Biophysics 101 Genomics and Computational Biology
... A set of 32 known thrombin inhibitors representing different chemical classes has been used to evaluate the performance of two implementations of incremental construction algorithms for flexible molecular docking: DOCK 4.0 and FlexX 1.5. Both docking tools are able to dock 10-35% of our test set wit ...
... A set of 32 known thrombin inhibitors representing different chemical classes has been used to evaluate the performance of two implementations of incremental construction algorithms for flexible molecular docking: DOCK 4.0 and FlexX 1.5. Both docking tools are able to dock 10-35% of our test set wit ...
GenScript - Protein Services
... Protein purification from the cell lysate if very little protein can be obtained from the medium (Extra fee is charged) Expression evaluations on both secretory expression with the signal peptide and intracellular expression without the signal peptide (Recommended) ...
... Protein purification from the cell lysate if very little protein can be obtained from the medium (Extra fee is charged) Expression evaluations on both secretory expression with the signal peptide and intracellular expression without the signal peptide (Recommended) ...
Slide 1
... • Genbank, EMBL, DDBJ • Each of the three groups collects a portion of the total sequence data reported worldwide, and all new and updated database entries are exchanged between the groups on a daily basis ...
... • Genbank, EMBL, DDBJ • Each of the three groups collects a portion of the total sequence data reported worldwide, and all new and updated database entries are exchanged between the groups on a daily basis ...
The EMBO Journal
... was concluded that these genes are very homologous (Tommassen et al., 1982b). Comparison of the primary structures of these proteins showed that almost 70% of their amino acid residues are identical. In contrast, their signal sequences are very different (Overbeeke et al., 1983). The use of hybrid g ...
... was concluded that these genes are very homologous (Tommassen et al., 1982b). Comparison of the primary structures of these proteins showed that almost 70% of their amino acid residues are identical. In contrast, their signal sequences are very different (Overbeeke et al., 1983). The use of hybrid g ...
Chapter summaries
... extracellular matrix delivering strength and rigidity to a wide range of tissues. 8. The triple helix is a repetitive structure containing the motif (Gly-Xaa-Yaa) in high frequency with Xaa and Yaa often found as proline and lysine residues. 9. Repeating sequences of amino acids are a feature of man ...
... extracellular matrix delivering strength and rigidity to a wide range of tissues. 8. The triple helix is a repetitive structure containing the motif (Gly-Xaa-Yaa) in high frequency with Xaa and Yaa often found as proline and lysine residues. 9. Repeating sequences of amino acids are a feature of man ...
Sirota, Marina : Protein Multiple Alignment
... which is usually used on HMMs to perform sequence alignment. The Viterbi algorithm picks a single alignment with the highest chance of being completely correct, which is analogous to Needleman-Wunch. It finds the maximum probability alignment, returning a single alignment with the maximum probabilit ...
... which is usually used on HMMs to perform sequence alignment. The Viterbi algorithm picks a single alignment with the highest chance of being completely correct, which is analogous to Needleman-Wunch. It finds the maximum probability alignment, returning a single alignment with the maximum probabilit ...
Signaling mechanistics: Aluminum fluoride for
... transfer enzymes is whether the transition state is mostly dissociative, with a metaphosphate-like intermediate, or associative, with a pentavalent phosphorus. The structures of the transition state mimics show distances between aluminum and the leaving group and nucleophilic oxygen that are interme ...
... transfer enzymes is whether the transition state is mostly dissociative, with a metaphosphate-like intermediate, or associative, with a pentavalent phosphorus. The structures of the transition state mimics show distances between aluminum and the leaving group and nucleophilic oxygen that are interme ...
Direct Comparison DNA and Amino Acid Sequences Based on a
... The algorithm we use to directly compare a DNA sequence with an amino acid sequence, has three steps : 1) translating the DNA sequence into an amino acid sequence nucleotide - by - nucleotide, 2) comparing the translated amino acid sequence with amino acid sequences in the database, allowing gaps to ...
... The algorithm we use to directly compare a DNA sequence with an amino acid sequence, has three steps : 1) translating the DNA sequence into an amino acid sequence nucleotide - by - nucleotide, 2) comparing the translated amino acid sequence with amino acid sequences in the database, allowing gaps to ...
biochem ch 7 [12-11
... Sequence of amino acids and primary structure determines way protein folds into 3D structure (native conformation); once folded, 3D structure of protein forms binding sites for other molecules, thereby dictating function of protein in body o Protein must fold in such a way that it is flexible, sta ...
... Sequence of amino acids and primary structure determines way protein folds into 3D structure (native conformation); once folded, 3D structure of protein forms binding sites for other molecules, thereby dictating function of protein in body o Protein must fold in such a way that it is flexible, sta ...
Study Guide Answer Key - Mayfield City Schools
... 1. What are the 3 steps in Protein Synthesis (in order)? Transcription, RNA splicing, translation 2. Transcription takes place in the nucleus. 3. What are the 3 main types of RNA? Describe what each type is used for. mRNA- messenger RNA, contains codons that code for amino acids tRNA – transfer RNA, ...
... 1. What are the 3 steps in Protein Synthesis (in order)? Transcription, RNA splicing, translation 2. Transcription takes place in the nucleus. 3. What are the 3 main types of RNA? Describe what each type is used for. mRNA- messenger RNA, contains codons that code for amino acids tRNA – transfer RNA, ...
