World History
... Christendom. For him, it was a spiritual kingdom that fanned out from Rome to the most distant Churches. ...
... Christendom. For him, it was a spiritual kingdom that fanned out from Rome to the most distant Churches. ...
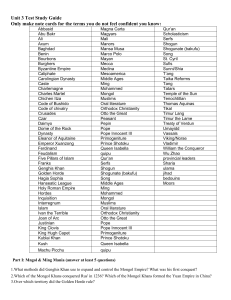
Unit 3 Test Study Guide Only make note cards for the terms you do
... 44.What was the three-field system? 45.What percentage of Europeans died during the Black Death? What were some results of the plague? 46.Be familiar with the technologies that contributed to the growth of metal working in the Middle Ages. 47.Know the relationship between trade and urbanization in ...
... 44.What was the three-field system? 45.What percentage of Europeans died during the Black Death? What were some results of the plague? 46.Be familiar with the technologies that contributed to the growth of metal working in the Middle Ages. 47.Know the relationship between trade and urbanization in ...
13.1 Germanic Kingdoms Unite Under Charlemagne
... If the king yielded to the authority of church matters and the pope yielded to the matter of politics all would be in harmony o However this is not how it played out Church Structure Ranks of clergy – all had different power; method of organization o Pope o Bishops o Priests Bishops settled di ...
... If the king yielded to the authority of church matters and the pope yielded to the matter of politics all would be in harmony o However this is not how it played out Church Structure Ranks of clergy – all had different power; method of organization o Pope o Bishops o Priests Bishops settled di ...
Ancient World History - Ash Grove R
... Trade was greatly changing the landscape of Western Europe through the middle ages During the High Middle Ages, cultural diffusion through trade with the east brought new and more advanced ideas that greatly change Europe ...
... Trade was greatly changing the landscape of Western Europe through the middle ages During the High Middle Ages, cultural diffusion through trade with the east brought new and more advanced ideas that greatly change Europe ...
christianity
... - The Fourth Crusade was a disaster, and it would be the final straw in the separation between the Christian East and West. - Troops were told they were going to Jerusalem, but instead they were going to Egypt. Once this secret got out, 2/3 of the troops deserted, and they were so broke they could n ...
... - The Fourth Crusade was a disaster, and it would be the final straw in the separation between the Christian East and West. - Troops were told they were going to Jerusalem, but instead they were going to Egypt. Once this secret got out, 2/3 of the troops deserted, and they were so broke they could n ...
CN Feudalism and Manorial System File
... for glory and wealth. For most of the Middle Ages, however, war was a major cause of suffering and hardship. The church tried to limit the general suffering caused by war by issuing several decrees that prohibited acts of violence and private warfare near churches and other holy buildings. If the de ...
... for glory and wealth. For most of the Middle Ages, however, war was a major cause of suffering and hardship. The church tried to limit the general suffering caused by war by issuing several decrees that prohibited acts of violence and private warfare near churches and other holy buildings. If the de ...
FROM THE FALL OF ROME TO CHARLEMAGNE
... • Germanic groups who had invaded Rome established many small kingdoms – After the fall of Rome, the Western Roman Empire became a number of states ruled by German kings • Visigoths occupied Spain and Italy and the Ostrogoths also took control of Italy • Two German tribes, the Angles and Saxons, mig ...
... • Germanic groups who had invaded Rome established many small kingdoms – After the fall of Rome, the Western Roman Empire became a number of states ruled by German kings • Visigoths occupied Spain and Italy and the Ostrogoths also took control of Italy • Two German tribes, the Angles and Saxons, mig ...
The Crusades
... After the fall of Jerusalem, the pope called for another crusade. Some of Europe’s most powerful leaders went on the Third Crusades like king Richard the Lion-Hearted. He became the Crusaders leader because of courage and skill in battle. The Crusaders never gained back Jerusalem but in 1192, ...
... After the fall of Jerusalem, the pope called for another crusade. Some of Europe’s most powerful leaders went on the Third Crusades like king Richard the Lion-Hearted. He became the Crusaders leader because of courage and skill in battle. The Crusaders never gained back Jerusalem but in 1192, ...
Many church officials helped political leaders run their
... After the fall of Jerusalem, the pope called for another crusade. Some of Europe’s most powerful leaders went on the Third Crusades like king Richard the Lion-Hearted. He became the Crusaders leader because of courage and skill in battle. The Crusaders never gained back Jerusalem but in 1192, ...
... After the fall of Jerusalem, the pope called for another crusade. Some of Europe’s most powerful leaders went on the Third Crusades like king Richard the Lion-Hearted. He became the Crusaders leader because of courage and skill in battle. The Crusaders never gained back Jerusalem but in 1192, ...
