Biology Summary
... - have a branched shape that allows them to form an interconnected network of cells - can conduct electric impulses and contract in unison - contain many large mitochondria to power their action - contain actin and myosin filaments that allow them to contract Parietal cells - within indentations in ...
... - have a branched shape that allows them to form an interconnected network of cells - can conduct electric impulses and contract in unison - contain many large mitochondria to power their action - contain actin and myosin filaments that allow them to contract Parietal cells - within indentations in ...
What Makes Up Your Body?
... Think about the different parts of your body. Your eyes, arms, and toes ate very different from each other. Yet they are all alike in one way, All the parts of your body are made of cells. Cells are the smallest part of a living thing. They are calltrd the building blocks of the body. Billions ofcel ...
... Think about the different parts of your body. Your eyes, arms, and toes ate very different from each other. Yet they are all alike in one way, All the parts of your body are made of cells. Cells are the smallest part of a living thing. They are calltrd the building blocks of the body. Billions ofcel ...
Stem Cell Therapy for Post-Polio Syndrome - Post
... usually discussed as targets for stem cell therapy. For example, in a spinal cord injury there is a loss of cells at the break in the spinal cord — where the body of nerve cells resides. Outside the cord, each cell projects into a long tube, sometimes three feet or more, which ends at a muscle fiber ...
... usually discussed as targets for stem cell therapy. For example, in a spinal cord injury there is a loss of cells at the break in the spinal cord — where the body of nerve cells resides. Outside the cord, each cell projects into a long tube, sometimes three feet or more, which ends at a muscle fiber ...
Cells - P5 GE Science 2011
... Producing new cells • Our bodies increase in size as we grow. • This is due to an increase in the number of cells in the body. • Cells increase in number by dividing themselves. • The nucleus and cytoplasm of one cell divide to produce two cells. • The two new cells later divide into four cells. • ...
... Producing new cells • Our bodies increase in size as we grow. • This is due to an increase in the number of cells in the body. • Cells increase in number by dividing themselves. • The nucleus and cytoplasm of one cell divide to produce two cells. • The two new cells later divide into four cells. • ...
Chapter 22 and 27 and 28
... • Tissues are groups of cells that perform a similar function. • Organs are groups of tissues that perform a specific or related function. • Organ systems are groups of organs that carry out similar functions. ...
... • Tissues are groups of cells that perform a similar function. • Organs are groups of tissues that perform a specific or related function. • Organ systems are groups of organs that carry out similar functions. ...
Downloaded - MsOttoliniBiology
... • These organisms have cell specialization— different types of cells with different structures for different jobs/purposes. • As cells specialize, only DNA related to the functions of a particular cell remains active. ...
... • These organisms have cell specialization— different types of cells with different structures for different jobs/purposes. • As cells specialize, only DNA related to the functions of a particular cell remains active. ...
The Tissue Level of Organization
... Description: single layer of columnar cells but the position of the nuclei make it appear as there are many layers; often ciliated Functions: Protection and secretion Locations: lining of nasal cavity, trachea and bronchi and portions of male reproductive tract ...
... Description: single layer of columnar cells but the position of the nuclei make it appear as there are many layers; often ciliated Functions: Protection and secretion Locations: lining of nasal cavity, trachea and bronchi and portions of male reproductive tract ...
Functions of Female Reproductive Organs
... – Fibroids are benign tumours within that develop within the uterus as the female gets older – Most are very small but some can grow large enough to ...
... – Fibroids are benign tumours within that develop within the uterus as the female gets older – Most are very small but some can grow large enough to ...
Energy in the Cell
... 3 kinds of stem cells 1. Totiopotent- the egg and the cells that result from early cell division. Human fertilized egg has the potential to form a whole organism. 2. Pluripotent- forms five days after fertilization (blastocyst- outer layer of cells and inner cell mass). Inner cells form tissue of h ...
... 3 kinds of stem cells 1. Totiopotent- the egg and the cells that result from early cell division. Human fertilized egg has the potential to form a whole organism. 2. Pluripotent- forms five days after fertilization (blastocyst- outer layer of cells and inner cell mass). Inner cells form tissue of h ...