View as PDF document
... natural selection, bioinformatics, and disease transmission. Many of these materials can be presented either at an introductory or an advanced level. For instance, materials are provided to allow students to compare DNA and protein sequences by hand, or these comparisons can be completed using progr ...
... natural selection, bioinformatics, and disease transmission. Many of these materials can be presented either at an introductory or an advanced level. For instance, materials are provided to allow students to compare DNA and protein sequences by hand, or these comparisons can be completed using progr ...
FT-IR Protein Structure Analyzer
... PROTA was introduced in 1998 as the first dedicated solution for structure elucidation of biologics and since has become the industry’s preferred choice. PROTA provides a fast, cost-effective and sensitive way to determine secondary structure of a protein or to follow structural changes due to pertu ...
... PROTA was introduced in 1998 as the first dedicated solution for structure elucidation of biologics and since has become the industry’s preferred choice. PROTA provides a fast, cost-effective and sensitive way to determine secondary structure of a protein or to follow structural changes due to pertu ...
Ensembl
... • These clusters represent the same gene based on the alignment of EST sequences with each other and with the genome sequences of the organism. • no attempt has been made to produce contigs – splicing variants for a gene are put into the same set. – Moreover, EST-containing sets often contain 5' and ...
... • These clusters represent the same gene based on the alignment of EST sequences with each other and with the genome sequences of the organism. • no attempt has been made to produce contigs – splicing variants for a gene are put into the same set. – Moreover, EST-containing sets often contain 5' and ...
A short guided tour through functional and structural features of
... activator-like effect of this domain and perhaps additionally an influence on enzyme stability [71]. The rapidly increasing mass of sequence data of growing genome projects reveal an unanticipated number of SAPLIP sequences in various organisms. Since the definite function of a SAPLIP is not deducib ...
... activator-like effect of this domain and perhaps additionally an influence on enzyme stability [71]. The rapidly increasing mass of sequence data of growing genome projects reveal an unanticipated number of SAPLIP sequences in various organisms. Since the definite function of a SAPLIP is not deducib ...
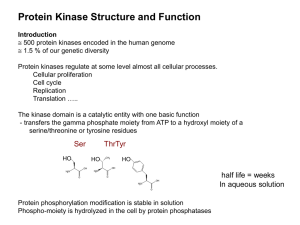
Substrate targeting mechanisms
... ii. strict conformational requirements for catalysis – perturb structure of any conserved element and kinase is inactivated iii. extensive surface provides opportunities for the evolution of secondary peptide binding sites to complement the peptide binding site at the catalytic site -although core c ...
... ii. strict conformational requirements for catalysis – perturb structure of any conserved element and kinase is inactivated iii. extensive surface provides opportunities for the evolution of secondary peptide binding sites to complement the peptide binding site at the catalytic site -although core c ...
Amino acids in proteins
... • border: polypeptide /protein is not sharp (~ 50 AAs) • AAs are bound by peptide bonds • the order of AAs in a chain (= primary structure) is given by a genetic information • the order of AAs is reported from N- to C- terminal ...
... • border: polypeptide /protein is not sharp (~ 50 AAs) • AAs are bound by peptide bonds • the order of AAs in a chain (= primary structure) is given by a genetic information • the order of AAs is reported from N- to C- terminal ...
Manual_AccuRapid™ Protein Synthesis Kit
... 1) Place the Ni-NTA magnetic bead tube in the separation rack of MagListo -2 without magnet plate. 2) Combine magnet plate with separation rack and remove supernatant from the bead. 3) After separating the magnet plate from separation rack, add 1.0 mL of Binding/washing buffer to the bead and resusp ...
... 1) Place the Ni-NTA magnetic bead tube in the separation rack of MagListo -2 without magnet plate. 2) Combine magnet plate with separation rack and remove supernatant from the bead. 3) After separating the magnet plate from separation rack, add 1.0 mL of Binding/washing buffer to the bead and resusp ...
Supplementary Methods Quantitative mass spectrometry
... Quantitative mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis of RNA-interacting proteins. Protein eluates and their respective mixed light/heavy input lysates were subjected to in-solution enzymatic digestion using a filter-aided sample preparation approach [1], as we described in [2]. Briefly, eluates w ...
... Quantitative mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis of RNA-interacting proteins. Protein eluates and their respective mixed light/heavy input lysates were subjected to in-solution enzymatic digestion using a filter-aided sample preparation approach [1], as we described in [2]. Briefly, eluates w ...
Protein Functional Annotation - Institute for Genome Sciences
... •! Local pairwise alignment tools do not worry about matching proteins over their entire lengths, they look for any regions of similarity within the proteins that score well.! –! BLAST! •! fast! •! comes in many varieties (see NCBI site)! ...
... •! Local pairwise alignment tools do not worry about matching proteins over their entire lengths, they look for any regions of similarity within the proteins that score well.! –! BLAST! •! fast! •! comes in many varieties (see NCBI site)! ...
Steps of Translation - Madison Public Schools
... A peptide bond forms between the two amino acids. The ribosome moves over one codon PROCESS CONTINUES ...
... A peptide bond forms between the two amino acids. The ribosome moves over one codon PROCESS CONTINUES ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.