Offensive Against Islam
... • Spain and Siciliy ‐ only areas where military campaign was successful ...
... • Spain and Siciliy ‐ only areas where military campaign was successful ...
The Birth of France & Germany
... • As the Carolingian Empire eroded into memory; Various local aristocrats began to seize local power forming small familial dynasties; • This dissolution of Carolingian power is known as Devolution. Power in the hands of the Counts not Carolingian Rulers; everyday power now held at lower level; • We ...
... • As the Carolingian Empire eroded into memory; Various local aristocrats began to seize local power forming small familial dynasties; • This dissolution of Carolingian power is known as Devolution. Power in the hands of the Counts not Carolingian Rulers; everyday power now held at lower level; • We ...
The Renaissance Period in the European Culture
... place in Spain, France, and England. The process was aided by modern diplomacy, which took its place beside the new warfare when the Italian city-states established resident embassies at foreign courts. By the 16th century, the institution of permanent embassies spread northwards to France, England, ...
... place in Spain, France, and England. The process was aided by modern diplomacy, which took its place beside the new warfare when the Italian city-states established resident embassies at foreign courts. By the 16th century, the institution of permanent embassies spread northwards to France, England, ...
Rational - HistoryMethods
... Empire of the West. The Church, which had become a branch of the Roman imperial government in the course of the 300's, survived the collapse of the political and military of the Roman Empire in the West. It tried to preserve Roman imperial institutions and principles to the point where local bishops ...
... Empire of the West. The Church, which had become a branch of the Roman imperial government in the course of the 300's, survived the collapse of the political and military of the Roman Empire in the West. It tried to preserve Roman imperial institutions and principles to the point where local bishops ...
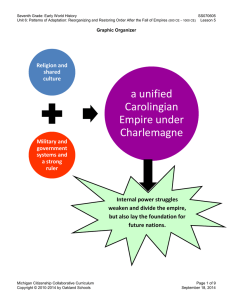
Student Handout #1 - The Carolingian Empire and Charlemagne
... At the end of Charlemagne’s rule, different members of his family were given power over different parts of the empire. The Carolingians, as you may have noted, believed that power and control of land should be inherited from father to son (along with certain names like Pepin and Charles!). This caus ...
... At the end of Charlemagne’s rule, different members of his family were given power over different parts of the empire. The Carolingians, as you may have noted, believed that power and control of land should be inherited from father to son (along with certain names like Pepin and Charles!). This caus ...
Daniel Hawkins Literature Review
... Franks, Umayyads, and the Most Important Early Medieval Battle: Scholarship on the Battle of Tours In the early Middle Ages, the political centralization and military ascendancy of the Franks—first under the Merovingians and then under the Carolingians— made them the largest and most powerful Christ ...
... Franks, Umayyads, and the Most Important Early Medieval Battle: Scholarship on the Battle of Tours In the early Middle Ages, the political centralization and military ascendancy of the Franks—first under the Merovingians and then under the Carolingians— made them the largest and most powerful Christ ...
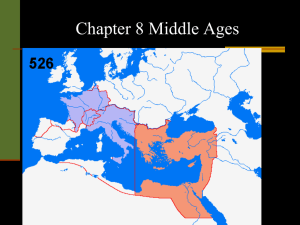
Germanic Kingdoms Unite Under Charlemagne
... You’ll recall that when we last left the Roman Empire, it was in decline, spurred largely by the barbarian Germanic tribes that were invading the empire. • By the beginning of the sixth century, the damage was pretty much done and the western Roman Empire was ...
... You’ll recall that when we last left the Roman Empire, it was in decline, spurred largely by the barbarian Germanic tribes that were invading the empire. • By the beginning of the sixth century, the damage was pretty much done and the western Roman Empire was ...
The Roman Empire - Carson
... the Caspian Sea and Constantinople on the Black Sea. By about 875, landing in England some Vikings continued to raid, but others were ready to settle down. A group of Danish Vikings, called Normans, settled on the coast of France. With William the Conqueror as their leader, they attacked and defeate ...
... the Caspian Sea and Constantinople on the Black Sea. By about 875, landing in England some Vikings continued to raid, but others were ready to settle down. A group of Danish Vikings, called Normans, settled on the coast of France. With William the Conqueror as their leader, they attacked and defeate ...
All material in this program is the exclusive
... Life in the British Isles around the year 1100 was stunningly different from the high-tech, post-industrial culture of today. Society was organized according to the principles of feudalism. Economic activity was almost exclusively agricultural and feudal manors tended to be self-sufficient. There wa ...
