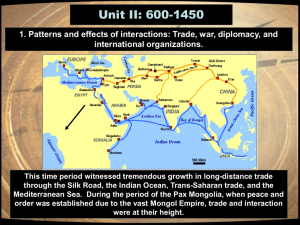
On Commerce, Institutions, and Underdevelopment: A
... on the services of a bureaucracy that was drawn from eunuchs, ex-slaves, and free soldiers not controlled by aristocracy.1 The Middle East is the region where “states” as political entities were born for the first time. From earlier periods, these states were modeled as “just and benevolent”; as suc ...
... on the services of a bureaucracy that was drawn from eunuchs, ex-slaves, and free soldiers not controlled by aristocracy.1 The Middle East is the region where “states” as political entities were born for the first time. From earlier periods, these states were modeled as “just and benevolent”; as suc ...
Activity Master 19 Extension 1: The Church in the
... the Short, was crowned King of the Franks in 751 by Saint Boniface—the same Boniface who had converted the Germans. Thus began the Carolingian dynasty. Since Boniface was acting as the pope’s representative, Pepin rewarded Pope Stephen III five years later by declaring him to be ruler of the middle ...
... the Short, was crowned King of the Franks in 751 by Saint Boniface—the same Boniface who had converted the Germans. Thus began the Carolingian dynasty. Since Boniface was acting as the pope’s representative, Pepin rewarded Pope Stephen III five years later by declaring him to be ruler of the middle ...
Germanic and Medieval Europe
... The rulers that followed Henry were not as strong as he his sons--Richard I and John • John looses English land to the French • John does many things that anger the people--raising taxes • 1215--the angry English force John to sign the Magna Carta • the Magna Carta was a charter that placed limits o ...
... The rulers that followed Henry were not as strong as he his sons--Richard I and John • John looses English land to the French • John does many things that anger the people--raising taxes • 1215--the angry English force John to sign the Magna Carta • the Magna Carta was a charter that placed limits o ...
“Deus le vault!” – “God wills it!” The First Crusade (1096
... First Crusade (1095-1099) Children’s Crusade (1212-1213) Second Crusade (1145-1148) Fifth Crusade (1217-1221) Third Crusade (1187–1192) Sixth Crusade (1228-1229) Fourth Crusade (1202-1204) Seventh Crusade (1248-1254) Albigensian Crusade (1209-1229) Eighth Crusade (1267-1270) Ninth Crusade (1271-1272 ...
... First Crusade (1095-1099) Children’s Crusade (1212-1213) Second Crusade (1145-1148) Fifth Crusade (1217-1221) Third Crusade (1187–1192) Sixth Crusade (1228-1229) Fourth Crusade (1202-1204) Seventh Crusade (1248-1254) Albigensian Crusade (1209-1229) Eighth Crusade (1267-1270) Ninth Crusade (1271-1272 ...
Version #1 - mrfarshtey.net
... and commerce. Under Abbasid rule, Baghdad became a city of museums, hospitals, libraries, and mosques. • Baghdad was one of the largest and most cosmopolitan cities in the world, home to Muslims, Christians, Jews and pagans from across the Middle East and Central Asia. ...
... and commerce. Under Abbasid rule, Baghdad became a city of museums, hospitals, libraries, and mosques. • Baghdad was one of the largest and most cosmopolitan cities in the world, home to Muslims, Christians, Jews and pagans from across the Middle East and Central Asia. ...
Chapter 27: Rise of Monarchies - Bellbrook
... SECTION 3 The Hundred Years’ War In the early 1300s, the English still held a small part of southwest France. The kings of France, who were growing more powerful, wanted to drive the English out. In 1337, the English king, Edward III, declared himself king of France. This angered the French even mo ...
... SECTION 3 The Hundred Years’ War In the early 1300s, the English still held a small part of southwest France. The kings of France, who were growing more powerful, wanted to drive the English out. In 1337, the English king, Edward III, declared himself king of France. This angered the French even mo ...
Chapter 27: The Rise of Monarchies
... SECTION 3 The Hundred Years’ War In the early 1300s, the English still held a small part of southwest France. The kings of France, who were growing more powerful, wanted to drive the English out. In 1337, the English king, Edward III, declared himself king of France. This angered the French even mo ...
