File
... still had in France. They also wanted to increase their control over the government and the Church in England. Henry II ruled from 1154 to 1189. He was one of the strongest of William’s descendants. He married Eleanor of Aquitaine, who had been married to King Louis VII of France. From this marriage ...
... still had in France. They also wanted to increase their control over the government and the Church in England. Henry II ruled from 1154 to 1189. He was one of the strongest of William’s descendants. He married Eleanor of Aquitaine, who had been married to King Louis VII of France. From this marriage ...
Feudal Europe
... required knights to show loyalty to the nobles they served and to protect the weaker members of society. During his years as a squire he also trained long and hard to use a sword and ride a horse. His knight, Sir Robert, recently let him join him on one of his missions. The two of them set out to ca ...
... required knights to show loyalty to the nobles they served and to protect the weaker members of society. During his years as a squire he also trained long and hard to use a sword and ride a horse. His knight, Sir Robert, recently let him join him on one of his missions. The two of them set out to ca ...
c. STOPPED AT THE BATTLE OF TOURS BY CHARLES MARTEL
... 1. FEUDALISM GOVERNMENTAL FORM WHICH DEVELOPED IN RESPONSE TO INVASION ...
... 1. FEUDALISM GOVERNMENTAL FORM WHICH DEVELOPED IN RESPONSE TO INVASION ...
ROUGHLY EDITED COPY CHURCH HISTORY 02 May 27, 2005 12
... The whole issue, however, pointed out two things. First of all, that the Medieval Popes were going to try to exercise greater control than bishops of Rome had in previous centuries, and it also shows the extent to which papal power and secular power became intertwined and were often at odds with eac ...
... The whole issue, however, pointed out two things. First of all, that the Medieval Popes were going to try to exercise greater control than bishops of Rome had in previous centuries, and it also shows the extent to which papal power and secular power became intertwined and were often at odds with eac ...
this file
... The idea that they thought it was flat was invented by an American journalist by the name of Washington Irving. In 1828, he wrote a biography of Columbus in which he described the great man confronting the Church leaders who accused him of heresy for claiming the earth was round when the Church taug ...
... The idea that they thought it was flat was invented by an American journalist by the name of Washington Irving. In 1828, he wrote a biography of Columbus in which he described the great man confronting the Church leaders who accused him of heresy for claiming the earth was round when the Church taug ...
Social Studies 8 Final Exam Review- History Section
... Use this guide to help you study and be successful for the exam. ...
... Use this guide to help you study and be successful for the exam. ...
File
... The First and Second Crusades • Pope promises Crusaders who die a place in heaven • First Crusade: three armies gather at Constantinople in 1097 • Crusaders capture Jerusalem in 1099 • Captured lands along coast divided into four Crusader states • Muslims take back Edessa in 1144; Second Crusade fai ...
... The First and Second Crusades • Pope promises Crusaders who die a place in heaven • First Crusade: three armies gather at Constantinople in 1097 • Crusaders capture Jerusalem in 1099 • Captured lands along coast divided into four Crusader states • Muslims take back Edessa in 1144; Second Crusade fai ...
PowerPoint Notes
... The First and Second Crusades • Pope promises Crusaders who die a place in heaven • First Crusade: three armies gather at Constantinople in 1097 • Crusaders capture Jerusalem in 1099 • Captured lands along coast divided into four Crusader states • Muslims take back Edessa in 1144; Second Crusade fai ...
... The First and Second Crusades • Pope promises Crusaders who die a place in heaven • First Crusade: three armies gather at Constantinople in 1097 • Crusaders capture Jerusalem in 1099 • Captured lands along coast divided into four Crusader states • Muslims take back Edessa in 1144; Second Crusade fai ...
Chapter 9 - Homestead
... census taken, which resulted in what was called the Domesday Book. This helped him know more about his kingdom and it helped him to build a better system of collecting taxes. Over the next 300 years, blending of Norman French and Anglo-Saxon customs, languages and traditions occurred. Increasing roy ...
... census taken, which resulted in what was called the Domesday Book. This helped him know more about his kingdom and it helped him to build a better system of collecting taxes. Over the next 300 years, blending of Norman French and Anglo-Saxon customs, languages and traditions occurred. Increasing roy ...
Continued - MMAMrClementiWiki
... The First and Second Crusades • Pope promises Crusaders who die a place in heaven • First Crusade: three armies gather at Constantinople in 1097 • Crusaders capture Jerusalem in 1099 • Captured lands along coast divided into four Crusader states • Muslims take back Edessa in 1144; Second Crusade fai ...
... The First and Second Crusades • Pope promises Crusaders who die a place in heaven • First Crusade: three armies gather at Constantinople in 1097 • Crusaders capture Jerusalem in 1099 • Captured lands along coast divided into four Crusader states • Muslims take back Edessa in 1144; Second Crusade fai ...
