
Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram March 16 −
... Hot-plate model of star: L=R2T4 Model of the solar interior X How to read H-R Diagram Spectrum of black body: Hotter=>bluer Energy generation in the sun X ...
... Hot-plate model of star: L=R2T4 Model of the solar interior X How to read H-R Diagram Spectrum of black body: Hotter=>bluer Energy generation in the sun X ...
wk9 (part 1)
... • A proto-star’s temperature and luminosity can be plotted on a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram or HR diagram • Proto-stars tend to become hotter but less luminous during the process of gravitational contraction; the decrease in luminosity is mostly a result of the proto-star becoming smaller • The exac ...
... • A proto-star’s temperature and luminosity can be plotted on a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram or HR diagram • Proto-stars tend to become hotter but less luminous during the process of gravitational contraction; the decrease in luminosity is mostly a result of the proto-star becoming smaller • The exac ...
Stages in the Formation of Stars
... 3. Name the process that causes a star to begin producing vast amounts of energy. _____________________________________________ 4. What two processes balance each other to make a star stable? ...
... 3. Name the process that causes a star to begin producing vast amounts of energy. _____________________________________________ 4. What two processes balance each other to make a star stable? ...
Four Homework Assignments
... radius (R), assuming Kramers opacity, and using the ideal gas law, derive a very approximate R(M ) for main-sequence stars from ∼1.5 M to 4.0 M . [Hint: You will need to know whether hydrogen burning is proceeding by the PP chain or the CNO cycle.] Retain the µ dependence of your result. What powe ...
... radius (R), assuming Kramers opacity, and using the ideal gas law, derive a very approximate R(M ) for main-sequence stars from ∼1.5 M to 4.0 M . [Hint: You will need to know whether hydrogen burning is proceeding by the PP chain or the CNO cycle.] Retain the µ dependence of your result. What powe ...
Unit 12 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... 5. What is the difference between absolute and apparent magnitude? What is luminosity? 6. What are the three types of spectra? How can scientists use absorption spectra to determine the elements that compose a star? 7. What are stars made of and how do they produce their light? What is the differenc ...
... 5. What is the difference between absolute and apparent magnitude? What is luminosity? 6. What are the three types of spectra? How can scientists use absorption spectra to determine the elements that compose a star? 7. What are stars made of and how do they produce their light? What is the differenc ...
Stellar Birth - ahsastronomy
... • At this stage the cloud begins to collapse on its self increasing the temperature and causing it to contract. ...
... • At this stage the cloud begins to collapse on its self increasing the temperature and causing it to contract. ...
Stars: Other Suns
... Mass-luminosity relation • A star’s mass and luminosity are related: a little more mass means a lot more luminosity! ...
... Mass-luminosity relation • A star’s mass and luminosity are related: a little more mass means a lot more luminosity! ...
Solution to Problem Set 1 1. The total number of nucleons in one
... to initiate the nuclear burning. [2 marks] Very massive stars are dominated by radiation pressure, such radiation dominated stars are unstable to radial perturbations, and hence this provides an upper limit on the stellar mass. [2 marks] At the late evolutionary stage of the Sun, helium nuclear burn ...
... to initiate the nuclear burning. [2 marks] Very massive stars are dominated by radiation pressure, such radiation dominated stars are unstable to radial perturbations, and hence this provides an upper limit on the stellar mass. [2 marks] At the late evolutionary stage of the Sun, helium nuclear burn ...
Homework 4
... Due November 2, 2012 at 5 p.m., either electronically or on paper. 1. If a protostar is forming out of a cold molecular cloud, how can its luminosity be upto one hundred times as large as the luminosity of the star it will become? ...
... Due November 2, 2012 at 5 p.m., either electronically or on paper. 1. If a protostar is forming out of a cold molecular cloud, how can its luminosity be upto one hundred times as large as the luminosity of the star it will become? ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... – Most stars fall in the region called main sequence. – Curved line sloping from top left to lower right of HR diagram. ...
... – Most stars fall in the region called main sequence. – Curved line sloping from top left to lower right of HR diagram. ...
Answer ALL questions from SECTION A and TWO questions from
... account should describe the structure and the resulting evolutionary tracks of protostars during contraction to the main sequence. Discuss why observations of circumstellar disks, stellar winds and accretion shocks associated with proto-stars have led to revisions of our ideas about the pre-main seq ...
... account should describe the structure and the resulting evolutionary tracks of protostars during contraction to the main sequence. Discuss why observations of circumstellar disks, stellar winds and accretion shocks associated with proto-stars have led to revisions of our ideas about the pre-main seq ...
INV 12B MOTION WITH CHANGING SPEED DRY LAB DATA
... 3. How does the sun compare to the other stars on the main sequence? (Hint: The sun’s color is …..What part of the main sequence is it in – upper left, lower left, etc.?) ...