... Life in the British Isles around the year 1100 was stunningly different from the high-tech, post-industrial culture of today. Society was organized according to the principles of feudalism. Economic activity was almost exclusively agricultural and feudal manors tended to be self-sufficient. There wa ...
The Middle Ages to 1800
... The Middle Ages to 1800 Medieval Theatre: For approximately 400 years there was no theatre, except for sparse folk festivals and a few wandering jugglers and minstrels, or wandering bands of tribes. The Church buried drama in the 5th century resurrected that same art sometime during the 9th cent ...
... The Middle Ages to 1800 Medieval Theatre: For approximately 400 years there was no theatre, except for sparse folk festivals and a few wandering jugglers and minstrels, or wandering bands of tribes. The Church buried drama in the 5th century resurrected that same art sometime during the 9th cent ...
A Time to Review Post-Classical Civilizations WHAP/Napp Islam
... Great literature, such as poetic works and The Arabian Nights, enriched Muslim culture Islamic mystics called Sufis focused on an emotional union with Allah and began missionary work to spread Islam Experienced a golden age Yet found their vast empire increasingly difficult to govern The d ...
... Great literature, such as poetic works and The Arabian Nights, enriched Muslim culture Islamic mystics called Sufis focused on an emotional union with Allah and began missionary work to spread Islam Experienced a golden age Yet found their vast empire increasingly difficult to govern The d ...
The Feudal System: Castles at War
... 1. After watching the video, review with students when the Middle Ages began and how long it lasted. (The Middle Ages began when the Western Roman empire fell in the 5th century and faded as the Renaissance took hold across Europe in the 13th, 14th, and 15th centuries.) What was medieval Europe like ...
... 1. After watching the video, review with students when the Middle Ages began and how long it lasted. (The Middle Ages began when the Western Roman empire fell in the 5th century and faded as the Renaissance took hold across Europe in the 13th, 14th, and 15th centuries.) What was medieval Europe like ...
Chivalry - White Plains Public Schools
... Europe in a fragmented state for centuries. Through warfare, feudal lords defended their estates, seized new territories, and increased their wealth. Lords and their armies lived in a violent society that prized combat skills. By the 1100s, though, a code of behavior began to arise. High ideals guid ...
... Europe in a fragmented state for centuries. Through warfare, feudal lords defended their estates, seized new territories, and increased their wealth. Lords and their armies lived in a violent society that prized combat skills. By the 1100s, though, a code of behavior began to arise. High ideals guid ...
power point for the middle ages - Humble Independent School District
... Let your mind drift back in time to a time before organized government, A time when ...
... Let your mind drift back in time to a time before organized government, A time when ...
Middle Ages 8
... extensively in England as the punishment for traitors. The condemned was hanged till they were half dead, and then taken down, and quartered alive. After that, their members and bowels were cut from their bodies, and thrown into a fire, while they were still alive. They would finally be killed by de ...
... extensively in England as the punishment for traitors. The condemned was hanged till they were half dead, and then taken down, and quartered alive. After that, their members and bowels were cut from their bodies, and thrown into a fire, while they were still alive. They would finally be killed by de ...
debate
... the land, with the latter being tied to the land, although many varieties of arrangements existed. The chapter analyses the causes of the rise of manorial organisation and its decline in the twelfth to fourteenth centuries. In coastal regions like coastal Flanders or Holland, occupation and reclamat ...
... the land, with the latter being tied to the land, although many varieties of arrangements existed. The chapter analyses the causes of the rise of manorial organisation and its decline in the twelfth to fourteenth centuries. In coastal regions like coastal Flanders or Holland, occupation and reclamat ...
STATION 1 - Georgetown ISD
... Social Classes in the Renaissance Within Renaissance city states like Florence, competition among different social classes was intense. There were four major social groups in Florence, which is relatively representative of other city-states in Italy at the time. Those social classes included: 1. The ...
... Social Classes in the Renaissance Within Renaissance city states like Florence, competition among different social classes was intense. There were four major social groups in Florence, which is relatively representative of other city-states in Italy at the time. Those social classes included: 1. The ...
The Renaissance—Life in Florence
... Social Classes in the Renaissance Within Renaissance city states like Florence, competition among different social classes was intense. There were four major social groups in Florence, which is relatively representative of other city-states in Italy at the time. Those social classes included: 1. The ...
... Social Classes in the Renaissance Within Renaissance city states like Florence, competition among different social classes was intense. There were four major social groups in Florence, which is relatively representative of other city-states in Italy at the time. Those social classes included: 1. The ...
