Stellar evolution, I
... If interstellar gas is cold enough and dense enough, it will collapse under its own gravitational power to form stars. The “free fall” time of a spherical cloud is given by: Tff = [3/(32 G )]1/2 , where G is Newton's gravitational constant and is the initial density of the cloud. If the densi ...
... If interstellar gas is cold enough and dense enough, it will collapse under its own gravitational power to form stars. The “free fall” time of a spherical cloud is given by: Tff = [3/(32 G )]1/2 , where G is Newton's gravitational constant and is the initial density of the cloud. If the densi ...
Lecture 15
... opacity over all wavelengths • Weight by the rate at which Intensity distribution (blackbody radiation) varies with temperature. • Determine dependence of other parameters such as temperature ...
... opacity over all wavelengths • Weight by the rate at which Intensity distribution (blackbody radiation) varies with temperature. • Determine dependence of other parameters such as temperature ...
Teacher Sheet 1. What variables does the HR Diagram compare
... 14. Describe stars A, B, C, and D in terms of their brightness and temperature. Star A is red and therefore, cool. Its luminosity is 1/1000 of that of the sun; therefore, it is dim. Star B is a hot, blue star and very luminous. Both A and B are on the Main Sequence. Star C is also a hot, blue star. ...
... 14. Describe stars A, B, C, and D in terms of their brightness and temperature. Star A is red and therefore, cool. Its luminosity is 1/1000 of that of the sun; therefore, it is dim. Star B is a hot, blue star and very luminous. Both A and B are on the Main Sequence. Star C is also a hot, blue star. ...
Ay123 Fall 2011 STELLAR STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION Problem Set 1
... toy star, and verify that the virial theorem is exactly satisfied. Be sure to discuss matter with a general equation of state, not just an ideal monatomic nonrelativistic gas. 2. The Kelvin-Helmholtz timescale: (10 pts) Use your results from Problem 1 to estimate the time it would take a large solar ...
... toy star, and verify that the virial theorem is exactly satisfied. Be sure to discuss matter with a general equation of state, not just an ideal monatomic nonrelativistic gas. 2. The Kelvin-Helmholtz timescale: (10 pts) Use your results from Problem 1 to estimate the time it would take a large solar ...
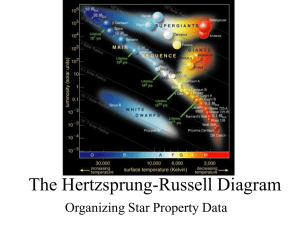
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Star Cycle [Recovered]
... fusion actually takes it out of the core. Thus, there is nothing left to combat ________________ gravity from the outer layers. The result: ___________! ...
... fusion actually takes it out of the core. Thus, there is nothing left to combat ________________ gravity from the outer layers. The result: ___________! ...
05spectralclasses
... Stellar Luminosity Classes • In 1930s, W. Morgan and P. Keenan noticed that stars with the same temperature could have different Balmer absorption depths. • Called the narrowest ones I and the deepest ones VI ...
... Stellar Luminosity Classes • In 1930s, W. Morgan and P. Keenan noticed that stars with the same temperature could have different Balmer absorption depths. • Called the narrowest ones I and the deepest ones VI ...
Stars Student Page Purpose To investigate stellar classification by
... in this portion of the graph are now as supergiants. 4. Stars in the lower right portion of the graph will remain on the Main Sequence the longest. This is because they will burn their fuel very slowly compared with larger stars on other parts of the Main Sequence. 5. The Sun radiates at a peak wave ...
... in this portion of the graph are now as supergiants. 4. Stars in the lower right portion of the graph will remain on the Main Sequence the longest. This is because they will burn their fuel very slowly compared with larger stars on other parts of the Main Sequence. 5. The Sun radiates at a peak wave ...
GIZMO H-RDiagramSE
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
ASTR 200 : Lecture 15 Ensemble Properties of Stars
... `evolutionary track' on the HR diagram of a solarmass star ...
... `evolutionary track' on the HR diagram of a solarmass star ...
Homework #8 1. Problem 10.21 2. The Origin of the Main Sequence
... stay the same? If you vote for one of the first two options, by how much? Hint: Pay attention to the proportionality constant in at least one of the equations. g) Objects that have central temperatures below ≈ 3 × 106 K do not undergo steady fusion of hydrogen via the proton-proton chain (the temper ...
... stay the same? If you vote for one of the first two options, by how much? Hint: Pay attention to the proportionality constant in at least one of the equations. g) Objects that have central temperatures below ≈ 3 × 106 K do not undergo steady fusion of hydrogen via the proton-proton chain (the temper ...
