Early Peoples Activity Sheet: The Aztecs
... Who were the highest rank of people in Aztec society behind the tlatoani? What special rights did nobles have? Who were the commoner class? What was the Calpolli? What was the role of the Calpolli? How did a commoner rise to a more powerful position? What position was a very important position in Az ...
... Who were the highest rank of people in Aztec society behind the tlatoani? What special rights did nobles have? Who were the commoner class? What was the Calpolli? What was the role of the Calpolli? How did a commoner rise to a more powerful position? What position was a very important position in Az ...
AMAZING AZTEC CYBERHUNT
... sentences, and used them to write down stories and keep records. Words that joined the nouns into sentences were extremely difficult to draw. The art of writing was very specialized and also difficult to learn. Scribes needed to know a lot of extra information that wasn't written down because the pi ...
... sentences, and used them to write down stories and keep records. Words that joined the nouns into sentences were extremely difficult to draw. The art of writing was very specialized and also difficult to learn. Scribes needed to know a lot of extra information that wasn't written down because the pi ...
Study Guide - Maya, Aztec, Inca test Friday 5/3
... Study Guide - Maya, Aztec, Inca test Friday 5/3 Facts about each civilization Maya ...
... Study Guide - Maya, Aztec, Inca test Friday 5/3 Facts about each civilization Maya ...
Aztecs - gmhistory9
... traditional way; the whisk is called a ‘molinillo’ in Mexico More info:-aztecs.org: aztec life: Blood of the gods ...
... traditional way; the whisk is called a ‘molinillo’ in Mexico More info:-aztecs.org: aztec life: Blood of the gods ...
AZTEC_CULTURE
... conquered peoples in the empire who wanted freedom from the Aztecs and headed for Tenochtitlan. The Aztecs, especially King Montezuma, thought Cortéz and his men were gods and this allowed Cortéz to march into Tenochtitlan as a guest and take the Aztec King Montezuma prisoner. Two years later he def ...
... conquered peoples in the empire who wanted freedom from the Aztecs and headed for Tenochtitlan. The Aztecs, especially King Montezuma, thought Cortéz and his men were gods and this allowed Cortéz to march into Tenochtitlan as a guest and take the Aztec King Montezuma prisoner. Two years later he def ...
File
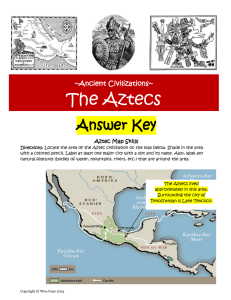
... Aztecs to settle where they saw an eagle sitting on a cactus with a serpent in its mouth A tribute is another word for taxes. The Aztec ruler would collect tribute from the enemies that they conquered. ...
... Aztecs to settle where they saw an eagle sitting on a cactus with a serpent in its mouth A tribute is another word for taxes. The Aztec ruler would collect tribute from the enemies that they conquered. ...
Ancient Civilizations of the Americas Study Guide
... 3. The Maya had a system of numbers, a system of writing, and a calendar, but not scientific tools. 4. The largest and most important buildings in Mayan cities were the pyramids. 5. The Aztecs built their civilization in Mexico. 6. Before the Aztecs built their civilization, they could be described ...
... 3. The Maya had a system of numbers, a system of writing, and a calendar, but not scientific tools. 4. The largest and most important buildings in Mayan cities were the pyramids. 5. The Aztecs built their civilization in Mexico. 6. Before the Aztecs built their civilization, they could be described ...
The Aztec Empire Forms in Mexico - Mr. Wisell`s Global History Web
... Aztec Society Takes Shape War brought immense wealth as well as power to the Aztec empire. Tribute, or payment from conquered peoples, helped the Aztecs turn their capital into a magnificent city. From its temples and royal palaces, to its zoos and floating gardens, Tenochtitlan seemed a city of wo ...
... Aztec Society Takes Shape War brought immense wealth as well as power to the Aztec empire. Tribute, or payment from conquered peoples, helped the Aztecs turn their capital into a magnificent city. From its temples and royal palaces, to its zoos and floating gardens, Tenochtitlan seemed a city of wo ...