... 3. How does the sun compare to the other stars on the main sequence? (Hint: The sun’s color is …..What part of the main sequence is it in – upper left, lower left, etc.?) ...
Quiz Solution: 1 April 2013 What does it mean when an astronomer
... What does it mean when an astronomer says that a star "moves" from one place to another on an H-R Diagram? Can you provide an example of this? As stars evolve and change structure, their radii and temperatures also change. Since a star's luminosity is dependent on both temperature and radius, the lu ...
... What does it mean when an astronomer says that a star "moves" from one place to another on an H-R Diagram? Can you provide an example of this? As stars evolve and change structure, their radii and temperatures also change. Since a star's luminosity is dependent on both temperature and radius, the lu ...
obafgkm - Piscataway High School
... Astronomers cannot physically measure properties of stars. They rely on interpreting data that can be gathered from the earth. Determine what information about stars can be revealed using the following methods: Parallax effect ...
... Astronomers cannot physically measure properties of stars. They rely on interpreting data that can be gathered from the earth. Determine what information about stars can be revealed using the following methods: Parallax effect ...
Properties of Main Sequence Stars
... Properties of Main Sequence Stars 10 points Extra Credit. Due next class. ...
... Properties of Main Sequence Stars 10 points Extra Credit. Due next class. ...
ppt
... = 5.6710-8 W/m2/K4 is a number called the Stephan-Boltzmann constant. Luminosity increases very rapidly with temperature (2 T gives 16 L) and radius (2 R gives 4 L). ...
... = 5.6710-8 W/m2/K4 is a number called the Stephan-Boltzmann constant. Luminosity increases very rapidly with temperature (2 T gives 16 L) and radius (2 R gives 4 L). ...
31 — Main-Sequence Stars [Revision : 1.1]
... ∗ High temperature sensitivity (∼ T 19 ) means centrally-concentrated energy generation ∗ So, luminosity Lr grows raidly in core, and F = Lr /4πr2 is large ∗ To transport all energy by radiation, temperature gradient very steep; convection sets in ∗ So, convective core ∗ Convection is very efficient ...
... ∗ High temperature sensitivity (∼ T 19 ) means centrally-concentrated energy generation ∗ So, luminosity Lr grows raidly in core, and F = Lr /4πr2 is large ∗ To transport all energy by radiation, temperature gradient very steep; convection sets in ∗ So, convective core ∗ Convection is very efficient ...
Lecture Notes-PPT
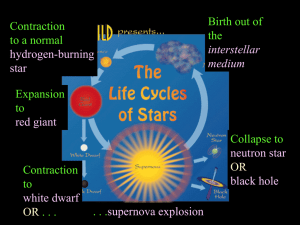
... Route to Main Sequence The track from stage 4 to stage 6 is known as the Hayashi track Stars on this track are called T Tauri stars Luminosity drops dramatically as contraction occurs;core temperature rises to 5 million K Heat and gravity compete between stages 6 and 7 until core reaches about 10 m ...
... Route to Main Sequence The track from stage 4 to stage 6 is known as the Hayashi track Stars on this track are called T Tauri stars Luminosity drops dramatically as contraction occurs;core temperature rises to 5 million K Heat and gravity compete between stages 6 and 7 until core reaches about 10 m ...
Stars and the Main Sequence
... Convective energy transport: takes over when necessary temperature gradient is too steep hot gas moves up, cool gas moves down, within convective zone fluid elements move adiabatically (adiabatic temperature gradient) driven by temperature dependent bouyancy Stars with M<1.2 M0 have radiative core ...
... Convective energy transport: takes over when necessary temperature gradient is too steep hot gas moves up, cool gas moves down, within convective zone fluid elements move adiabatically (adiabatic temperature gradient) driven by temperature dependent bouyancy Stars with M<1.2 M0 have radiative core ...
Stars - BrainBytes
... Majority of stars (about 90%) fall in this category Runs from upper left (high luminosity, high surface temperature ) to lower right (low luminosity, low surface temperature) Life span: 1 million – 1 billion yrs Actively fuse hydrogen and helium Example: our Sun ...
... Majority of stars (about 90%) fall in this category Runs from upper left (high luminosity, high surface temperature ) to lower right (low luminosity, low surface temperature) Life span: 1 million – 1 billion yrs Actively fuse hydrogen and helium Example: our Sun ...
Mark scheme for Support Worksheet – Topic E, Worksheet 1
... A constellation is a collection of stars usually in a recognisable pattern that are not necessarily physically close to each other; whereas a stellar cluster consists of stars that are close to each other and attract each other gravitationally. ...
... A constellation is a collection of stars usually in a recognisable pattern that are not necessarily physically close to each other; whereas a stellar cluster consists of stars that are close to each other and attract each other gravitationally. ...















![31 — Main-Sequence Stars [Revision : 1.1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015926256_1-97d746cbe97ccc13b433136b208bf071-300x300.png)





