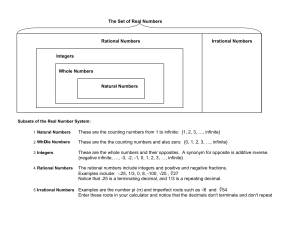
Rational and Irrational Numbers
... cannot be expressed as a fraction. Also, irrational numbers cannot be represented as terminating or repeating decimals. • Irrational numbers are non-terminating, nonrepeating decimals. ...
... cannot be expressed as a fraction. Also, irrational numbers cannot be represented as terminating or repeating decimals. • Irrational numbers are non-terminating, nonrepeating decimals. ...
PDF
... to another. For example, for squarefree n, the Möbius function µ(n) = (−1)ω(n) (where ω(n) is the number of distinct prime factors function). As a consequence of these sign changes, a positive real number x2 technically has two square roots, x and −x. The specific case of x2 = 25 was used in The S ...
... to another. For example, for squarefree n, the Möbius function µ(n) = (−1)ω(n) (where ω(n) is the number of distinct prime factors function). As a consequence of these sign changes, a positive real number x2 technically has two square roots, x and −x. The specific case of x2 = 25 was used in The S ...
Introduction to factoring
... 3. Divide polynomial by the GCF to find the other factor 4. To check, multiply the two factors to see if you get the original product ...
... 3. Divide polynomial by the GCF to find the other factor 4. To check, multiply the two factors to see if you get the original product ...
Adding and Subtracting Real Numbers - peacock
... number line to model addition and subtraction of real numbers. Addition To model addition of a positive number, move right. To model addition of a negative number, move left. Subtraction To model subtraction of a positive number, move left. To model subtraction of a negative number, move right. ...
... number line to model addition and subtraction of real numbers. Addition To model addition of a positive number, move right. To model addition of a negative number, move left. Subtraction To model subtraction of a positive number, move left. To model subtraction of a negative number, move right. ...