Aztec Spy Notes - World History Reiff 2
... The king priest and government officials made VP the Inca upper class while most noble men worked for the government. Women from noble families had house hold duties such as, cooling and making clothes. ...
... The king priest and government officials made VP the Inca upper class while most noble men worked for the government. Women from noble families had house hold duties such as, cooling and making clothes. ...
Aztec gods - Primary Resources
... He is always shown as a warrior. He carries a shield with five feather ornaments in one hand. In his other hand he carries his magic weapon: a blue snake of fire. His body and clothes are painted blue. He is the god of war and the rising sun. His temple on the main pyramid was the place where prison ...
... He is always shown as a warrior. He carries a shield with five feather ornaments in one hand. In his other hand he carries his magic weapon: a blue snake of fire. His body and clothes are painted blue. He is the god of war and the rising sun. His temple on the main pyramid was the place where prison ...
Document
... Around 700 years ago the tribe searched for new places to settle. They came upon Lake Texcoco. They decided to settle here because they got a sign: an eagle, perched on cactus, holding a snake in its mouth. ...
... Around 700 years ago the tribe searched for new places to settle. They came upon Lake Texcoco. They decided to settle here because they got a sign: an eagle, perched on cactus, holding a snake in its mouth. ...
ComparingAztec Maya IncaNotes
... During the Neolithic Revolution, these nomads settled into _____________ villages; Some of which became advanced civilizations. The first American civilization were people known as the _____________ in an area known as _____________________ o The Olmecs are often called the “____________________ ...
... During the Neolithic Revolution, these nomads settled into _____________ villages; Some of which became advanced civilizations. The first American civilization were people known as the _____________ in an area known as _____________________ o The Olmecs are often called the “____________________ ...
The Aztec Empire
... spinning at four and cooking at twelve. The schooling of girls was a basic training for marriage, except that noble girls spent a year at the age of twelve or thirteen helping in the temples. Because of this temple training, some girls went on to become priestesses. Religion and the Arts Religion mo ...
... spinning at four and cooking at twelve. The schooling of girls was a basic training for marriage, except that noble girls spent a year at the age of twelve or thirteen helping in the temples. Because of this temple training, some girls went on to become priestesses. Religion and the Arts Religion mo ...
Mesoamerica 2016 Power Point
... another agricultural society that developed and adapted to its environment on the Yucatan Peninsula of what is present day Mexico. The Maya were not unified in one empire. Instead, they were a society of city-states and kingdoms linked by culture, political ties, and trade. 1. religion - was at the ...
... another agricultural society that developed and adapted to its environment on the Yucatan Peninsula of what is present day Mexico. The Maya were not unified in one empire. Instead, they were a society of city-states and kingdoms linked by culture, political ties, and trade. 1. religion - was at the ...
Pre-Columbian Civilizations in the Americas
... Slaves could own and buy The sun god was the chief freedom. Aztec god. Long-distance traders traveled around the empire and beyond. ...
... Slaves could own and buy The sun god was the chief freedom. Aztec god. Long-distance traders traveled around the empire and beyond. ...
The Aztecs Control Central Mexico SETTING THE STAGE
... The Aztecs arrived in the Valley of Mexico around a.d. 1200. The valley contained a number of small city-states that had survived the collapse of Toltec rule. The Aztecs, who were then called the Mexica, were a poor, nomadic people from the harsh deserts of northern Mexico. According to one of the A ...
... The Aztecs arrived in the Valley of Mexico around a.d. 1200. The valley contained a number of small city-states that had survived the collapse of Toltec rule. The Aztecs, who were then called the Mexica, were a poor, nomadic people from the harsh deserts of northern Mexico. According to one of the A ...
Fall of the Aztec Empire
... Hernán Cortés. They first took over the capital city of Tenochtitlan. During this time, many of the people died of hunger and smallpox. The Spanish were helped by enemies of the Aztecs. They were from the city-state of Tlaxcala. The Aztecs were hated by many city-states. So, it was easy for Cortés t ...
