protostars low mass stars intermediatemass stars red giant planetary
... Briefly goes through the TTauri stage in a few years. These have a much shorter life cycle than intermediatemass stars, as massive stars only stay in the main sequence (middle age) for ~ 10 million years. Energy continues to be generated as the star converts hydrogen into helium. Not ma ...
... Briefly goes through the TTauri stage in a few years. These have a much shorter life cycle than intermediatemass stars, as massive stars only stay in the main sequence (middle age) for ~ 10 million years. Energy continues to be generated as the star converts hydrogen into helium. Not ma ...
Answers to Coursebook questions – Chapter E2
... In turn this implies that they orbit in different orbits, and so the inner star is a slower star and the more massive. ...
... In turn this implies that they orbit in different orbits, and so the inner star is a slower star and the more massive. ...
Ay123 Fall 2011 STELLAR STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION Problem Set 2
... (3) Stein 2051, M = 0.50 M⊙ or 0.72 M⊙ , R = 0.0115 R⊙ , and try to infer their compositions. e. The results you have derived above should show that as M → 0, R → ∞. Clearly, at some point this result must break down (think about where Jupiter would fall on this plot !). This is because when the den ...
... (3) Stein 2051, M = 0.50 M⊙ or 0.72 M⊙ , R = 0.0115 R⊙ , and try to infer their compositions. e. The results you have derived above should show that as M → 0, R → ∞. Clearly, at some point this result must break down (think about where Jupiter would fall on this plot !). This is because when the den ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... A planetary nebula is typically formed at the same time as a(n) _______________. The process in which many stars form from a single interstellar cloud is called _______. Interstellar clouds cause stars behind them to appear __________. Most stars in our Galaxy are __________. In a neutron star, the ...
... A planetary nebula is typically formed at the same time as a(n) _______________. The process in which many stars form from a single interstellar cloud is called _______. Interstellar clouds cause stars behind them to appear __________. Most stars in our Galaxy are __________. In a neutron star, the ...
File - Mr. Goodyear Astronomy
... moves back toward main sequence area of H-R diagram. - Star fluctuates on and off main sequence. Gravity tries to contact star creating other elements in star increasing fusion process. - This increase energy causes an explosion-like occurrence. This cause star to lose large quantities of mass. - Al ...
... moves back toward main sequence area of H-R diagram. - Star fluctuates on and off main sequence. Gravity tries to contact star creating other elements in star increasing fusion process. - This increase energy causes an explosion-like occurrence. This cause star to lose large quantities of mass. - Al ...
Background Information - Eu-Hou
... In order to plot a HR diagram, the temperature and luminosity of the stars need to be known. The simplest indication of a star’s temperature is its colour. A star’s colour is simply a measure of the amount of light from the star in one filter compared to another. The most common colour system is B-V ...
... In order to plot a HR diagram, the temperature and luminosity of the stars need to be known. The simplest indication of a star’s temperature is its colour. A star’s colour is simply a measure of the amount of light from the star in one filter compared to another. The most common colour system is B-V ...
Chapter 18 Study Guide
... White dwarf 9. What type of star has a low temperature but a high luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) Red supergiant 10. According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, what relationship exist between the brightness and temperature of a main sequence star? The Hertzsprung- Russell diagram shows ...
... White dwarf 9. What type of star has a low temperature but a high luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) Red supergiant 10. According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, what relationship exist between the brightness and temperature of a main sequence star? The Hertzsprung- Russell diagram shows ...
Star Life Cycle Computer Lab
... 10. Do the Interactive Equilibrium Lab and Practice Quizzes. 11. After their life on the main sequence, what happens to massive stars? 12. What is the 3rd fuel that stars can use after Hydrogen and Helium? The Beginning of the End 13. When a star is fusing helium, what stage of its life is it consid ...
... 10. Do the Interactive Equilibrium Lab and Practice Quizzes. 11. After their life on the main sequence, what happens to massive stars? 12. What is the 3rd fuel that stars can use after Hydrogen and Helium? The Beginning of the End 13. When a star is fusing helium, what stage of its life is it consid ...
Stellar structure
... T ~ GMmp/kBR. For a sufficiently large value of M/R (e.g. take one solar mass and one solar radius) T is large enough (> 107 K) that nuclear reactions will take place (high density also satisfied because also M/R3 very large) -- nuclear reactions establish a pressure/temperature gradient that suppo ...
... T ~ GMmp/kBR. For a sufficiently large value of M/R (e.g. take one solar mass and one solar radius) T is large enough (> 107 K) that nuclear reactions will take place (high density also satisfied because also M/R3 very large) -- nuclear reactions establish a pressure/temperature gradient that suppo ...
characteristics of stars/lives of stars
... Building Vocabulary From the list below, choose the term that best completes each sentence and write it in the space provided. spectrograph constellation light-year ...
... Building Vocabulary From the list below, choose the term that best completes each sentence and write it in the space provided. spectrograph constellation light-year ...
Evolution of Massive Stars
... stars of lower initial mass. Like lower-mass stars, high-mass stars fuse hydrogen in their cores during their main sequence lifetime. Massive stars also spend 90% of the total lifetimes as stars located on the main sequence. The main sequence is also a time sequence – more massive stars complete the ...
... stars of lower initial mass. Like lower-mass stars, high-mass stars fuse hydrogen in their cores during their main sequence lifetime. Massive stars also spend 90% of the total lifetimes as stars located on the main sequence. The main sequence is also a time sequence – more massive stars complete the ...
