Extending Mathematical Understanding
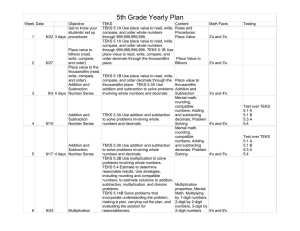
... 3. Count back/Counts down 4. Basic Strategies Strategies: to/ counts up from Multiplication & 1. Count all (multiple groups) 2. Modelling multiplication & division 3. Abstracting multiplication and Division Strategies: when all items are perceived division ...
... 3. Count back/Counts down 4. Basic Strategies Strategies: to/ counts up from Multiplication & 1. Count all (multiple groups) 2. Modelling multiplication & division 3. Abstracting multiplication and Division Strategies: when all items are perceived division ...
Fractions, Decimals, and Percents
... NOT: /A/Did you calculate your denominator correctly? /B/Correct! /C/Did you calculate the equivalent fractions properly? /D/Did you calculate your numerator correctly? 22. ANS: A Add or subtract the fractions by finding the lowest common denominator and rewriting them as equivalent fractions. Add o ...
... NOT: /A/Did you calculate your denominator correctly? /B/Correct! /C/Did you calculate the equivalent fractions properly? /D/Did you calculate your numerator correctly? 22. ANS: A Add or subtract the fractions by finding the lowest common denominator and rewriting them as equivalent fractions. Add o ...
Introduction - csns - California State University, Los Angeles
... The modulo operation creates a set, which in modular arithmetic is referred to as the set of least residues modulo n, or Zn ...
... The modulo operation creates a set, which in modular arithmetic is referred to as the set of least residues modulo n, or Zn ...
document
... • Deallocates the memory so that it may be re-used by malloc() • Danger: may accidentally deallocate memory when still have a pointer into it, causing the same problem as with pointers to stack space ...
... • Deallocates the memory so that it may be re-used by malloc() • Danger: may accidentally deallocate memory when still have a pointer into it, causing the same problem as with pointers to stack space ...
Ch6_IntrotoCS2013
... Multi-Dimensional Arrays arr = Array.new arr[0] = “ Hi y’all” arr[1] = 3.14159265 arr[2] = 17 arr[3] = [1,2,3] arr is [“ Hi y’all” , 3.14159265 , 17, [1,2,3] ] ...
... Multi-Dimensional Arrays arr = Array.new arr[0] = “ Hi y’all” arr[1] = 3.14159265 arr[2] = 17 arr[3] = [1,2,3] arr is [“ Hi y’all” , 3.14159265 , 17, [1,2,3] ] ...