Unit_4_Math_Study_Guide_6th_01
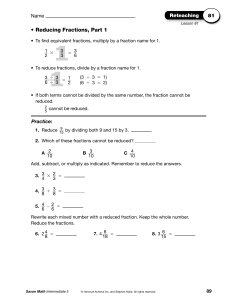
... To change 35/8 back to a mixed number, 35 divided by 8 equals 4 with 3 left over. Place the 3 over the denominator 8, so your answer is ...
... To change 35/8 back to a mixed number, 35 divided by 8 equals 4 with 3 left over. Place the 3 over the denominator 8, so your answer is ...
Full text
... which U(RhR2) is finite, where R2 = {i + ja:i,j e Z + } , Rx=R2+y, and Z+ denotes the nonnegative integers. Let sn =in+jna be the sequence obtained by arranging the .elements of R2 in increasing order. The main objective of this study can now be indicated specifically by this question: If y is ratio ...
... which U(RhR2) is finite, where R2 = {i + ja:i,j e Z + } , Rx=R2+y, and Z+ denotes the nonnegative integers. Let sn =in+jna be the sequence obtained by arranging the .elements of R2 in increasing order. The main objective of this study can now be indicated specifically by this question: If y is ratio ...
Fraction Study Guide **page numbers refer to our blue math book
... common denominator for the fractions by using equivalent fractions (this is the strategy to master because you will use it in other grades). Compare using <, >, or =. You can also use this strategy for ordering fractions. http://www.mathplayground.com/howto_comparefractions.html Multiply the denomin ...
... common denominator for the fractions by using equivalent fractions (this is the strategy to master because you will use it in other grades). Compare using <, >, or =. You can also use this strategy for ordering fractions. http://www.mathplayground.com/howto_comparefractions.html Multiply the denomin ...
Document
... one Discontinuity Note: Negative Numbers still have 1 for the most significant bit (MSB) ...
... one Discontinuity Note: Negative Numbers still have 1 for the most significant bit (MSB) ...
Full text
... This approach facilitates a clearer understanding of existing identities, and can be extended in a number of ways. For instance, by allowing tiles of length 3 or longer, we can give combinatorial interpretation to higher-order recurrences; however, the initial conditions do not work out so neatly, s ...
... This approach facilitates a clearer understanding of existing identities, and can be extended in a number of ways. For instance, by allowing tiles of length 3 or longer, we can give combinatorial interpretation to higher-order recurrences; however, the initial conditions do not work out so neatly, s ...