Ch. 12 Power Point
... • Elite - participated in bloodletting rituals and other religious ceremonies • Common – agricultural and textile production ...
... • Elite - participated in bloodletting rituals and other religious ceremonies • Common – agricultural and textile production ...
Mexican flag and coat of arms
... Sacrifices were necessary to satisfy their hungry sun-god who demanded blood as payment for creating the world. The limbs of a victim would be given as a reward to the victim’s captor to be eaten. According to Aztec beliefs, the sacrifices were necessary to satisfy their hungry sun-god who demanded ...
... Sacrifices were necessary to satisfy their hungry sun-god who demanded blood as payment for creating the world. The limbs of a victim would be given as a reward to the victim’s captor to be eaten. According to Aztec beliefs, the sacrifices were necessary to satisfy their hungry sun-god who demanded ...
How did the Conquistadores conquer the Aztecs and the Incas?
... that the Aztecs have a wealthy empire in central Mexico. He conquers Montezuma and his empire with 600 men and with the help of Aztec enemies from surrounding villages. • 1533 Francisco Pizarro, also of Spain, conquered the Incan empire with 200 men. ...
... that the Aztecs have a wealthy empire in central Mexico. He conquers Montezuma and his empire with 600 men and with the help of Aztec enemies from surrounding villages. • 1533 Francisco Pizarro, also of Spain, conquered the Incan empire with 200 men. ...
File - Ms. Thatcher`s Class Page
... • Toltecs build large empire in central Mexico (Capital at Tula)- 968 CE • Aztecs consider the Toltecs their givers of civilization ...
... • Toltecs build large empire in central Mexico (Capital at Tula)- 968 CE • Aztecs consider the Toltecs their givers of civilization ...
Aztec*s and spanish
... promised sign: an eagle sitting on a prickly pear cactus, eating a snake. After 200 years of wondering, they found the eagle and a small, swampy island in Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. ...
... promised sign: an eagle sitting on a prickly pear cactus, eating a snake. After 200 years of wondering, they found the eagle and a small, swampy island in Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. ...
Aztec Everyday Life
... They spoke their own ________________ (Nahuatal) and used an accurate 365-day ____________________ based around their harvest seasons. The Aztec’s entire culture was dominated by ___________________., and worshipping their many gods. They made colorful ___________ and masks and covered the bodies of ...
... They spoke their own ________________ (Nahuatal) and used an accurate 365-day ____________________ based around their harvest seasons. The Aztec’s entire culture was dominated by ___________________., and worshipping their many gods. They made colorful ___________ and masks and covered the bodies of ...
Act 8.3 Key Aztec Political And Economic Systems pages 273
... members of their calpullis, they were the greatest warriors and wisest priests. ...
... members of their calpullis, they were the greatest warriors and wisest priests. ...
The Aztec – Mexico`s Great Empire
... In 1519, Spanish conquistadors, or conquerors, arrived in Tenochtitlan. The Aztec emperor, Montezuma II, believed the Spanish were representatives of Quetzalcoatl and welcomed them. The Spaniards saw the wealth of the Aztecs and wanted it for themselves. They took Montezuma hostage and looted the ci ...
... In 1519, Spanish conquistadors, or conquerors, arrived in Tenochtitlan. The Aztec emperor, Montezuma II, believed the Spanish were representatives of Quetzalcoatl and welcomed them. The Spaniards saw the wealth of the Aztecs and wanted it for themselves. They took Montezuma hostage and looted the ci ...
The Development of the Aztec Empire
... and rain – which caused floods and destruction of crops. Animals began coming in to eat the dead people and attack those still alive. The Aztec response was to increase human sacrifice to try to make the gods happy again. When the famine was over, the priests took it as a sign that the gods should n ...
... and rain – which caused floods and destruction of crops. Animals began coming in to eat the dead people and attack those still alive. The Aztec response was to increase human sacrifice to try to make the gods happy again. When the famine was over, the priests took it as a sign that the gods should n ...
APWH Ch 11 Notes Pre-Columbian America
... Rise of the Aztecs • Aztecs (Mexica) migrate to Lake Texcoco in central Mexico c. 1325 • Founded city of Tenochtitlan in 1325 • Empire started in 1434 • Aztec kings represented civil power and served as a representative of the gods on Earth ...