The Great Schism - arcofhistory.org
... Still, the Eastern church didn't mind--as long as the pope claimed absolute power only in the West. Nicholas I was a reforming pope, with an exalted idea--at least according to the Orthodox--of the prerogatives of his office. He believed his absolute power extended to the East. As he put it in a let ...
... Still, the Eastern church didn't mind--as long as the pope claimed absolute power only in the West. Nicholas I was a reforming pope, with an exalted idea--at least according to the Orthodox--of the prerogatives of his office. He believed his absolute power extended to the East. As he put it in a let ...
File
... King Clovis won this battle—and many others. The kingdom he established was one of many Germanic kingdoms that replaced the unifying force of the Roman empire in Western Europe. ...
... King Clovis won this battle—and many others. The kingdom he established was one of many Germanic kingdoms that replaced the unifying force of the Roman empire in Western Europe. ...
Works Cited - mariakmuseum
... This bronze sculpture was made in Aachen (Aix-la-Chapelle) around 1155 to 1171. It is of Frederick I, known as Barbarossa. Barbarossa was a Holy Roman emperor who spent decades in the 12th century battling in the third crusade. Frederick died before reaching the Holy Lands, after his death, his troo ...
... This bronze sculpture was made in Aachen (Aix-la-Chapelle) around 1155 to 1171. It is of Frederick I, known as Barbarossa. Barbarossa was a Holy Roman emperor who spent decades in the 12th century battling in the third crusade. Frederick died before reaching the Holy Lands, after his death, his troo ...
Chapter 7 Section 1
... King Clovis won this battle—and many others. The kingdom he established was one of many Germanic kingdoms that replaced the unifying force of the Roman empire in Western Europe. ...
... King Clovis won this battle—and many others. The kingdom he established was one of many Germanic kingdoms that replaced the unifying force of the Roman empire in Western Europe. ...
High Middle Ages

The High Middle Ages or High Medieval Period was the period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries (c. 1001–1300). The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which by convention end around 1500.The key historical trend of the High Middle Ages was the rapidly increasing population of Europe, which brought about great social and political change from the preceding era, the Renaissance of the 12th century, including the first developments of rural exodus and urbanization. By 1250 the robust population increase greatly benefited the European economy, reaching levels it would not see again in some areas until the 19th century. This trend was checked in the Late Middle Ages by a series of calamities, notably the Black Death but also including numerous wars and economic stagnation.From about the year 780 onwards, Europe saw the last of the barbarian invasions and became more socially and politically organized. The Carolingian Renaissance led to scientific and philosophical revival of Europe. The first universities were established in Bologna, Paris, Oxford and Modena. The Vikings had settled in the British Isles, France and elsewhere, whilst Norse Christian kingdoms were developing in their Scandinavian homelands. The Magyars had ceased their expansion in the 10th century, and by the year 1000, a Christian Kingdom of Hungary was recognized in central Europe, forming alliances with regional powers. With the brief exception of the Mongol invasions in the 13th century, major nomadic incursions ceased. The powerful Byzantine Empire of the Macedonian and Komnenos dynasties gradually gave way to resurrected Serbia and Bulgaria and to a successor Crusade state from 1204 to 1261, while countering the continuous threat of the Seljuk Turks in Asia Minor.In the 11th century, populations north of the Alps began to settle new lands, some of which had reverted to wilderness after the end of the Roman Empire. In what is known as the ""great clearances"", vast forests and marshes of Europe were cleared and cultivated. At the same time settlements moved beyond the traditional boundaries of the Frankish Empire to new frontiers in Europe, beyond the Elbe River, tripling the size of Germany in the process. The Catholic Church, reaching the peak of its political power at this time, called armies from across Europe to a series of Crusades against the Seljuk Turks, who occupied the Holy Land, thereby founding the Crusader States in the Levant. Other wars led to the Northern Crusades, while Christian kingdoms conquered the Iberian Peninsula from the Moors, and the Normans colonized southern Italy, all part of the major population increase and resettlement pattern of the era.The High Middle Ages produced many different forms of intellectual, spiritual and artistic works. This age saw the rise of ethnocentrism, which evolved later into modern civic nationalisms in most of Europe, the ascent of the great Italian city-states, and the rise and fall of the Muslim civilization of Al-Andalus. The rediscovery of the works of Aristotle led Thomas Aquinas and other thinkers of the period to develop Scholasticism, a combination of Catholicism and ancient philosophy. For much of the time period Constantinople remained Europe's most populous city and Byzantine art reached a peak in the 12th century. In architecture, many of the most notable Gothic cathedrals were built or completed during this era.The Crisis of the Late Middle Ages, beginning at the start of the 14th century, marked the end of this era.