... SECTION 3 The Hundred Years’ War In the early 1300s, the English still held a small part of southwest France. The kings of France, who were growing more powerful, wanted to drive the English out. In 1337, the English king, Edward III, declared himself king of France. This angered the French even mo ...
ISLAM Muhammad (570-632)
... Saint market days and holidays grew locally at first with the consecration of local bishops but about 1200 only the Pope in the West could decide who was “regarded” as a saint. ...
... Saint market days and holidays grew locally at first with the consecration of local bishops but about 1200 only the Pope in the West could decide who was “regarded” as a saint. ...
ENG literature - medieval drama
... into place. Next, the Gospel dialogue between the angel and the three Marys at the tomb of Christ was sometimes chanted by the choir in those responses which are called "tropes": Whom seek ye in the sepulcher, O Christians? Jesus of Nazareth the crucified, O angel. He is not here; he has arisen as h ...
... into place. Next, the Gospel dialogue between the angel and the three Marys at the tomb of Christ was sometimes chanted by the choir in those responses which are called "tropes": Whom seek ye in the sepulcher, O Christians? Jesus of Nazareth the crucified, O angel. He is not here; he has arisen as h ...
File - History with Halkuff
... Romans and established a kingdom centered in Paris. Clovis was a Frank, one of the many Germanic tribes that lived in Western Europe in the fifth century. Clovis worshipped pagan gods, in fact, his people believed Clovis to be the descendent of Wotan, the most powerful of the Frankish gods. In 496, ...
... Romans and established a kingdom centered in Paris. Clovis was a Frank, one of the many Germanic tribes that lived in Western Europe in the fifth century. Clovis worshipped pagan gods, in fact, his people believed Clovis to be the descendent of Wotan, the most powerful of the Frankish gods. In 496, ...
Medieval Theatre
... Mainland Europe (except Spain and parts of Italy) Mansions set up in available spaces (courtyards, town squares, etc.), usually arranged in straight lines or rectangles or circles, depending on the space. Heaven and Hell were at opposite ends, if possible. ...
... Mainland Europe (except Spain and parts of Italy) Mansions set up in available spaces (courtyards, town squares, etc.), usually arranged in straight lines or rectangles or circles, depending on the space. Heaven and Hell were at opposite ends, if possible. ...
The Middle Ages - The Heritage School
... The years 500 to 1000 AD are known as the tough times or the Dark Ages. During this time Vikings were invading much of Europe. Tribal disputes were causing constant war. Pagan worshipping was common place. Only the monks in the monasteries kept learning alive. During the Early Middle Ages Charlemagn ...
... The years 500 to 1000 AD are known as the tough times or the Dark Ages. During this time Vikings were invading much of Europe. Tribal disputes were causing constant war. Pagan worshipping was common place. Only the monks in the monasteries kept learning alive. During the Early Middle Ages Charlemagn ...
Hst 101: Western Civilization
... Baccalaureate Core Course. Provides an awareness and understanding of the Western cultural heritage. Stresses the major ideas and developments that have been of primary importance in shaping the Western tradition. Covers the Ancient World to 1000 A.D. HST 101, HST 102 and HST 103 need not be taken i ...
... Baccalaureate Core Course. Provides an awareness and understanding of the Western cultural heritage. Stresses the major ideas and developments that have been of primary importance in shaping the Western tradition. Covers the Ancient World to 1000 A.D. HST 101, HST 102 and HST 103 need not be taken i ...
DBQ blank.notebook
... crusaders proclaimed a Latin empire of Constantinople with its emperor as patriarch. The Byzantine government went into exile in Nicaea and continued to fight the Latin occupiers until 1261, when they recaptured their capital. After the 4th Crusade, crusading lost much of its appeal for most Eur ...
... crusaders proclaimed a Latin empire of Constantinople with its emperor as patriarch. The Byzantine government went into exile in Nicaea and continued to fight the Latin occupiers until 1261, when they recaptured their capital. After the 4th Crusade, crusading lost much of its appeal for most Eur ...
