources, Consequences
... are difficult to use as a base line because of the inevitable lack of consistency in methods. In parallel, there have been laboratory studies which have exposed organisms to microplastics in order to determine the potential for this debris to result in harm to the creatures that encounter it in the ...
... are difficult to use as a base line because of the inevitable lack of consistency in methods. In parallel, there have been laboratory studies which have exposed organisms to microplastics in order to determine the potential for this debris to result in harm to the creatures that encounter it in the ...
Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Sources
... are difficult to use as a base line because of the inevitable lack of consistency in methods. In parallel, there have been laboratory studies which have exposed organisms to microplastics in order to determine the potential for this debris to result in harm to the creatures that encounter it in the ...
... are difficult to use as a base line because of the inevitable lack of consistency in methods. In parallel, there have been laboratory studies which have exposed organisms to microplastics in order to determine the potential for this debris to result in harm to the creatures that encounter it in the ...
Chapter 11 - COSEE Florida
... SC.912.L.17.2 - Explain the general distribution of life in aquatic systems as a function of chemistry, geography, light, depth, salinity, and temperature. SC.912.L.17.3 - Discuss how various oceanic and freshwater processes, such as currents, tides, and waves, affect the abundance of aquatic organi ...
... SC.912.L.17.2 - Explain the general distribution of life in aquatic systems as a function of chemistry, geography, light, depth, salinity, and temperature. SC.912.L.17.3 - Discuss how various oceanic and freshwater processes, such as currents, tides, and waves, affect the abundance of aquatic organi ...
Print flyer - Loch Ness Productions
... pelican eels, and the mysterious fangtooth — all perfectly adapted to the extreme pressures and temperatures of their alien environment. In addition to teaching about marine biology and ocean exploration, Into the Deep documents submersible exploration, and describes the basic physical principles th ...
... pelican eels, and the mysterious fangtooth — all perfectly adapted to the extreme pressures and temperatures of their alien environment. In addition to teaching about marine biology and ocean exploration, Into the Deep documents submersible exploration, and describes the basic physical principles th ...
Oceanography Seminar-Oscar Abraham Sosa (PDF)
... nutrients to the water column making them key regulators of the cycles of carbon and of marine productivity. Yet we know very few details of how bacteria catalyze the decomposition of DOM and the types of metabolism that this process supports. My thesis project aims to identify suitable bacterial sy ...
... nutrients to the water column making them key regulators of the cycles of carbon and of marine productivity. Yet we know very few details of how bacteria catalyze the decomposition of DOM and the types of metabolism that this process supports. My thesis project aims to identify suitable bacterial sy ...
Oceanography Final Study Guide
... 43. How do marine animals sense the location of objects in water? 44. Why aren’t marine organisms crushed by hydrostatic pressure at depth? 45. What is the most common adaptation in marine animals for overcoming water resistance? Chapter 14 All Sections 46. Which ecosystem is made up of plankton tha ...
... 43. How do marine animals sense the location of objects in water? 44. Why aren’t marine organisms crushed by hydrostatic pressure at depth? 45. What is the most common adaptation in marine animals for overcoming water resistance? Chapter 14 All Sections 46. Which ecosystem is made up of plankton tha ...
PDF
... - Analyzing protein structure of enzymes that are related to marine algae in Ulleung-do and Dok-do regions - Research on converting microorganisms into resources utilizing deep sea water of the East Sea and its industrialization - Improving marine environment of the Gyeongbuk East Sea area and devel ...
... - Analyzing protein structure of enzymes that are related to marine algae in Ulleung-do and Dok-do regions - Research on converting microorganisms into resources utilizing deep sea water of the East Sea and its industrialization - Improving marine environment of the Gyeongbuk East Sea area and devel ...
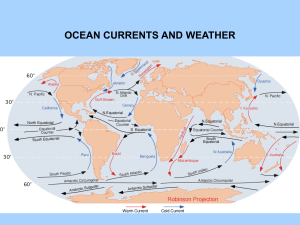
ocean currents and weather
... WATER PILES UP IN THE DIRECTION THE WIND IS BLOWING. 3. GRAVITY - WATER WANTS TO FLOW DOWN HILL AGAINST THE PRESSURE GRADIENT. 4. CORIOLIS FORCE - THE CORIOLIS FORCE TURNS THE CURRENTS TO THE RIGHT IN THE NORTHERN HEMISPHERE AND TO THE LEFT IN THE SOUTHERN HEMISPHERE. ALL OF THESE FORCES COMBINE T ...
... WATER PILES UP IN THE DIRECTION THE WIND IS BLOWING. 3. GRAVITY - WATER WANTS TO FLOW DOWN HILL AGAINST THE PRESSURE GRADIENT. 4. CORIOLIS FORCE - THE CORIOLIS FORCE TURNS THE CURRENTS TO THE RIGHT IN THE NORTHERN HEMISPHERE AND TO THE LEFT IN THE SOUTHERN HEMISPHERE. ALL OF THESE FORCES COMBINE T ...