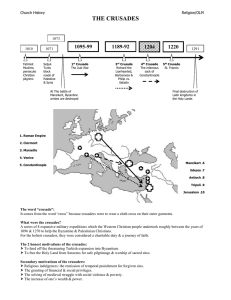
THE CRUSADES
... Godfrey of Bouillon, the first king of Jerusalem; Richard the Lionhearted, king of England; Barbarossa, king of Germany; and Philip, king of France. Alexis, emperor of Byzantium, who feared the crusades as much as he needed them. Pope Innocent III who condemned the 4 th crusade. ...
... Godfrey of Bouillon, the first king of Jerusalem; Richard the Lionhearted, king of England; Barbarossa, king of Germany; and Philip, king of France. Alexis, emperor of Byzantium, who feared the crusades as much as he needed them. Pope Innocent III who condemned the 4 th crusade. ...
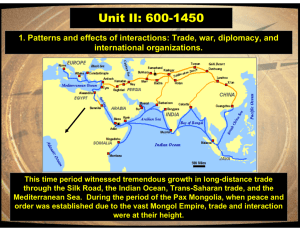
Unit II: 600-1450 international organizations.
... bureaucracy in the image of the Chinese Confucian model. Emissaries and scholars were sent to China to study. The Rise of Feudalism: Eventually a system of feudalism developed in which a central figure, the Shogun, reigned as supreme military general and political authority over Japan. The power of ...
... bureaucracy in the image of the Chinese Confucian model. Emissaries and scholars were sent to China to study. The Rise of Feudalism: Eventually a system of feudalism developed in which a central figure, the Shogun, reigned as supreme military general and political authority over Japan. The power of ...
Village Life
... 1. What types of foods were eaten during the Middle Ages? 2. Were the types of foods determined by whether the people were rich or poor? 3. How did the people get their food? 4. How was food prepared? Give examples of each. 6. What types of seasonings were used? Was there a reason for the use of cer ...
... 1. What types of foods were eaten during the Middle Ages? 2. Were the types of foods determined by whether the people were rich or poor? 3. How did the people get their food? 4. How was food prepared? Give examples of each. 6. What types of seasonings were used? Was there a reason for the use of cer ...
Document
... agricultural production. He discussed proportional tax on produce instead of is one of the most important figures in the late middle ages in Europe. (1) The greatest poem of the European middle ages Dante's fixed taxes on property as being superior as an incentive to bring more land Divine Comedy ...
... agricultural production. He discussed proportional tax on produce instead of is one of the most important figures in the late middle ages in Europe. (1) The greatest poem of the European middle ages Dante's fixed taxes on property as being superior as an incentive to bring more land Divine Comedy ...
End of Middle Ages worksheet
... New weapons: English longbow (better than old cross bow). Knights were easy targets – clumsy when off horse. Guns/cannons gave foot soldiers an advantage over traditional knight (who was becoming obsolete) How did the 100 years War change the role of the King? More power shifted from Lord to King. F ...
... New weapons: English longbow (better than old cross bow). Knights were easy targets – clumsy when off horse. Guns/cannons gave foot soldiers an advantage over traditional knight (who was becoming obsolete) How did the 100 years War change the role of the King? More power shifted from Lord to King. F ...
High Middle Ages - Marshall Community Schools
... • In 1054, the power struggle bubbled over when the Patriarch of Constantinople, Michael Cerularius, dared to condemn some of the religious practices of the Western Church. • He even went as far as to close down Eastern churches that followed the same practices. • Now these were fighting actions, an ...
... • In 1054, the power struggle bubbled over when the Patriarch of Constantinople, Michael Cerularius, dared to condemn some of the religious practices of the Western Church. • He even went as far as to close down Eastern churches that followed the same practices. • Now these were fighting actions, an ...
Powerpoint - WordPress.com
... enormous navy. They arrived at Constantinople in 1204, but not to fight Muslim invaders. Rather, the Venetians pillaged the city, killed Eastern Orthodox Christians, and set up a Latin Empire. The Children’s Crusade—Although the historical nature of this crusade has been debated, the legend goes t ...
... enormous navy. They arrived at Constantinople in 1204, but not to fight Muslim invaders. Rather, the Venetians pillaged the city, killed Eastern Orthodox Christians, and set up a Latin Empire. The Children’s Crusade—Although the historical nature of this crusade has been debated, the legend goes t ...
European Middle Ages - Loudoun County Public Schools
... Charlemagne Takes Center Stage Charlemagne built an empire greater than any known since ancient Rome. Each summer Charlemagne led his armies against the enemies that surrounded his kingdom. He fought the Muslims in Spain and tribes from other Germanic kingdoms. Charlemagne conquered new lands to bot ...
... Charlemagne Takes Center Stage Charlemagne built an empire greater than any known since ancient Rome. Each summer Charlemagne led his armies against the enemies that surrounded his kingdom. He fought the Muslims in Spain and tribes from other Germanic kingdoms. Charlemagne conquered new lands to bot ...