World Geography A
... What role did technology and trade play in the transformation of medieval Europe? (WH1B*, 4A, 4B, 23A, WG18A*, WG20A*) What was the impact of the Crusades on Europe in the Middle Ages? (WH1B*, 3C, 19B, WG18A*) How did the Black Death accelerate change in Europe? (WH1B*, 4A, 12B*, WG1A*, 1B, an ...
... What role did technology and trade play in the transformation of medieval Europe? (WH1B*, 4A, 4B, 23A, WG18A*, WG20A*) What was the impact of the Crusades on Europe in the Middle Ages? (WH1B*, 3C, 19B, WG18A*) How did the Black Death accelerate change in Europe? (WH1B*, 4A, 12B*, WG1A*, 1B, an ...
Middle Ages
... Christians carried out military expeditions to regain the Holy Land from Muslims. • In 1095, Pope Urban II challenged all Christians to take up weapons. He promised: “All who die... Shall have immediate remission of sins.” ...
... Christians carried out military expeditions to regain the Holy Land from Muslims. • In 1095, Pope Urban II challenged all Christians to take up weapons. He promised: “All who die... Shall have immediate remission of sins.” ...
The Middle Ages - Scott County School District 1
... Clovis: Frankish Leader of Gaul (France) United a Kingdom & Spread ...
... Clovis: Frankish Leader of Gaul (France) United a Kingdom & Spread ...
Development of Feudalism in Europe
... of Champagne by sending them the knights whose services I owe them from the fief which I hold from them. Feudalism, then, was this system of a vassal being paid in land for his service to a king, because the king was not strong enought to defende his kingdom. The Vassal owned the land and the people ...
... of Champagne by sending them the knights whose services I owe them from the fief which I hold from them. Feudalism, then, was this system of a vassal being paid in land for his service to a king, because the king was not strong enought to defende his kingdom. The Vassal owned the land and the people ...
Early Medieval Europe & Medieval Christianity
... payments to the lord in the form of money, crops, and labor services. Manorialism established a social and political order that paralleled feudalism. ...
... payments to the lord in the form of money, crops, and labor services. Manorialism established a social and political order that paralleled feudalism. ...
Europe Turns Outward
... loyal to, the caliph. The Turks, however, rallied behind leaders of their own and wrested territory in Persia, Syria, and Egypt away from their caliph. Some Abbasids put up a good fight, but in 945 Baghdad's caliph submitted to the Persian Buyids. While the Buyids brought Persia and Iraq under contr ...
... loyal to, the caliph. The Turks, however, rallied behind leaders of their own and wrested territory in Persia, Syria, and Egypt away from their caliph. Some Abbasids put up a good fight, but in 945 Baghdad's caliph submitted to the Persian Buyids. While the Buyids brought Persia and Iraq under contr ...
The Middle Ages in Western Europe
... d. The Fourth Crusade (1202 – 1204 CE) 1. Pope Innocent III calls for a Fourth Crusade upon the death of Saladin in 1193. 2. The leaders of this crusade, the nobility of Venice, decide to eliminate their biggest trade competitor, The Byzantine ...
... d. The Fourth Crusade (1202 – 1204 CE) 1. Pope Innocent III calls for a Fourth Crusade upon the death of Saladin in 1193. 2. The leaders of this crusade, the nobility of Venice, decide to eliminate their biggest trade competitor, The Byzantine ...
RP units 5-8 - Northside Middle School
... Role of the shogun, samurai, farmers, artisans, merchants ...
... Role of the shogun, samurai, farmers, artisans, merchants ...
The Middle Ages - Harrison Humanities
... These tribes also helped shape the feudal system that spread through medieval Europe. The act of vassalage, in which one lord swears allegiance to another in exchange for privileges or “feuds,” originated in tribal organization. The concepts of kingship, knighthood, and chivalry all emerged from the ...
... These tribes also helped shape the feudal system that spread through medieval Europe. The act of vassalage, in which one lord swears allegiance to another in exchange for privileges or “feuds,” originated in tribal organization. The concepts of kingship, knighthood, and chivalry all emerged from the ...
File
... soldiers formed a siege around Rome. When the city was close to starvation, the Roman citizens opened the gates and allowed the conquering army to enter. The Visigoths rampaged through the streets for three days, pillaging ...
... soldiers formed a siege around Rome. When the city was close to starvation, the Roman citizens opened the gates and allowed the conquering army to enter. The Visigoths rampaged through the streets for three days, pillaging ...