PowerPoint
... (…but our Sun is not very bright compared to the typical stars one sees in the sky!) (…in other words, compared to the “celebrities” of the star kingdom…) ...
... (…but our Sun is not very bright compared to the typical stars one sees in the sky!) (…in other words, compared to the “celebrities” of the star kingdom…) ...
Stellar Evolution - FSU High Energy Physics
... • Thermal motion of the ions will become less important and eventually degenerate electron pressure opposes gravitational collapse. ...
... • Thermal motion of the ions will become less important and eventually degenerate electron pressure opposes gravitational collapse. ...
Chapter 30 Section 2 Handout
... The band that runs diagonally through the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram and extends from cool, dim, red stars at the lower right to hot, bright, blue stars at the upper left. ...
... The band that runs diagonally through the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram and extends from cool, dim, red stars at the lower right to hot, bright, blue stars at the upper left. ...
Problem set 2
... small main-sequence star of mass 0.123 solar. Using the empirical scaling between the mass and luminosity from the textbook, and between mass and radius (you can assume it’s linear, R ∼ M), compute Proxima’s effective temperature Tef f . Comparing with sun’s temperature, prove that the star appears ...
... small main-sequence star of mass 0.123 solar. Using the empirical scaling between the mass and luminosity from the textbook, and between mass and radius (you can assume it’s linear, R ∼ M), compute Proxima’s effective temperature Tef f . Comparing with sun’s temperature, prove that the star appears ...
April 1st
... • The dense cloud fragment gets hotter as it contracts • The cloud becomes denser and radiation cannot escape • The thermal pressure and gas temperature start to rise and rise • The dense cloud fragment becomes a protostar ...
... • The dense cloud fragment gets hotter as it contracts • The cloud becomes denser and radiation cannot escape • The thermal pressure and gas temperature start to rise and rise • The dense cloud fragment becomes a protostar ...
Stellar Evolution
... are very large, cool and quite bright. Ex. Betelgeuse is 100,000 times more luminous than the Sun but is only 3,500K on the surface. It’s radius is 1,000 times that of the Sun. ...
... are very large, cool and quite bright. Ex. Betelgeuse is 100,000 times more luminous than the Sun but is only 3,500K on the surface. It’s radius is 1,000 times that of the Sun. ...
Study Guide for the 4TH Astronomy Exam
... Study Guide for the 4TH Astronomy Exam Stellar Evolution The successful student will be able to… 1. Star Formation a. Describe the physical characteristics of a giant molecular cloud b. Identify the source of heating (energy production) in protostars c. Explain why more low-mass K & M main sequence ...
... Study Guide for the 4TH Astronomy Exam Stellar Evolution The successful student will be able to… 1. Star Formation a. Describe the physical characteristics of a giant molecular cloud b. Identify the source of heating (energy production) in protostars c. Explain why more low-mass K & M main sequence ...
Understanding Stars
... Every element has it’s own unique spectrum – Use this to identify the composition of a gas • Chromosphere or corona Extremely dense things (opaque gases, liquids or solids) the atoms are too close – Emit a continuous spectrum • photosphere Stefan-Boltzman Law A dense hot object emits light of all co ...
... Every element has it’s own unique spectrum – Use this to identify the composition of a gas • Chromosphere or corona Extremely dense things (opaque gases, liquids or solids) the atoms are too close – Emit a continuous spectrum • photosphere Stefan-Boltzman Law A dense hot object emits light of all co ...
Document
... are about to form new stars. They also create the heavier elements (such as gold, silver, lead, and uranium) and distribute these as well. Their remnants generate the cosmic rays which lead to mutation and evolution in living cells. These supernovae, then, are key to the evolution of the Universe an ...
... are about to form new stars. They also create the heavier elements (such as gold, silver, lead, and uranium) and distribute these as well. Their remnants generate the cosmic rays which lead to mutation and evolution in living cells. These supernovae, then, are key to the evolution of the Universe an ...
Review Game
... There is a balance within the Sun between the outward push of pressure and the inward pull of gravity. They are cooler because their strong magnetic fields suppress convection and prevent hotter material from flowing into them. Because they are cooler, they emit less thermal radiation per unit area ...
... There is a balance within the Sun between the outward push of pressure and the inward pull of gravity. They are cooler because their strong magnetic fields suppress convection and prevent hotter material from flowing into them. Because they are cooler, they emit less thermal radiation per unit area ...



![Star Cycle [Recovered]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008086481_1-2d8d14aa9163345f6c20c4baab23c80a-300x300.png)