The Middle-Ages, 1066-1485, The Tales They Told
... The Crusades: Bloodbath over the Holy Land • In Chaucer’s The Canterbury Tales we meet a knight who has fought in “heathen” places—along the Mediterranean Sea and in North Africa. The knight’s adventures in the fourteenth century were really an extension of the Crusades (1095-1270), a series of hol ...
... The Crusades: Bloodbath over the Holy Land • In Chaucer’s The Canterbury Tales we meet a knight who has fought in “heathen” places—along the Mediterranean Sea and in North Africa. The knight’s adventures in the fourteenth century were really an extension of the Crusades (1095-1270), a series of hol ...
Chapter 11: The Later Middle Ages ~ Study Guide
... c. it illustrates the highly religious interests of most people. d. it shows how people were obsessed with the next world. ...
... c. it illustrates the highly religious interests of most people. d. it shows how people were obsessed with the next world. ...
No Slide Title - Cloudfront.net
... The First and Second Crusades • Pope promises Crusaders who die a place in heaven • First Crusade: three armies gather at Constantinople in 1097 • Crusaders capture Jerusalem in 1099 • Captured lands along coast divided into four Crusader states • Muslims take back Edessa in 1144; Second Crusade fai ...
... The First and Second Crusades • Pope promises Crusaders who die a place in heaven • First Crusade: three armies gather at Constantinople in 1097 • Crusaders capture Jerusalem in 1099 • Captured lands along coast divided into four Crusader states • Muslims take back Edessa in 1144; Second Crusade fai ...
The Early Middle Ages: Germanic Kingdoms Unite
... • Gained support of the Church in Rome • United the Franks into one kingdom ...
... • Gained support of the Church in Rome • United the Franks into one kingdom ...
WHI: SOL 12a
... The Holy Roman Empire The Eastern part of Charlemagne’s Kingdom later became known as the Holy Roman Empire (later Germany). The territory was broken into divisions known as duchies ruled by dukes. These dukes elected a king, ...
... The Holy Roman Empire The Eastern part of Charlemagne’s Kingdom later became known as the Holy Roman Empire (later Germany). The territory was broken into divisions known as duchies ruled by dukes. These dukes elected a king, ...
High Middle Ages

The High Middle Ages or High Medieval Period was the period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries (c. 1001–1300). The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which by convention end around 1500.The key historical trend of the High Middle Ages was the rapidly increasing population of Europe, which brought about great social and political change from the preceding era, the Renaissance of the 12th century, including the first developments of rural exodus and urbanization. By 1250 the robust population increase greatly benefited the European economy, reaching levels it would not see again in some areas until the 19th century. This trend was checked in the Late Middle Ages by a series of calamities, notably the Black Death but also including numerous wars and economic stagnation.From about the year 780 onwards, Europe saw the last of the barbarian invasions and became more socially and politically organized. The Carolingian Renaissance led to scientific and philosophical revival of Europe. The first universities were established in Bologna, Paris, Oxford and Modena. The Vikings had settled in the British Isles, France and elsewhere, whilst Norse Christian kingdoms were developing in their Scandinavian homelands. The Magyars had ceased their expansion in the 10th century, and by the year 1000, a Christian Kingdom of Hungary was recognized in central Europe, forming alliances with regional powers. With the brief exception of the Mongol invasions in the 13th century, major nomadic incursions ceased. The powerful Byzantine Empire of the Macedonian and Komnenos dynasties gradually gave way to resurrected Serbia and Bulgaria and to a successor Crusade state from 1204 to 1261, while countering the continuous threat of the Seljuk Turks in Asia Minor.In the 11th century, populations north of the Alps began to settle new lands, some of which had reverted to wilderness after the end of the Roman Empire. In what is known as the ""great clearances"", vast forests and marshes of Europe were cleared and cultivated. At the same time settlements moved beyond the traditional boundaries of the Frankish Empire to new frontiers in Europe, beyond the Elbe River, tripling the size of Germany in the process. The Catholic Church, reaching the peak of its political power at this time, called armies from across Europe to a series of Crusades against the Seljuk Turks, who occupied the Holy Land, thereby founding the Crusader States in the Levant. Other wars led to the Northern Crusades, while Christian kingdoms conquered the Iberian Peninsula from the Moors, and the Normans colonized southern Italy, all part of the major population increase and resettlement pattern of the era.The High Middle Ages produced many different forms of intellectual, spiritual and artistic works. This age saw the rise of ethnocentrism, which evolved later into modern civic nationalisms in most of Europe, the ascent of the great Italian city-states, and the rise and fall of the Muslim civilization of Al-Andalus. The rediscovery of the works of Aristotle led Thomas Aquinas and other thinkers of the period to develop Scholasticism, a combination of Catholicism and ancient philosophy. For much of the time period Constantinople remained Europe's most populous city and Byzantine art reached a peak in the 12th century. In architecture, many of the most notable Gothic cathedrals were built or completed during this era.The Crisis of the Late Middle Ages, beginning at the start of the 14th century, marked the end of this era.