Levels of Organization - Ms. Stanford`s Science Page 2016
... organism alive is divided (division) among the different parts of the body. Each part has a job to do and as each part does its special job, it works in harmony with all the other parts. The arrangement of specialized parts within a living thing is sometimes referred to as levels of organization. Ce ...
... organism alive is divided (division) among the different parts of the body. Each part has a job to do and as each part does its special job, it works in harmony with all the other parts. The arrangement of specialized parts within a living thing is sometimes referred to as levels of organization. Ce ...
B Cell Development
... stage of embryonic development (as soon as blood vessels form), but the last one is only needed mainly after birth. So not all blood cell types are produced at the same time in the embryo ...
... stage of embryonic development (as soon as blood vessels form), but the last one is only needed mainly after birth. So not all blood cell types are produced at the same time in the embryo ...
Document
... Which statement concerning the reproductive cells in the diagram below is correct? (1) The cells are produced by mitosis and contain all the genetic information of the father. (2) If one of these cells fertilizes an egg, the offspring will be identical to the father. (3) Each of these cells contain ...
... Which statement concerning the reproductive cells in the diagram below is correct? (1) The cells are produced by mitosis and contain all the genetic information of the father. (2) If one of these cells fertilizes an egg, the offspring will be identical to the father. (3) Each of these cells contain ...
F212 2.6 Cell Division and Diversity
... Haploid gametes are produced, which can undergo random fusion with gametes derived from another organism of the same species Questions 1. Explain why sexual reproduction involves meiosis? ...
... Haploid gametes are produced, which can undergo random fusion with gametes derived from another organism of the same species Questions 1. Explain why sexual reproduction involves meiosis? ...
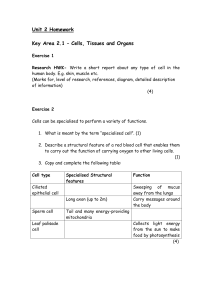
Unit 2 Homework
... 2. Give two similarities and two differences between the control of body functions by the nervous system and the control by the endocrine system. (4) 3. Give an example of a target organ and the effect that a particular hormone has on that target organ. (2) 4. Copy the flow chart below describing th ...
... 2. Give two similarities and two differences between the control of body functions by the nervous system and the control by the endocrine system. (4) 3. Give an example of a target organ and the effect that a particular hormone has on that target organ. (2) 4. Copy the flow chart below describing th ...
Cell Theory
... animals. In 1839, Schwann concluded that all animal tissues were made of cells. Soon after that, Schwann wrote the first two parts of what is now known as the cell theory. ...
... animals. In 1839, Schwann concluded that all animal tissues were made of cells. Soon after that, Schwann wrote the first two parts of what is now known as the cell theory. ...
kaloleni-rabai district joint mock exam
... (3marks) (a)Cellulose (1mark) (b)Active transport (1mark) The cell sap is hypertonic to the solution / distilled water; hence water molecules move into the cell; by osmosis; making it to swell and eventually burst; (3ma2. (a) X – Phalanges ; Y – Humerus; Z – Carpals; 4. (b) ...
... (3marks) (a)Cellulose (1mark) (b)Active transport (1mark) The cell sap is hypertonic to the solution / distilled water; hence water molecules move into the cell; by osmosis; making it to swell and eventually burst; (3ma2. (a) X – Phalanges ; Y – Humerus; Z – Carpals; 4. (b) ...
Fall 2013 Exam Review Review Which statement best describes
... b. The diagram shows the digestive system, which produces oxygen for the body cells. c. The diagram shows the muscular system, which moves oxygen to the cells. d. The diagram shows the circulatory system, which transports oxygen from the lungs to the cells of the body. 65. Which of these is an examp ...
... b. The diagram shows the digestive system, which produces oxygen for the body cells. c. The diagram shows the muscular system, which moves oxygen to the cells. d. The diagram shows the circulatory system, which transports oxygen from the lungs to the cells of the body. 65. Which of these is an examp ...