... Rise of the Aztecs • Aztecs (Mexica) migrate to Lake Texcoco in central Mexico c. 1325 • Founded city of Tenochtitlan in 1325 • Empire started in 1434 • Aztec kings represented civil power and served as a representative of the gods on Earth ...
документ
... of land to farm on and it was totally surrounded by more marshes . The Aztec families some how converted these disadvantages to a might empire known as they Aztec Empire. People say the empire was partially formed by a deeply believed legend. As the the legend went it said that Aztec people would cr ...
... of land to farm on and it was totally surrounded by more marshes . The Aztec families some how converted these disadvantages to a might empire known as they Aztec Empire. People say the empire was partially formed by a deeply believed legend. As the the legend went it said that Aztec people would cr ...
The Aztec Indians Essay, Research Paper The Aztec Indians, who
... of land to farm on and it was totally surrounded by more marshes . The Aztec families some how converted these disadvantages to a might empire known as they Aztec Empire. People say the empire was partially formed by a deeply believed legend. As the the legend went it said that Aztec people would cr ...
... of land to farm on and it was totally surrounded by more marshes . The Aztec families some how converted these disadvantages to a might empire known as they Aztec Empire. People say the empire was partially formed by a deeply believed legend. As the the legend went it said that Aztec people would cr ...
The Aztecs
... In those times, it must have been an impressive sight to arrive in the city of Tenochtitlan and see the Great Temple towering over the surrounding buildings and houses. This pyramid had twin temples on the top. One of these temples was dedicated to the God of rain, Tlaloc, and the other to the God o ...
... In those times, it must have been an impressive sight to arrive in the city of Tenochtitlan and see the Great Temple towering over the surrounding buildings and houses. This pyramid had twin temples on the top. One of these temples was dedicated to the God of rain, Tlaloc, and the other to the God o ...
Rise and Fall of Tenochtitlan Evidence Analysis Exercise
... Valley of Mexico resided in cities and towns. The Aztec capital of Tenochtitlán, the site of modern Mexico City near the ancient center of Teotihuacán, was built on swampland in the Valley of Mexico. This and other urban centers were supported by the rural populations of the surrounding areas, who w ...
... Valley of Mexico resided in cities and towns. The Aztec capital of Tenochtitlán, the site of modern Mexico City near the ancient center of Teotihuacán, was built on swampland in the Valley of Mexico. This and other urban centers were supported by the rural populations of the surrounding areas, who w ...
File - EMS Secondary Department
... Sacrifices for the Sun God • Most important rituals are for sun god, Huitzilopochtli • He needs human sacrifices to be strong • Aztecs engage in war to provide captives for these ...
... Sacrifices for the Sun God • Most important rituals are for sun god, Huitzilopochtli • He needs human sacrifices to be strong • Aztecs engage in war to provide captives for these ...
Study Guide - Maya, Aztec, Inca test Friday 5/3
... Sun god requires human sacrifice to rise each day. Tenochtitlan was their capital and it was in Lake Texcoco. The Spanish conquistadors played a part in their empire collapsing. They built a giant temple to the sun god in Tenochtitlan. They built artificial islands, chimapas, to raise crops They wer ...
... Sun god requires human sacrifice to rise each day. Tenochtitlan was their capital and it was in Lake Texcoco. The Spanish conquistadors played a part in their empire collapsing. They built a giant temple to the sun god in Tenochtitlan. They built artificial islands, chimapas, to raise crops They wer ...
Blank Student Copy
... _______________ for unknown reasons. Possible theories include civil war, disease, or famine. Mayan ______________ is still spoken today in portions of Mexico and Guatemala. ...
... _______________ for unknown reasons. Possible theories include civil war, disease, or famine. Mayan ______________ is still spoken today in portions of Mexico and Guatemala. ...
Pre-Columbian Civilizations in the Americas
... Central Mexico Tenochtitlan: major city –Island in Lake Texcoco Present-day Mexico City ...
... Central Mexico Tenochtitlan: major city –Island in Lake Texcoco Present-day Mexico City ...