PPT
... surface waters during photosynthesis Essential to the growth of phytoplankton If these biolimiting nutrients increase in sea water, life increases If these biolimiting nutrients decrease in sea water, life decreases Where would you expect to find the highest biomass in the Pacific?? ...
... surface waters during photosynthesis Essential to the growth of phytoplankton If these biolimiting nutrients increase in sea water, life increases If these biolimiting nutrients decrease in sea water, life decreases Where would you expect to find the highest biomass in the Pacific?? ...
Open Ocean Notes
... Where is algae (phytoplankton) found in the open ocean? The surface zone Algae is the base of the open ocean food web Many open ocean animals stay in deep water during the day and surface at night to feed. ...
... Where is algae (phytoplankton) found in the open ocean? The surface zone Algae is the base of the open ocean food web Many open ocean animals stay in deep water during the day and surface at night to feed. ...
File
... So who oversees the high seas? The answer is a host of groups, each of which handles only a very specific issue. The International Maritime Organization, for example, regulates shipping. The International Seabed Authority is in charge of deep-sea mining. And various regional organizations manage fi ...
... So who oversees the high seas? The answer is a host of groups, each of which handles only a very specific issue. The International Maritime Organization, for example, regulates shipping. The International Seabed Authority is in charge of deep-sea mining. And various regional organizations manage fi ...
Ocean Structure and Circulation
... 6. Draw the direction of geostrophic flow on a map of an ocean basin between 0 and 60° N or S, and explain why the water moves around the gyre as it does in response to gravity and the Coriolis effect. 7. Predict whether currents flowing along the eastern and western sides of an ocean basin will be ...
... 6. Draw the direction of geostrophic flow on a map of an ocean basin between 0 and 60° N or S, and explain why the water moves around the gyre as it does in response to gravity and the Coriolis effect. 7. Predict whether currents flowing along the eastern and western sides of an ocean basin will be ...
THINKING CRITICALLY Circumpolar Currents and Ocean
... waters to the entire globe. The circulation of ocean waters is driven in part by the formation of sea ice in the Antarctic waters. As sea ice forms, the salinity of the surrounding ocean water increases. The increased salinity increases the density of the water, which causes the water to sink. This ...
... waters to the entire globe. The circulation of ocean waters is driven in part by the formation of sea ice in the Antarctic waters. As sea ice forms, the salinity of the surrounding ocean water increases. The increased salinity increases the density of the water, which causes the water to sink. This ...
Harbor Branch Executive Director Presents “Our Changing Oceans
... celebrates its 40th anniversary this year, and research during that time shows that our global oceans have undergone remarkable changes -- more extensive than we would have thought possible 40 years ago -- and that the ocean is continuing to change in ways that will affect climate, sea level and oce ...
... celebrates its 40th anniversary this year, and research during that time shows that our global oceans have undergone remarkable changes -- more extensive than we would have thought possible 40 years ago -- and that the ocean is continuing to change in ways that will affect climate, sea level and oce ...
Spanish researchers sequence the genome of global deep ocean
... Millions of new genes According to Josep Maria Gasol, CSIC researcher at the Institute of Marine Sciences and leader of the Malaspina block of microorganisms, samples "are especially valuable because they come from areas that have been poorly studied in a scientific sense up to now, such as the Indi ...
... Millions of new genes According to Josep Maria Gasol, CSIC researcher at the Institute of Marine Sciences and leader of the Malaspina block of microorganisms, samples "are especially valuable because they come from areas that have been poorly studied in a scientific sense up to now, such as the Indi ...
Sea-Floor Spreading
... A trench is a steep-walled valley on the sea floor adjacent to a continental margin. For example, ocean crust formed at the East Pacific Rise, an oceanic ridge in the east Pacific, plunges into the trench adjacent to the Andes Mountains on the west side of the South American continent. In Hess' mode ...
... A trench is a steep-walled valley on the sea floor adjacent to a continental margin. For example, ocean crust formed at the East Pacific Rise, an oceanic ridge in the east Pacific, plunges into the trench adjacent to the Andes Mountains on the west side of the South American continent. In Hess' mode ...
Marine debris

Marine debris, also known as marine litter, is human-created waste that has deliberately or accidentally been released in a lake, sea, ocean or waterway. Floating oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the centre of gyres and on coastlines, frequently washing aground, when it is known as beach litter or tidewrack. Deliberate disposal of wastes at sea is called ocean dumping. Naturally occurring debris, such as driftwood, are also present.With the increasing use of plastic, human influence has become an issue as many types of plastics do not biodegrade. Waterborne plastic poses a serious threat to fish, seabirds, marine reptiles, and marine mammals, as well as to boats and coasts. Dumping, container spillages, litter washed into storm drains and waterways and wind-blown landfill waste all contribute to this problem.