Ch02
... Need For Protocol Architecture • E.g. File transfer —Source must activate communication path or inform network of destination —Source must check destination is prepared to receive —File transfer application on source must check destination file management system will accept and store file for his u ...
... Need For Protocol Architecture • E.g. File transfer —Source must activate communication path or inform network of destination —Source must check destination is prepared to receive —File transfer application on source must check destination file management system will accept and store file for his u ...
LAN / WAN / Extranet และ Network Topology แบบต่าง ๆ
... Example: X.25 standard for network access procedures on packet-switching networks ...
... Example: X.25 standard for network access procedures on packet-switching networks ...
slides - TNC15
... When they had an opportunity move in the right direction with application names, they didn’t. They did DNS. When they had an opportunity to move in the right direction with node addresses, they didn’t. They did IPv6. More than Botched Network Management Botched the Congestion Control twice Once so b ...
... When they had an opportunity move in the right direction with application names, they didn’t. They did DNS. When they had an opportunity to move in the right direction with node addresses, they didn’t. They did IPv6. More than Botched Network Management Botched the Congestion Control twice Once so b ...
ICN lecture1 - OSI & TCP_IP
... Agreed rules form the basis of harmonious data exchange between network nodes. These rules are referred to as protocols in the telecoms world. All telecommunications technologies are underpinned by protocols that should be recognised internationally managed by established standards bodies. A protoco ...
... Agreed rules form the basis of harmonious data exchange between network nodes. These rules are referred to as protocols in the telecoms world. All telecommunications technologies are underpinned by protocols that should be recognised internationally managed by established standards bodies. A protoco ...
Introduction - Department of Information Technologies
... structure of networks and how they operate. At the end of this course a student should be able to: Explain basic networking concepts by studying client/server architecture, network scalability, geographical scope, the Internet, intranets and extranets. Identify, describe and give examples of the net ...
... structure of networks and how they operate. At the end of this course a student should be able to: Explain basic networking concepts by studying client/server architecture, network scalability, geographical scope, the Internet, intranets and extranets. Identify, describe and give examples of the net ...
Protocol Suites - York Technical College
... TCP/IP - Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol ...
... TCP/IP - Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol ...
TCP
... • The layer boundaries should be chosen to minimise the information flow across the interfaces; • The number of layers should be large enough that distinct functions need not be thrown together in the same layer out of necessity, and small enough that the architecture does not become unwieldy. ...
... • The layer boundaries should be chosen to minimise the information flow across the interfaces; • The number of layers should be large enough that distinct functions need not be thrown together in the same layer out of necessity, and small enough that the architecture does not become unwieldy. ...
Chapter 10
... Transport layer divides stream into packets Can optimize transfer if knows largest packet size that will fit in one frame If strict layering is used, transport layer will not know the datagram or frame formats, or number of header ...
... Transport layer divides stream into packets Can optimize transfer if knows largest packet size that will fit in one frame If strict layering is used, transport layer will not know the datagram or frame formats, or number of header ...
VB Lecture 1 - American University of Beirut
... In this visionary paper, the authors described how the spread of programs and information among a large number of computers connected by a universal network would create a system more powerful than could be built by any organization. ...
... In this visionary paper, the authors described how the spread of programs and information among a large number of computers connected by a universal network would create a system more powerful than could be built by any organization. ...
PowerPoint format - Computer Science
... • IP (Internet Protocol): focal point of the architecture, provides host-to-host connection, defines common methods of exchanging packets • TCP (transmission Control Protocol): reliable, in-order stream ...
... • IP (Internet Protocol): focal point of the architecture, provides host-to-host connection, defines common methods of exchanging packets • TCP (transmission Control Protocol): reliable, in-order stream ...
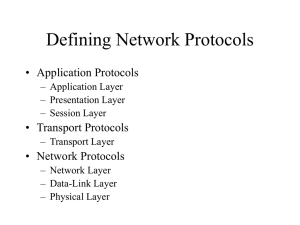
Defining Network Protocols
... arp -a or multi show/arp only local (router port) addresses shown ARP entries have a finite (timed) lifetime ARP entries are created by routers for non ethernet ...
... arp -a or multi show/arp only local (router port) addresses shown ARP entries have a finite (timed) lifetime ARP entries are created by routers for non ethernet ...
Judul
... support. It allows different types of network hardware and software to communicate with each other. It prevents changes in one layer from affecting other layers. It divides network communication into smaller parts to make learning it easier to ...
... support. It allows different types of network hardware and software to communicate with each other. It prevents changes in one layer from affecting other layers. It divides network communication into smaller parts to make learning it easier to ...
Začátek formuláře Which Application layer protocol is widely used to
... An application is using a protocol that exchanges data without using windowing or flow control and must rely on higher layer pro transmit data. Which protocol and transfer method are being used? UDP, connection-oriented UDP, connectionless TCP, connection-oriented TCP, connectionless ...