Global History Final Review Pascale Dugue Early Peoples and
... Sparta-–“Nation of Soldiers” Spartans developed a system of strict control over their citizens From childhood a Spartan prepared to be part of a military state Girls were included in this Rigorous upbringing Spartans –Decline of City-State Spartan isolated themselves looking down on trade and wealth ...
... Sparta-–“Nation of Soldiers” Spartans developed a system of strict control over their citizens From childhood a Spartan prepared to be part of a military state Girls were included in this Rigorous upbringing Spartans –Decline of City-State Spartan isolated themselves looking down on trade and wealth ...
middle-ages-germanic-kingdoms
... Historians argue that if the Christians had lost, Muslims could have taken over Europe Charles was a Christian hero; Christianity wins At his death, he passed his power to Pepin the Short (not necessarily short) Pope anoints Pepin “King by the grace of God,” thus beginning the Carolingian Dynasty- f ...
... Historians argue that if the Christians had lost, Muslims could have taken over Europe Charles was a Christian hero; Christianity wins At his death, he passed his power to Pepin the Short (not necessarily short) Pope anoints Pepin “King by the grace of God,” thus beginning the Carolingian Dynasty- f ...
The Middle Ages
... • In the Fourth Crusade, crusaders got sidetracked and greedy on their way to the Holy Land and ended up conquering and plundering Constantinople, the Christian city they had originally come to protect! (Schism Timeline) • For the next 68 years, four more crusades were fought, but the Holy Land rema ...
... • In the Fourth Crusade, crusaders got sidetracked and greedy on their way to the Holy Land and ended up conquering and plundering Constantinople, the Christian city they had originally come to protect! (Schism Timeline) • For the next 68 years, four more crusades were fought, but the Holy Land rema ...
Chapter 10, Lesson 2 Feudalism and the Rise of Towns
... • Law and order disappeared in many places • Most people spent their entire short lives in the village where they were born ...
... • Law and order disappeared in many places • Most people spent their entire short lives in the village where they were born ...
Europe in the High Middle Ages
... German states on the European continent was the kingdom of the Franks. The establishment of a Frankish kingdom was the work of Clovis (KLOH-viss) (c. 482–511), a member of the Merovingian (meh-ruh-VIN-jee-un) dynasty who became a Catholic Christian around 500. He was not the first German king to conv ...
... German states on the European continent was the kingdom of the Franks. The establishment of a Frankish kingdom was the work of Clovis (KLOH-viss) (c. 482–511), a member of the Merovingian (meh-ruh-VIN-jee-un) dynasty who became a Catholic Christian around 500. He was not the first German king to conv ...
England in the Middle Ages
... strengthened the army.[8] These reforms bought the Empire time, but they demanded money. Roman power had been maintained by its well-trained and equipped armies. These armies, however, were a constant drain on the Empire's finances. As warfare became more dependent on heavy cavalry, the infantry-bas ...
... strengthened the army.[8] These reforms bought the Empire time, but they demanded money. Roman power had been maintained by its well-trained and equipped armies. These armies, however, were a constant drain on the Empire's finances. As warfare became more dependent on heavy cavalry, the infantry-bas ...
A Short History of Europe: From Charlemagne to the Treaty of Lisbon
... Charles the Bald, paid them off. Unfortunately for him, and the terrified people of his kingdom, th raids continued. Charles ordered every settlement to prepare itself with defences, fortifications an troops but it was to no avail and, when 40,000 Vikings laid siege to Paris itself, Charles was forc ...
... Charles the Bald, paid them off. Unfortunately for him, and the terrified people of his kingdom, th raids continued. Charles ordered every settlement to prepare itself with defences, fortifications an troops but it was to no avail and, when 40,000 Vikings laid siege to Paris itself, Charles was forc ...
Jeopardy - cloudfront.net
... 20 pts. During the European Schism, there were two popes. From which two countries were those popes from? France and Italy **What was one consequence of the European schism? A decline in the authority of the church 30 pts. What causes the Black Death? A bacteria carried in fleas on rats **In approxi ...
