Life Cycle of Stars
... Not all stars are the same: • Stars exist that are significantly larger and significantly smaller than our sun. • Not all stars have planets. • Some stars are older than our sun and some are younger. ...
... Not all stars are the same: • Stars exist that are significantly larger and significantly smaller than our sun. • Not all stars have planets. • Some stars are older than our sun and some are younger. ...
characteristics of stars
... Stars evolve from clouds of _______________ and dust. They go through a series of stages - they ____________ (are ‘born’), develop, and ________________ (‘die’). Each life may take _______________ of years. All stars begin their lives in ____________________, which are huge clouds of dust and gases, ...
... Stars evolve from clouds of _______________ and dust. They go through a series of stages - they ____________ (are ‘born’), develop, and ________________ (‘die’). Each life may take _______________ of years. All stars begin their lives in ____________________, which are huge clouds of dust and gases, ...
Stars and Sun
... Billions of galaxies make up a universe In 1995, the Hubble Space Telescope discovered over 1,500 galaxies in a tiny sector of the sky ...
... Billions of galaxies make up a universe In 1995, the Hubble Space Telescope discovered over 1,500 galaxies in a tiny sector of the sky ...
I. Parallax
... B. The scale was initially set up by Norman Pogson in 1856 with a magnitude ___ given to the brightest star in the sky and a magnitude ___ being the dimmest star that could be seen ____ ____________. C. The apparent magnitude of a star is a measure of its brightness _________________. The brighter a ...
... B. The scale was initially set up by Norman Pogson in 1856 with a magnitude ___ given to the brightest star in the sky and a magnitude ___ being the dimmest star that could be seen ____ ____________. C. The apparent magnitude of a star is a measure of its brightness _________________. The brighter a ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #16
... 10-5. The star Zubenelgenubi (from Arabic for “scorpion’s southern claw”) has apparent magnitude 2.75 while the star Sulafat (Arabic for “tortoise”) has apparent magnitude 3.25. Which star appears brighter? From this information alone, what can you conclude about the luminosities of these stars? Exp ...
... 10-5. The star Zubenelgenubi (from Arabic for “scorpion’s southern claw”) has apparent magnitude 2.75 while the star Sulafat (Arabic for “tortoise”) has apparent magnitude 3.25. Which star appears brighter? From this information alone, what can you conclude about the luminosities of these stars? Exp ...
Constellation Notes
... How many constellations are there? The sky was divided up into 88 different constellations in 1922. This included 48 ancient constellations listed by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy as well as 40 new constellations. Star Maps The 88 different constellations divide up the entire night sky as seen from a ...
... How many constellations are there? The sky was divided up into 88 different constellations in 1922. This included 48 ancient constellations listed by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy as well as 40 new constellations. Star Maps The 88 different constellations divide up the entire night sky as seen from a ...
Slide 1
... After the Sun's core hydrogen is depleted by nuclear fusion the core will consist primarily of 1) carbon. 2) deuterium. 3) helium. 4) oxygen. ...
... After the Sun's core hydrogen is depleted by nuclear fusion the core will consist primarily of 1) carbon. 2) deuterium. 3) helium. 4) oxygen. ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... giants then white dwarfs More massive stars explode into a variety of objects ...
... giants then white dwarfs More massive stars explode into a variety of objects ...
Groups of Stars
... MOVING TOWARDS THE MILKY WAY, THEY WILL EVENTUALLY COLLIDE!!! This event will occur in about 5 billion years…) ...
... MOVING TOWARDS THE MILKY WAY, THEY WILL EVENTUALLY COLLIDE!!! This event will occur in about 5 billion years…) ...
Hertzsprung Russell diagram
... main sequence stars – the Sun is a main sequence star. In a way stars that lie on the main sequence are ‘normal’ stars while those that lie to one side or other of this area are ‘unusual’ stars – these stars such as white dwarfs, red giants and supergiants. Notice that supergiant stars can be either ...
... main sequence stars – the Sun is a main sequence star. In a way stars that lie on the main sequence are ‘normal’ stars while those that lie to one side or other of this area are ‘unusual’ stars – these stars such as white dwarfs, red giants and supergiants. Notice that supergiant stars can be either ...
Understanding Stars
... – luminosity is a measure of the energy in the form of photons • Big luminosities are bright – 1 order of magnitude is roughly equal to 20 units of luminosity Absolute Magnitude and Luminosity • 2 different ways of measuring the same thing ...
