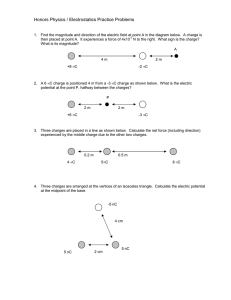
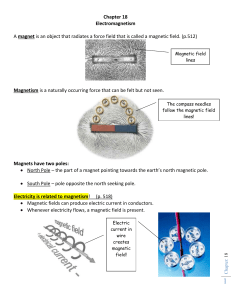
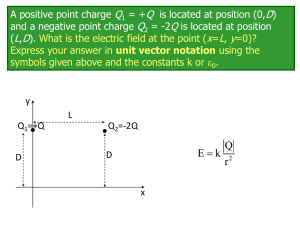
E=- V/ x= -400 volts/8 cm =-400 V/0.08 m=
... Three points, labeled a, b, c are shown in the figure. As shown: ‘a’ is midway between the leftmost and top charges, ‘b’ is equidistant from all three charges(lies on the intersection of the bisectors of all three 60o angles), ‘c’ is just as far below the line connecting the bottom two charges as ‘b ...
... Three points, labeled a, b, c are shown in the figure. As shown: ‘a’ is midway between the leftmost and top charges, ‘b’ is equidistant from all three charges(lies on the intersection of the bisectors of all three 60o angles), ‘c’ is just as far below the line connecting the bottom two charges as ‘b ...
PROBLEMA A-1 An electron is emitted in the x direction with velocity
... An electron is emitted in the x direction with velocity v. At the time t=0 the electron enters into a parallel plate empty capacitor (squared plates of side l and separation distance h) exactly at half height of the separation between the plates. The plates are electrically charged with a surface ch ...
... An electron is emitted in the x direction with velocity v. At the time t=0 the electron enters into a parallel plate empty capacitor (squared plates of side l and separation distance h) exactly at half height of the separation between the plates. The plates are electrically charged with a surface ch ...
Unit 14: Electric Charge
... charge, positive and negative. Charges of the same sign repel each other and opposite charges attract each other. o Conductors are materials that permit charge to move easily and insulators so not allow charge to move easily o Coulomb’s law is the basic law of interaction for point electric charges. ...
... charge, positive and negative. Charges of the same sign repel each other and opposite charges attract each other. o Conductors are materials that permit charge to move easily and insulators so not allow charge to move easily o Coulomb’s law is the basic law of interaction for point electric charges. ...
Electromagnetics-1
... is the equation of continuity. Q. 10 For silver, and σ = 3 x 10 7 mhos/m, calculate the skin depth at 10 8 Hz frequency. Q. 11 If in a time invariant field, the magnetic field associated with a plane electromagnetic wave has only z – component which is expressed as then obtain an expression for curr ...
... is the equation of continuity. Q. 10 For silver, and σ = 3 x 10 7 mhos/m, calculate the skin depth at 10 8 Hz frequency. Q. 11 If in a time invariant field, the magnetic field associated with a plane electromagnetic wave has only z – component which is expressed as then obtain an expression for curr ...
Dielectric
A dielectric material (dielectric for short) is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric polarization. Because of dielectric polarization, positive charges are displaced toward the field and negative charges shift in the opposite direction. This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polarized, but also reorient so that their symmetry axes align to the field.The study of dielectric properties concerns storage and dissipation of electric and magnetic energy in materials. Dielectrics are important for explaining various phenomena in electronics, optics, and solid-state physics.