... 20 pts. During the European Schism, there were two popes. From which two countries were those popes from? France and Italy **What was one consequence of the European schism? A decline in the authority of the church 30 pts. What causes the Black Death? A bacteria carried in fleas on rats **In approxi ...
chapter 7 the end of the classical era world history in
... ancient intellectual world. Under Benedict of Nursia, western Christianity developed a formal monasticism in the sixth century C.E. Monasticism was also typical of eastern Christianity. The popular message of Christianity appealed to all social levels and provided some unity across class divisions. ...
... ancient intellectual world. Under Benedict of Nursia, western Christianity developed a formal monasticism in the sixth century C.E. Monasticism was also typical of eastern Christianity. The popular message of Christianity appealed to all social levels and provided some unity across class divisions. ...
`Europe was created by history.` Margaret Thatcher
... Charles the Bald, paid them off. Unfortunately for him, and the terrified people of his kingdom, the raids continued. Charles ordered every settlement to prepare itself with defences, fortifications and troops but it was to no avail and, when 40,000 Vikings laid siege to Paris itself, Charles was fo ...
... Charles the Bald, paid them off. Unfortunately for him, and the terrified people of his kingdom, the raids continued. Charles ordered every settlement to prepare itself with defences, fortifications and troops but it was to no avail and, when 40,000 Vikings laid siege to Paris itself, Charles was fo ...
High Middle Ages

The High Middle Ages or High Medieval Period was the period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries (c. 1001–1300). The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which by convention end around 1500.The key historical trend of the High Middle Ages was the rapidly increasing population of Europe, which brought about great social and political change from the preceding era, the Renaissance of the 12th century, including the first developments of rural exodus and urbanization. By 1250 the robust population increase greatly benefited the European economy, reaching levels it would not see again in some areas until the 19th century. This trend was checked in the Late Middle Ages by a series of calamities, notably the Black Death but also including numerous wars and economic stagnation.From about the year 780 onwards, Europe saw the last of the barbarian invasions and became more socially and politically organized. The Carolingian Renaissance led to scientific and philosophical revival of Europe. The first universities were established in Bologna, Paris, Oxford and Modena. The Vikings had settled in the British Isles, France and elsewhere, whilst Norse Christian kingdoms were developing in their Scandinavian homelands. The Magyars had ceased their expansion in the 10th century, and by the year 1000, a Christian Kingdom of Hungary was recognized in central Europe, forming alliances with regional powers. With the brief exception of the Mongol invasions in the 13th century, major nomadic incursions ceased. The powerful Byzantine Empire of the Macedonian and Komnenos dynasties gradually gave way to resurrected Serbia and Bulgaria and to a successor Crusade state from 1204 to 1261, while countering the continuous threat of the Seljuk Turks in Asia Minor.In the 11th century, populations north of the Alps began to settle new lands, some of which had reverted to wilderness after the end of the Roman Empire. In what is known as the ""great clearances"", vast forests and marshes of Europe were cleared and cultivated. At the same time settlements moved beyond the traditional boundaries of the Frankish Empire to new frontiers in Europe, beyond the Elbe River, tripling the size of Germany in the process. The Catholic Church, reaching the peak of its political power at this time, called armies from across Europe to a series of Crusades against the Seljuk Turks, who occupied the Holy Land, thereby founding the Crusader States in the Levant. Other wars led to the Northern Crusades, while Christian kingdoms conquered the Iberian Peninsula from the Moors, and the Normans colonized southern Italy, all part of the major population increase and resettlement pattern of the era.The High Middle Ages produced many different forms of intellectual, spiritual and artistic works. This age saw the rise of ethnocentrism, which evolved later into modern civic nationalisms in most of Europe, the ascent of the great Italian city-states, and the rise and fall of the Muslim civilization of Al-Andalus. The rediscovery of the works of Aristotle led Thomas Aquinas and other thinkers of the period to develop Scholasticism, a combination of Catholicism and ancient philosophy. For much of the time period Constantinople remained Europe's most populous city and Byzantine art reached a peak in the 12th century. In architecture, many of the most notable Gothic cathedrals were built or completed during this era.The Crisis of the Late Middle Ages, beginning at the start of the 14th century, marked the end of this era.