Project Abstract (150 words max): Scientific Inquiry: The protein
... structure of a cell. Mutations associated within the Ig4 domain of palladin have been observed in pancreatic cancer. In the hydrophobic core of the mutated Ig4 domain the amino acid tryptophan has been replaced with the amino acid cysteine, and we hypothesize that the mutation will affect the struct ...
... structure of a cell. Mutations associated within the Ig4 domain of palladin have been observed in pancreatic cancer. In the hydrophobic core of the mutated Ig4 domain the amino acid tryptophan has been replaced with the amino acid cysteine, and we hypothesize that the mutation will affect the struct ...
Amino Acid Alphabet
... Enzyme from 9 amino acids Can a reduced amino acid alphabet support enzymatic catalysis? Designing/engineering an enzyme is difficult because of the precise positioning of residues required for catalysis Chorismate mutase (CM) catalyzes the rearrangement of chorismate to prephenate and is essential ...
... Enzyme from 9 amino acids Can a reduced amino acid alphabet support enzymatic catalysis? Designing/engineering an enzyme is difficult because of the precise positioning of residues required for catalysis Chorismate mutase (CM) catalyzes the rearrangement of chorismate to prephenate and is essential ...
09.06.11 Intro to Biochemistry w. Clinical
... Intro To Protein Structure • Why start with proteins? • Historical: 1957 Solved Crystal Structures – The first three-dimensional protein structures (myoglobin and hemoglobin) were determined by M.F.Perutz and J. C. Kendrew (Mb at 6 A resolution in 1957, Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1962). The en ...
... Intro To Protein Structure • Why start with proteins? • Historical: 1957 Solved Crystal Structures – The first three-dimensional protein structures (myoglobin and hemoglobin) were determined by M.F.Perutz and J. C. Kendrew (Mb at 6 A resolution in 1957, Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1962). The en ...
Protein Digestion
... blood albumin) is a specific sequence of 20 different amino acids. Each amino acid contains at least one atom of nitrogen. ...
... blood albumin) is a specific sequence of 20 different amino acids. Each amino acid contains at least one atom of nitrogen. ...
Explanation of Scaffold`s Display Options - Proteome Software
... question. This number is the number of assigned spectra for this protein divided by the total spectra in the sample (as seen in the Load Data View). Assigned spectra: This is the number of spectra which Protein Prophet assigns to the protein in question.The peptides represented by these spectra may ...
... question. This number is the number of assigned spectra for this protein divided by the total spectra in the sample (as seen in the Load Data View). Assigned spectra: This is the number of spectra which Protein Prophet assigns to the protein in question.The peptides represented by these spectra may ...
Anti-Ribosomal Protein L26 (N-terminal) (R0655)
... and immunofluorescence. Staining of the ribosomal protein L26 band in immunoblotting is specifically inhibited by the immunizing peptide. Ribosomes are the machinery responsible for protein translation in every living cell. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic ribosomes are very similar in design and function ...
... and immunofluorescence. Staining of the ribosomal protein L26 band in immunoblotting is specifically inhibited by the immunizing peptide. Ribosomes are the machinery responsible for protein translation in every living cell. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic ribosomes are very similar in design and function ...
Analyzing Amino-Acid Sequences to Determine
... Between Humans and Other Vertebrate Species Species ...
... Between Humans and Other Vertebrate Species Species ...
The tmRNA website
... is added to the abnormally short protein product of a broken mRNA, as a signal for proteolysis of the entire tagged protein. The tmRNA website was established in 1997 as a resource for phylogenetic considerations of tmRNA structure and function. Since then, three partial tmRNA sequences have been co ...
... is added to the abnormally short protein product of a broken mRNA, as a signal for proteolysis of the entire tagged protein. The tmRNA website was established in 1997 as a resource for phylogenetic considerations of tmRNA structure and function. Since then, three partial tmRNA sequences have been co ...
Recombinant Ebola virus VP40 matrix protein
... Storage: -80°C. It is recommended to dispense single-use aliquots and store aliquots at -80°C to avoid multiple freeze/thaw cycles. Size: 100 µg of protein is supplied in HEPES buffer pH 7.5 containing sodium chloride, 5% glycerol and 0.1% Triton-X, at a concentration of 1.602 mg/mL. The theoretical ...
... Storage: -80°C. It is recommended to dispense single-use aliquots and store aliquots at -80°C to avoid multiple freeze/thaw cycles. Size: 100 µg of protein is supplied in HEPES buffer pH 7.5 containing sodium chloride, 5% glycerol and 0.1% Triton-X, at a concentration of 1.602 mg/mL. The theoretical ...
PowerPoint
... acid sequences? If you think you have an Open Reading Frame (ORF) then align at protein level – (i) Many mutations within DNA are synonymous, leading to overestimation of sequence divergence if compared at the DNA level. – (ii) Evolutionary relationships can be more finely expressed using a 20×20 am ...
... acid sequences? If you think you have an Open Reading Frame (ORF) then align at protein level – (i) Many mutations within DNA are synonymous, leading to overestimation of sequence divergence if compared at the DNA level. – (ii) Evolutionary relationships can be more finely expressed using a 20×20 am ...
Introduction to Protein Folding and Molecular Simulation
... frequency of calculation of the most time-demanding part (nonbonded energy terms). ...