... An application is using a protocol that exchanges data without using windowing or flow control and must rely on higher layer pro transmit data. Which protocol and transfer method are being used? UDP, connection-oriented UDP, connectionless TCP, connection-oriented TCP, connectionless ...
Chapter 1 Data Communications and Networks Overview
... Trace of Simple Operation • Process associated with port 1 in host A sends message to port 2 in host B • Process at A hands down message to TCP to send to port 2 • TCP hands down to IP to send to host B • IP hands down to network layer (e.g. Ethernet) to send to router J • Generates a set of encaps ...
... Trace of Simple Operation • Process associated with port 1 in host A sends message to port 2 in host B • Process at A hands down message to TCP to send to port 2 • TCP hands down to IP to send to host B • IP hands down to network layer (e.g. Ethernet) to send to router J • Generates a set of encaps ...
Chapter 1 Data Communications and Networks Overview
... Trace of Simple Operation • Process associated with port 1 in host A sends message to port 2 in host B • Process at A hands down message to TCP to send to port 2 • TCP hands down to IP to send to host B • IP hands down to network layer (e.g. Ethernet) to send to router J • Generates a set of encaps ...
... Trace of Simple Operation • Process associated with port 1 in host A sends message to port 2 in host B • Process at A hands down message to TCP to send to port 2 • TCP hands down to IP to send to host B • IP hands down to network layer (e.g. Ethernet) to send to router J • Generates a set of encaps ...
pptx
... Inter-layer dependencies in implementations for performance reasons Some dependencies in the standards (header checksums) ...
... Inter-layer dependencies in implementations for performance reasons Some dependencies in the standards (header checksums) ...
CSC 335 Data Communications and Networking I
... pieces all arrive correctly at the other end. • The transport layer also determines the type of services, connection-oriented or connectionless. • Congestion control ...
... pieces all arrive correctly at the other end. • The transport layer also determines the type of services, connection-oriented or connectionless. • Congestion control ...
15-441 Computer Networking Lecture 2 - Protocol Stacks
... • Implementing a functionality at a lower level should have minimum performance impact on the applications that do not use the functionality ...
... • Implementing a functionality at a lower level should have minimum performance impact on the applications that do not use the functionality ...
Chapter 2 Protocols and Architecture
... Trace of Simple Operation • Process associated with port 1 in host A sends message to port 2 in host B • Process at A hands down message to TCP to send to port 2 • TCP hands down to IP to send to host B • IP hands down to network layer (e.g. Ethernet) to send to router J • Generates a set of encaps ...
... Trace of Simple Operation • Process associated with port 1 in host A sends message to port 2 in host B • Process at A hands down message to TCP to send to port 2 • TCP hands down to IP to send to host B • IP hands down to network layer (e.g. Ethernet) to send to router J • Generates a set of encaps ...
Chapter 2 Protocols and Architecture
... Trace of Simple Operation • Process associated with port 1 in host A sends message to port 2 in host B • Process at A hands down message to TCP to send to port 2 • TCP hands down to IP to send to host B • IP hands down to network layer (e.g. Ethernet) to send to router J • Generates a set of encaps ...
... Trace of Simple Operation • Process associated with port 1 in host A sends message to port 2 in host B • Process at A hands down message to TCP to send to port 2 • TCP hands down to IP to send to host B • IP hands down to network layer (e.g. Ethernet) to send to router J • Generates a set of encaps ...
foundationsChap1
... ◦ Multiplex a single bus/wire/channel across multiple hosts ◦ Limitations :geographical distance limitations and number of nodes connected. All styles of Networks must cope with Scalability ...
... ◦ Multiplex a single bus/wire/channel across multiple hosts ◦ Limitations :geographical distance limitations and number of nodes connected. All styles of Networks must cope with Scalability ...
Chapter 2 Protocols and Architecture
... Trace of Simple Operation • Process associated with port 1 in host A sends message to port 2 in host B • Process at A hands down message to TCP to send to port 2 • TCP hands down to IP to send to host B • IP hands down to network layer (e.g. Ethernet) to send to router J • Generates a set of encaps ...
... Trace of Simple Operation • Process associated with port 1 in host A sends message to port 2 in host B • Process at A hands down message to TCP to send to port 2 • TCP hands down to IP to send to host B • IP hands down to network layer (e.g. Ethernet) to send to router J • Generates a set of encaps ...
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA)

The Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) is a computer network architecture that unifies distributed computing and telecommunications. RINA's fundamental principle is that computer networking is just Inter-Process Communication or IPC. RINA reconstructs the overall structure of the Internet, forming a model that comprises a single repeating layer, the DIF (Distributed IPC Facility), which is the minimal set of components required to allow distributed IPC between application processes. RINA inherently supports mobility, multi-homing and Quality of Service without the need for extra mechanisms, provides a secure and programmable environment, motivates for a more competitive marketplace, and allows for a seamless adoption.