... – luminosity is a measure of the energy in the form of photons • Big luminosities are bright – 1 order of magnitude is roughly equal to 20 units of luminosity Absolute Magnitude and Luminosity • 2 different ways of measuring the same thing ...
a. Recognize the physical attributes of stars in the night sky such as
... This is not meant to be printed off and given as a test…this document is to give you ideas of how this standard might be assessed. Please use these as an example when you are developing your own formative assessments. Remember formative assessment is to be given throughout the teaching of a standard ...
... This is not meant to be printed off and given as a test…this document is to give you ideas of how this standard might be assessed. Please use these as an example when you are developing your own formative assessments. Remember formative assessment is to be given throughout the teaching of a standard ...
Stars - Madison County Schools
... If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black hole ...
... If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black hole ...
Document
... stars, fill in the chart on the reverse side. The circle is the ecliptic going through the twelve constellations indicated by big arrows. Label each big arrow with the name of the constellation and try to start remembering each shape. I have done one for you. 4. The fifteen small arrows indicate the ...
... stars, fill in the chart on the reverse side. The circle is the ecliptic going through the twelve constellations indicated by big arrows. Label each big arrow with the name of the constellation and try to start remembering each shape. I have done one for you. 4. The fifteen small arrows indicate the ...
Answers Universe Cornell Notes Chapter 8, Sec 2
... Name the colors of the stars from coolest to hottest: What does a star’s brightness depend on? What is apparent magnitude? What is absolute magnitude? What is the HertsprungRussell Diagram? What does it show? ...
... Name the colors of the stars from coolest to hottest: What does a star’s brightness depend on? What is apparent magnitude? What is absolute magnitude? What is the HertsprungRussell Diagram? What does it show? ...
KOI-54 Claude Plymate There is a star system about 45 light years
... There is a star system about 45 light years away in the constellation Cygnus. The system we know as HD 187091 (also known as KOI-54 for Kepler Object of Interest 54) is an undistinguished 8th magnitude A star or was before the Kepler telescope took a close look. As it turns out, the system is anythi ...
... There is a star system about 45 light years away in the constellation Cygnus. The system we know as HD 187091 (also known as KOI-54 for Kepler Object of Interest 54) is an undistinguished 8th magnitude A star or was before the Kepler telescope took a close look. As it turns out, the system is anythi ...
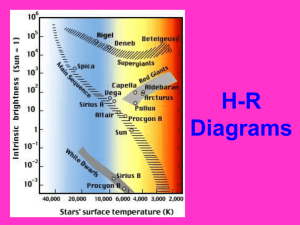
H-R Diagrams
... An H-R Diagram is… • A graph of stars’ BRIGHTNESS and TEMPERATURE – It also shows color since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. ...
... An H-R Diagram is… • A graph of stars’ BRIGHTNESS and TEMPERATURE – It also shows color since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. ...
Astronomy – Studying the Stars & Space
... and dense that even use their hydrogen quickly and may light cannot escape explode in a huge its gravity bright flash • Gas or dust that sink • Can be brighter than into black hole from a an entire galaxy for star form x-ray light several days which may indicate a • A collapsed star can black holes’ ...
... and dense that even use their hydrogen quickly and may light cannot escape explode in a huge its gravity bright flash • Gas or dust that sink • Can be brighter than into black hole from a an entire galaxy for star form x-ray light several days which may indicate a • A collapsed star can black holes’ ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explo ...
... E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explo ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explo ...
... E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explo ...
After Dark in Allenspark
... January 9: Since January 1, Venus has been getting much lower in the sky at sunset each night. This is probably the last night to see Venus, but only if you have a good Western horizon. January 12: In the morning eastern sky, Jupiter is less than 1 degree North of the star Alpha Libra (that is, the ...
... January 9: Since January 1, Venus has been getting much lower in the sky at sunset each night. This is probably the last night to see Venus, but only if you have a good Western horizon. January 12: In the morning eastern sky, Jupiter is less than 1 degree North of the star Alpha Libra (that is, the ...
The Hot-plate Model of a Star Model of Stars— 3 Oct
... hot-plate get to my hand? What are two ways to make a hot plate produce more energy per second? (The same question applies to a star: What are two ways to make a star brighter or more luminous?) What can I do to make the same hot-plate at the same setting burn my hand and not burn my hand? ...
... hot-plate get to my hand? What are two ways to make a hot plate produce more energy per second? (The same question applies to a star: What are two ways to make a star brighter or more luminous?) What can I do to make the same hot-plate at the same setting burn my hand and not burn my hand? ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.