... frequency of calculation of the most time-demanding part (nonbonded energy terms). ...
Word file - UC Davis
... permutation). As BLAST (just like most sequence comparison techniques) works with the sequence given from Nter to Cter, it is not designed to detect domain swap. d) From these results, do you expect the structures of ConA and peanut lectin to be similar? Justify your answer (2 points). As the two al ...
... permutation). As BLAST (just like most sequence comparison techniques) works with the sequence given from Nter to Cter, it is not designed to detect domain swap. d) From these results, do you expect the structures of ConA and peanut lectin to be similar? Justify your answer (2 points). As the two al ...
ppt
... •Use modern package such as T-coffee •Manual verification and editing essential •Secondary structure can serve as guide in alignment (Praline) •Non-homologous regions may have to be removed (subjective) •Remove Indels •Gaps regions may belong to signature indels and contain phylogenetic information ...
... •Use modern package such as T-coffee •Manual verification and editing essential •Secondary structure can serve as guide in alignment (Praline) •Non-homologous regions may have to be removed (subjective) •Remove Indels •Gaps regions may belong to signature indels and contain phylogenetic information ...
Van der Waals bonds
... • Several proteins are cleaved into smaller proteins or peptides following translation. For example, the enkephalins are small peptides which are derived from proteins in this manner . • Active enzymes are sometimes formed by cleaving a larger protein precursor. Often, this serves to protect the cel ...
... • Several proteins are cleaved into smaller proteins or peptides following translation. For example, the enkephalins are small peptides which are derived from proteins in this manner . • Active enzymes are sometimes formed by cleaving a larger protein precursor. Often, this serves to protect the cel ...
You find all these questions again in the ′Test
... This page contains a randomly selected series of exam questions that we have used in the past in real exams, and that you should be able to answer by now. You find all these questions again in the ′Test-exams′ section, and in that section, you often also find the answers. Exam questions used in the ...
... This page contains a randomly selected series of exam questions that we have used in the past in real exams, and that you should be able to answer by now. You find all these questions again in the ′Test-exams′ section, and in that section, you often also find the answers. Exam questions used in the ...
7-phylogeny_ch7&8 - of Timothy L. Bailey
... – But all we get to see is the final result! – So a position with a different nucleic acid may be the result of one or more mutation events. – And positions with the same nucleic acid can also have had an even number of mutations. Seq 1: A ->T ...
... – But all we get to see is the final result! – So a position with a different nucleic acid may be the result of one or more mutation events. – And positions with the same nucleic acid can also have had an even number of mutations. Seq 1: A ->T ...
Proposta di ricerca: Introduction Ever since the observation that
... in (i.e. solubilizers, called „chaotrops”). One approach had been to correlate these attributes with effects on water structure, in particular the fraction of hydrogen-bonded water molecules: precipitants give a higher fraction and are therefore called kosmotropes, and solubilizers give a lower frac ...
... in (i.e. solubilizers, called „chaotrops”). One approach had been to correlate these attributes with effects on water structure, in particular the fraction of hydrogen-bonded water molecules: precipitants give a higher fraction and are therefore called kosmotropes, and solubilizers give a lower frac ...
Tertiary Protein Structure Prediction with Profile Analysis: A Case Study
... Profilemake, part of the Genetics Computing Group suite of programs, was used to make profiles from the files of known helices and a structure-correlated scoring matrix. In addition, leave-one-out profiles were made by omitting one sequence from the set of sequences used to create the profiles. The ...
... Profilemake, part of the Genetics Computing Group suite of programs, was used to make profiles from the files of known helices and a structure-correlated scoring matrix. In addition, leave-one-out profiles were made by omitting one sequence from the set of sequences used to create the profiles. The ...
here
... Background Information on Project: Transcription Factor IIIA is the archetypal zinc finger protein, the founding member of a family of proteins that make use of the same structural fold to recognize specific DNA sequences (1). In fact, the zinc finger structural motif is by far the most commonly use ...
... Background Information on Project: Transcription Factor IIIA is the archetypal zinc finger protein, the founding member of a family of proteins that make use of the same structural fold to recognize specific DNA sequences (1). In fact, the zinc finger structural motif is by far the most commonly use ...
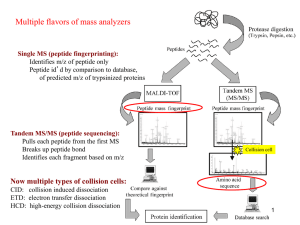
Proteomics2_2012
... instrument sensitivity, others - this reduces search space - can miss some peptides - comparisons based on several different scores (eg. correlation between obs. and theoretical profiles) ...
... instrument sensitivity, others - this reduces search space - can miss some peptides - comparisons based on several different scores (eg. correlation between obs. and theoretical profiles) ...
HHMI meeting, FOLDING
... in “normal” synthetic polymers is not of an “all-or-none” type. Besides, globule-to-coil transition in polymers resembles evaporation rather than melting or sublimation, while protein denaturation resembles melting or sublimation of a crystal rather than evaporation of a liquid. Why? Special constru ...
... in “normal” synthetic polymers is not of an “all-or-none” type. Besides, globule-to-coil transition in polymers resembles evaporation rather than melting or sublimation, while protein denaturation resembles melting or sublimation of a crystal rather than evaporation of a liquid. Why? Special constru ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.