Unit 1 – Biology – Cells PowerPoint
... Information that results in plants and animals having similar characteristics to their parents is carried by ________________, which are passed on in the __________________________ from which the offspring develop. ...
... Information that results in plants and animals having similar characteristics to their parents is carried by ________________, which are passed on in the __________________________ from which the offspring develop. ...
22-Premedical_Tissue
... 1. Epithelia – ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm 2. Connective tissue - mesoderm 3. Muscular tissue - mesoderm 4. Nervous tissue - ectoderm ...
... 1. Epithelia – ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm 2. Connective tissue - mesoderm 3. Muscular tissue - mesoderm 4. Nervous tissue - ectoderm ...
Levels of Organization
... 4. The endocrine system consists of skin, hair, nails and their underlying tissue. 5. The lymphatic system returns leaked fluids to blood vessels. ...
... 4. The endocrine system consists of skin, hair, nails and their underlying tissue. 5. The lymphatic system returns leaked fluids to blood vessels. ...
Tissues
... How do cells stick together? Tight Junctions rows of proteins that seal cells together Prevents molecules from getting stuck in between cells Important in epithelial cells of the intestines Adhering Junctions Mass of proteins (called desmosomes) that spot weld the cell together at a very specifi ...
... How do cells stick together? Tight Junctions rows of proteins that seal cells together Prevents molecules from getting stuck in between cells Important in epithelial cells of the intestines Adhering Junctions Mass of proteins (called desmosomes) that spot weld the cell together at a very specifi ...
• B2.1.1 Cells and cell structure • B2.1.2 Dissolved substances No
... Goblet (mucus) and cilia cells are found in the lining of the gut and the tubes into the lungs. They are specialised to release and move mucus. Helps food slide down easily in the gut and helps trap dirt and bacteria before they enter the lungs. The cilia cells help move the mucus especially in the ...
... Goblet (mucus) and cilia cells are found in the lining of the gut and the tubes into the lungs. They are specialised to release and move mucus. Helps food slide down easily in the gut and helps trap dirt and bacteria before they enter the lungs. The cilia cells help move the mucus especially in the ...
PiXL AQA – Knowledge PowerPoint
... Goblet (mucus) and cilia cells are found in the lining of the gut and the tubes into the lungs. They are specialised to release and move mucus. Helps food slide down easily in the gut and helps trap dirt and bacteria before they enter the lungs. The cilia cells help move the mucus especially in the ...
... Goblet (mucus) and cilia cells are found in the lining of the gut and the tubes into the lungs. They are specialised to release and move mucus. Helps food slide down easily in the gut and helps trap dirt and bacteria before they enter the lungs. The cilia cells help move the mucus especially in the ...
LC Biology Sample Paper 6 HL Solutions
... (iv) The walls dissolve and a zygospore is formed by the fusion of the haploid nuclei. (n) (v) When conditions are favourable the zygospore germinates (divides by meiosis) to form a haploid hypha. 6 x (2) 1) Gametes move from each strand into the zygospore. 2) Fertilization is internal 3) A zygospor ...
... (iv) The walls dissolve and a zygospore is formed by the fusion of the haploid nuclei. (n) (v) When conditions are favourable the zygospore germinates (divides by meiosis) to form a haploid hypha. 6 x (2) 1) Gametes move from each strand into the zygospore. 2) Fertilization is internal 3) A zygospor ...
Chimera (genetics)

A chimera (also spelled chimaera) (from the creature Chimera in Greek mythology) is a single organism composed of genetically distinct cells. This can result in male and female organs, two blood types, or subtle variations in form. Animal chimeras are produced by the merger of multiple fertilized eggs. In plant chimeras, however, the distinct types of tissue may originate from the same zygote, and the difference is often due to mutation during ordinary cell division. Normally, chimerism is not visible on casual inspection; however, it has been detected in the course of proving parentage.Another way that chimerism can occur in animals is by organ transplantation, giving one individual tissues that developed from two genomes. For example, a bone marrow transplant can change someone's blood type.