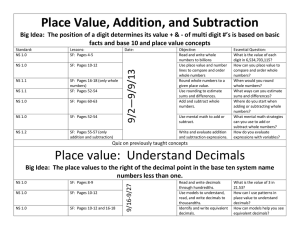
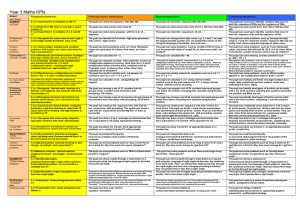
Place Value, Addition, and Subtraction Big Idea: The position of a
... compare and order whole numbers? When would you round whole numbers? What ways can you estimate sums and differences? Where do you start when adding or subtracting whole numbers? What mental math strategies can you use to add or subtract whole numbers? How do you evaluate expressions with variables? ...
... compare and order whole numbers? When would you round whole numbers? What ways can you estimate sums and differences? Where do you start when adding or subtracting whole numbers? What mental math strategies can you use to add or subtract whole numbers? How do you evaluate expressions with variables? ...
Perfect numbers - Harvard Math Department
... • Conway and Guy write: ”There probably aren’t any!” [4] • Stan Wagon writes in [32] ”Maybe some simple combination of a dozen or so primes in fact yield an odd perfect number!” • P. Ribenboim: ”This is a question which has been extensively searched, but its answer is still unknown.” [27] and • P. R ...
... • Conway and Guy write: ”There probably aren’t any!” [4] • Stan Wagon writes in [32] ”Maybe some simple combination of a dozen or so primes in fact yield an odd perfect number!” • P. Ribenboim: ”This is a question which has been extensively searched, but its answer is still unknown.” [27] and • P. R ...
1.7 Greatest Common Factor and Least Common Multiple
... In this lesson, we learn how to find the GCF (Greatest Common Factor) and LCM (Least Common Multiple) of a group of numbers (usually two numbers). For example, the GCF of 6 and 8 is 2. The LCM of 6 and 8 is 24. These two concepts will help you better understand numbers. In later lessons, we need to ...
... In this lesson, we learn how to find the GCF (Greatest Common Factor) and LCM (Least Common Multiple) of a group of numbers (usually two numbers). For example, the GCF of 6 and 8 is 2. The LCM of 6 and 8 is 24. These two concepts will help you better understand numbers. In later lessons, we need to ...
Recursion - UWO Computer Science
... • Evaluating algebraic expressions in postfix form (how did we do this earlier?) • etc. ...
... • Evaluating algebraic expressions in postfix form (how did we do this earlier?) • etc. ...
Further Algebra
... cannot be expressed as a rational number. Ö2, Ö5, 3Ö10 are all surds, whereas Ö25 and 3Ö8 are not surds as Ö25 = 5 and 3Ö8 = 2. The following examples could be used to show students how to simplify surds: Example 1 ...
... cannot be expressed as a rational number. Ö2, Ö5, 3Ö10 are all surds, whereas Ö25 and 3Ö8 are not surds as Ö25 = 5 and 3Ö8 = 2. The following examples could be used to show students how to simplify surds: Example 1 ...
Document
... Because the 3 is where the last significant figure will be and the number after it is 4 or less. • 0.0237 rounds to 0.024 or 2.4 × 10-2. Because the 3 is where the last significant figure will be and the number after it is 5 or greater. • 0.02349865 rounds to 0.023 or 2.3 × 10-2. Because the 3 ...
... Because the 3 is where the last significant figure will be and the number after it is 4 or less. • 0.0237 rounds to 0.024 or 2.4 × 10-2. Because the 3 is where the last significant figure will be and the number after it is 5 or greater. • 0.02349865 rounds to 0.023 or 2.3 × 10-2. Because the 3 ...
Section 1 - OER Africa
... In real life it is often indicated that products will rise in price with a certain percentage. We could hear on the news that bread, for example, will increase in price with 3% as from next week. What does such a percentage increase mean in cash terms? Example If bread currently costs R 7,50 and inc ...
... In real life it is often indicated that products will rise in price with a certain percentage. We could hear on the news that bread, for example, will increase in price with 3% as from next week. What does such a percentage increase mean in cash terms? Example If bread currently costs R 7,50 and inc ...
Rational and Irrational Numbers
... They were successful in understanding the mathematical principals behind music. By examining the vibrations of a single string they discovered that harmonious tones only occurred when the string was fixed at points along its length that were ratios of whole numbers. For instance when a string is fix ...
... They were successful in understanding the mathematical principals behind music. By examining the vibrations of a single string they discovered that harmonious tones only occurred when the string was fixed at points along its length that were ratios of whole numbers. For instance when a string is fix ...
Key performance indicators maths
... many numbers from 1 to 30 as you can' and solve word problems such as 'I have a number of cupcakes. I can pack them in boxes which contain four cakes, three cakes or eight cakes. In each case I will fill all of the boxes with none left over. What is the least number of cupcakes I could have?' ...
... many numbers from 1 to 30 as you can' and solve word problems such as 'I have a number of cupcakes. I can pack them in boxes which contain four cakes, three cakes or eight cakes. In each case I will fill all of the boxes with none left over. What is the least number of cupcakes I could have?' ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.