... Hernán Cortés. They first took over the capital city of Tenochtitlan. During this time, many of the people died of hunger and smallpox. The Spanish were helped by enemies of the Aztecs. They were from the city-state of Tlaxcala. The Aztecs were hated by many city-states. So, it was easy for Cortés t ...
Mexico`s Great Empire – The Aztecs
... The Aztecs The Aztecs settled in Mexico in the 1200AD. Their capital, Tenochtitlan, was located on the site of present day Mexico City. The Aztecs built temples, public buildings, and houses on an island in the center of Lake Texcoco. They connected the city to the mainland using causeways, or large ...
... The Aztecs The Aztecs settled in Mexico in the 1200AD. Their capital, Tenochtitlan, was located on the site of present day Mexico City. The Aztecs built temples, public buildings, and houses on an island in the center of Lake Texcoco. They connected the city to the mainland using causeways, or large ...
The Aztecs by Ciara and Amy
... 1100 - The Aztecs leave their homeland of Aztla in northern Mexico and begin their journey south. Over the next 225 years the Aztecs will move many times until they finally settle down at the city of Tenochtitlán. 1200 - The Aztecs arrive in the Valley of Mexico. ...
... 1100 - The Aztecs leave their homeland of Aztla in northern Mexico and begin their journey south. Over the next 225 years the Aztecs will move many times until they finally settle down at the city of Tenochtitlán. 1200 - The Aztecs arrive in the Valley of Mexico. ...
Chapter 9 part 2
... • They learned bookkeeping and business practices and became merchants. • They bought goods coming from Spain and then sold them in the colony, especially to the Indigenous peoples. ...
... • They learned bookkeeping and business practices and became merchants. • They bought goods coming from Spain and then sold them in the colony, especially to the Indigenous peoples. ...
Pre- Columbian Art
... which was located North of present day Mexico City. Teotihuacán was also an important city. Below is a picture of one of the ruins. ...
... which was located North of present day Mexico City. Teotihuacán was also an important city. Below is a picture of one of the ruins. ...
Aztec Empire
... contained 80,000 to 250,000 people. Canals served as roads for trade and travel between villages. Markets- 60,000 people visited daily. The Aztecs built huge pyramids, some lined with thousands of skulls. ...
... contained 80,000 to 250,000 people. Canals served as roads for trade and travel between villages. Markets- 60,000 people visited daily. The Aztecs built huge pyramids, some lined with thousands of skulls. ...
The Legend of the Aztecs The Aztec were hunter
... Around 1300 CE, a wandering tribe of Indians wandered into the Valley of Mexico. These people were called the Aztecs. When the Aztecs arrived in the Valley of Mexico, other tribes were already in residence. They had already taken the best land. The Aztecs had to make do with the swampy shores of Lak ...
... Around 1300 CE, a wandering tribe of Indians wandered into the Valley of Mexico. These people were called the Aztecs. When the Aztecs arrived in the Valley of Mexico, other tribes were already in residence. They had already taken the best land. The Aztecs had to make do with the swampy shores of Lak ...
Aztec warfare

Aztec warfare concerns the aspects associated with the militaristic conventions, forces, weaponry and strategic expansions conducted by the Late Postclassic Aztec civilizations of Mesoamerica, including particularly the military history of the Aztec Triple Alliance involving the city-states of Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, Tlacopan and other allied polities of the central Mexican region.The Aztec armed forces were typically composed of a large number of commoners (yāōquīzqueh [jaː.oːˈkiːskeʔ], ""those who have gone to war"") who possessed only basic military training, and a smaller but still considerable number of professional warriors belonging to the nobility (pīpiltin [piːˈpiɬtin]) and who were organized into warrior societies and ranked according to their achievements. The Aztec state was centered on political expansion and dominance of and exaction of tribute from other city states, and warfare was the basic dynamic force in Aztec politics. Aztec society was also centered on warfare: every Aztec male received basic military training from an early age and the only possibility of upwards social mobility for commoners(mācehualtin [maːseˈwaɬtin]) was through military achievement — especially the taking of captives (māltin [ˈmaːɬtin], singular malli). The sacrifice of war captives was an important part of many of the Aztec religious festivals. Warfare was thus the main driving force of both the Aztec economy and religion.