Answer all questions in Section A and two and only two questions in
... where G is the Gravitational constant, Pc is the central density, r is radius within the star, and lis a scale length such that l << R, where R is the outer radius of the star. Show that in this model the pressure at a radius r is given by: ...
... where G is the Gravitational constant, Pc is the central density, r is radius within the star, and lis a scale length such that l << R, where R is the outer radius of the star. Show that in this model the pressure at a radius r is given by: ...
Introduction to the HR Diagram
... 3) As humans age, their height and weight do change, so the position of an individual person in this diagram will evolve with time. 4) Over most of the lifetime of an individual, their height and weight will not change much, so there will be a region in this diagram where a human spends most of thei ...
... 3) As humans age, their height and weight do change, so the position of an individual person in this diagram will evolve with time. 4) Over most of the lifetime of an individual, their height and weight will not change much, so there will be a region in this diagram where a human spends most of thei ...
Characteristics of Main Sequence Stars
... and more of the star participates in the contraction. This competes with the overall stellar expansion. (A 1M¯ main-sequence star actually becomes hotter with age.) • As a fully convective star (M < 0.3M¯ ) evolves, the change in its molecular weight just moves the star to a higher helium content ZA ...
... and more of the star participates in the contraction. This competes with the overall stellar expansion. (A 1M¯ main-sequence star actually becomes hotter with age.) • As a fully convective star (M < 0.3M¯ ) evolves, the change in its molecular weight just moves the star to a higher helium content ZA ...
HW #5 Answers (Due 9/29)
... make Helium, the protons have to over come the repulsive force between them. This means that they have to be moving extremely fast or their average kinetic energy has to be very large. That means a high temperature. Also, collisions have to be head-on collisions. If not the particles will just scatt ...
... make Helium, the protons have to over come the repulsive force between them. This means that they have to be moving extremely fast or their average kinetic energy has to be very large. That means a high temperature. Also, collisions have to be head-on collisions. If not the particles will just scatt ...
Unit 8 Astronomy
... A neutron star is an imploded core of an exploded star made up almost entirely of neutrons. A teaspoon of their material would weigh more than all of automobiles in the U.S. together The most massive stars become supernovae and die as: ______________________ BLACK HOLE A black hole is an extremely m ...
... A neutron star is an imploded core of an exploded star made up almost entirely of neutrons. A teaspoon of their material would weigh more than all of automobiles in the U.S. together The most massive stars become supernovae and die as: ______________________ BLACK HOLE A black hole is an extremely m ...
10.5 The Hertzsprung
... Once many stars are plotted on an H-R diagram, a pattern begins to form: These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the Main Sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but ...
... Once many stars are plotted on an H-R diagram, a pattern begins to form: These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the Main Sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but ...
the free PDF resource
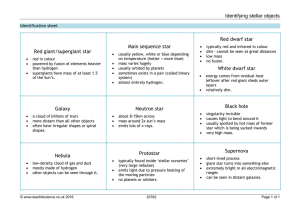
... usually yellow, white or blue depending on temperature (hotter = more blue) mass varies hugely usually orbited by planets sometimes exists in a pair (called binary system) almost entirely hydrogen. ...
... usually yellow, white or blue depending on temperature (hotter = more blue) mass varies hugely usually orbited by planets sometimes exists in a pair (called binary system) almost entirely hydrogen. ...
Section 1
... Although the fundamental physical properties are parameters such as M , R, and L, these translate into observational parameters such as absolute magnitude and colour index (cf. Appendix E), or spectral type. The ultimate goal is to relate these observationally accessible quantities to the physical p ...
... Although the fundamental physical properties are parameters such as M , R, and L, these translate into observational parameters such as absolute magnitude and colour index (cf. Appendix E), or spectral type. The ultimate goal is to relate these observationally accessible quantities to the physical p ...
Slide 1
... shell produce more energy than needed for pressure support Expansion and cooling of the outer layers of the star Red ...
... shell produce more energy than needed for pressure support Expansion and cooling of the outer layers of the star Red ...
Stellar Evolution of Single Stars
... Then the core begins a nearly adiabatic Kelvin-Helmholtz contraction. ρc, Tc, and L increase. ...
... Then the core begins a nearly adiabatic Kelvin-Helmholtz contraction. ρc, Tc, and L increase. ...
Astronomy HOMEWORK Chapter 12 - 9th Edition 1. Consider a star
... Answer: Cepheids are stars which pulsate in brightness in a distinctive way due to a thermal instability. A higher-mass star becomes a Cepheid when its evolutionary path takes it across the instability strip. The most important characteristic of Cepheids is that their pulsation period correltates wi ...
... Answer: Cepheids are stars which pulsate in brightness in a distinctive way due to a thermal instability. A higher-mass star becomes a Cepheid when its evolutionary path takes it across the instability strip. The most important characteristic of Cepheids is that their pulsation period correltates wi ...
Main Sequence Stars
... If star A is 2 times as hot as star B, and the same radius, then it will be 24 = 16 times as luminous. ...
... If star A is 2 times as hot as star B, and the same radius, then it will be 24 = 16 times as luminous. ...
Question: Fossilized footprints of Coelophysis
... boundary between Earth’s mantle and core? Key words: temperature, mantle, core, star Picking the right table: The Inferred Properties of Earth’s Interior table (p. NY28) has a diagram of Earth’s interior, along with graphs that show how pressure and temperature change with depth. From this table, yo ...
... boundary between Earth’s mantle and core? Key words: temperature, mantle, core, star Picking the right table: The Inferred Properties of Earth’s Interior table (p. NY28) has a diagram of Earth’s interior, along with graphs that show how pressure and temperature change with depth. From this table, yo ...