File study guide 16a
... Hanseatic League), and state-sponsored commercial infrastructures E. The expansion of empires facilitated Trans-Eurasian trade and communication as new peoples were drawn into their conquerors’ economies and trade networks. Required examples of empires: The Byzantine Empire Key Concept 3.2. Continui ...
... Hanseatic League), and state-sponsored commercial infrastructures E. The expansion of empires facilitated Trans-Eurasian trade and communication as new peoples were drawn into their conquerors’ economies and trade networks. Required examples of empires: The Byzantine Empire Key Concept 3.2. Continui ...
The Roman Empire and Medieval England
... A drawing of the centre of Ancient Rome – the centre of the Roman Empire ...
... A drawing of the centre of Ancient Rome – the centre of the Roman Empire ...
Essential Standards
... knowledge of Roman language, law, philosophy, and art to early medieval Western Europe. Students may discuss why the empire survived in the east. Comparative factors include the benefits of having greater manufacturing and commerce, more tax revenues, and more effective defenses against nomadic cava ...
... knowledge of Roman language, law, philosophy, and art to early medieval Western Europe. Students may discuss why the empire survived in the east. Comparative factors include the benefits of having greater manufacturing and commerce, more tax revenues, and more effective defenses against nomadic cava ...
The Rise of Europe - Regina Catholic Education Center
... CHURCH IN THE MIDDLE AGES Rome falls & the church splits eastern (Byzantine Eastern Orthodox) & western (Roman Catholic) Influence is both spiritual & secular. ...
... CHURCH IN THE MIDDLE AGES Rome falls & the church splits eastern (Byzantine Eastern Orthodox) & western (Roman Catholic) Influence is both spiritual & secular. ...
Chapter 13
... • The Monks will give up their possessions to convert the tribes. • Benedict will write a rule that will be the guide for religious communities in the West ...
... • The Monks will give up their possessions to convert the tribes. • Benedict will write a rule that will be the guide for religious communities in the West ...
High Middle Ages

The High Middle Ages or High Medieval Period was the period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries (c. 1001–1300). The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which by convention end around 1500.The key historical trend of the High Middle Ages was the rapidly increasing population of Europe, which brought about great social and political change from the preceding era, the Renaissance of the 12th century, including the first developments of rural exodus and urbanization. By 1250 the robust population increase greatly benefited the European economy, reaching levels it would not see again in some areas until the 19th century. This trend was checked in the Late Middle Ages by a series of calamities, notably the Black Death but also including numerous wars and economic stagnation.From about the year 780 onwards, Europe saw the last of the barbarian invasions and became more socially and politically organized. The Carolingian Renaissance led to scientific and philosophical revival of Europe. The first universities were established in Bologna, Paris, Oxford and Modena. The Vikings had settled in the British Isles, France and elsewhere, whilst Norse Christian kingdoms were developing in their Scandinavian homelands. The Magyars had ceased their expansion in the 10th century, and by the year 1000, a Christian Kingdom of Hungary was recognized in central Europe, forming alliances with regional powers. With the brief exception of the Mongol invasions in the 13th century, major nomadic incursions ceased. The powerful Byzantine Empire of the Macedonian and Komnenos dynasties gradually gave way to resurrected Serbia and Bulgaria and to a successor Crusade state from 1204 to 1261, while countering the continuous threat of the Seljuk Turks in Asia Minor.In the 11th century, populations north of the Alps began to settle new lands, some of which had reverted to wilderness after the end of the Roman Empire. In what is known as the ""great clearances"", vast forests and marshes of Europe were cleared and cultivated. At the same time settlements moved beyond the traditional boundaries of the Frankish Empire to new frontiers in Europe, beyond the Elbe River, tripling the size of Germany in the process. The Catholic Church, reaching the peak of its political power at this time, called armies from across Europe to a series of Crusades against the Seljuk Turks, who occupied the Holy Land, thereby founding the Crusader States in the Levant. Other wars led to the Northern Crusades, while Christian kingdoms conquered the Iberian Peninsula from the Moors, and the Normans colonized southern Italy, all part of the major population increase and resettlement pattern of the era.The High Middle Ages produced many different forms of intellectual, spiritual and artistic works. This age saw the rise of ethnocentrism, which evolved later into modern civic nationalisms in most of Europe, the ascent of the great Italian city-states, and the rise and fall of the Muslim civilization of Al-Andalus. The rediscovery of the works of Aristotle led Thomas Aquinas and other thinkers of the period to develop Scholasticism, a combination of Catholicism and ancient philosophy. For much of the time period Constantinople remained Europe's most populous city and Byzantine art reached a peak in the 12th century. In architecture, many of the most notable Gothic cathedrals were built or completed during this era.The Crisis of the Late Middle Ages, beginning at the start of the 14th century, marked the end of this era.