Chapter 20 I. Aztecs - Liberty Union High School District
... drawings depict rubber offering balls in the hands of gods and officiating priests. The ritual ballgame, too, has strong religious connotations and was practiced by various Mesoamerican societies. In this rolled-out version of a Maya cylinder vessel, two elaborately outfitted players are captured in ...
... drawings depict rubber offering balls in the hands of gods and officiating priests. The ritual ballgame, too, has strong religious connotations and was practiced by various Mesoamerican societies. In this rolled-out version of a Maya cylinder vessel, two elaborately outfitted players are captured in ...
Emperor
... their many gods. • Believed the sun god battled its way across the heavens each day. • Compared this to their battles calling themselves “warriors of the sun”. • Believed the sun god required human sacrifices in order to rise each day. • Sacrificed thousands of captives each year. ...
... their many gods. • Believed the sun god battled its way across the heavens each day. • Compared this to their battles calling themselves “warriors of the sun”. • Believed the sun god required human sacrifices in order to rise each day. • Sacrificed thousands of captives each year. ...
Early Civilizations of the Americas
... known as the Mexica people) arrive in central Mexico Valley ...
... known as the Mexica people) arrive in central Mexico Valley ...
Aztec PPT - Effingham County Schools
... • Montezuma and the Aztec mistakenly thought Cortes was a god at first • Cortes captured Montezuma and held him prisoner • Cortes and his men defeated the Aztec and Montezuma was killed • In time the Spanish sent more troops to Mexico and destroyed Tenochtitlan • Thousands of natives died in a massi ...
... • Montezuma and the Aztec mistakenly thought Cortes was a god at first • Cortes captured Montezuma and held him prisoner • Cortes and his men defeated the Aztec and Montezuma was killed • In time the Spanish sent more troops to Mexico and destroyed Tenochtitlan • Thousands of natives died in a massi ...
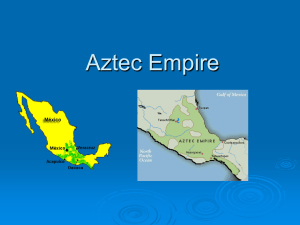
Aztec Empire
... called themselves Mexica (mehhee-ka) They were skilled warriors One ruler ruled over the Aztec Empire under the leader Moctezuma they expanded to 1/3 of southern Mexico Population of 25 million at peak Grew stronger through war, tribute, and trade ...
... called themselves Mexica (mehhee-ka) They were skilled warriors One ruler ruled over the Aztec Empire under the leader Moctezuma they expanded to 1/3 of southern Mexico Population of 25 million at peak Grew stronger through war, tribute, and trade ...
Aztec Empire

The Mexica Aztec Empire or the Triple Alliance (Nahuatl: Ēxcān Tlahtōlōyān, [ˈjéːʃkaːn̥ t͡ɬaʔtoːˈlóːjaːn̥]) began as an alliance of three Nahua ""altepetl"" city-states: Mexico-Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and Tlacopan. These three city-states ruled the area in and around the Valley of Mexico from 1428 until they were defeated by the combined forces of the Spanish conquistadores and their native allies under Hernán Cortés in 1521.The Triple Alliance was formed from the victorious faction in a civil war fought between the city of Azcapotzalco and its former tributary provinces. Despite the initial conception of the empire as an alliance of three self-governed city-states, Tenochtitlan quickly established itself as the dominant partner militarily. By the time the Spanish arrived in 1520, the lands of the Alliance were effectively ruled from Tenochtitlan, and the other partners in the alliance had assumed subsidiary roles.The alliance waged wars of conquest and expanded rapidly after its formation. At its height, the alliance controlled most of central Mexico as well as some more distant territories within Mesoamerica such as the Xoconochco province, an Aztec exclave near the present-day Guatemalan border. Aztec rule has been described by scholars as ""hegemonic"" or ""indirect"". Rulers of conquered cities were left in power so long as they agreed to pay semi-annual tribute to the alliance as well as supplying military support for the Aztec war efforts. In return, the imperial authority offered protection and political stability as well as facilitating an integrated economic network of diverse lands and peoples with significant local autonomy despite their tributary status.