Ourdraft
... Nebula, that is being excited by a young, very hot star called Rigel. Because Rigel is so energetic, it sends off shock waves that hit the nebula, compressing some of the gas (at least, this is what astronomers think is happening). The gas starts to clump as it’s compressed, which creates a gravitat ...
... Nebula, that is being excited by a young, very hot star called Rigel. Because Rigel is so energetic, it sends off shock waves that hit the nebula, compressing some of the gas (at least, this is what astronomers think is happening). The gas starts to clump as it’s compressed, which creates a gravitat ...
I : Internal structure of main sequence stars
... The luminosity L The efficiency of the fusion η The mass of the star M The fraction of the stellar mass that can participate in the fusion reactions f ...
... The luminosity L The efficiency of the fusion η The mass of the star M The fraction of the stellar mass that can participate in the fusion reactions f ...
PowerPoint Presentation - ASTR498E High energy
... The mass of the star M The fraction of the stellar mass that can participate in the fusion reactions f ...
... The mass of the star M The fraction of the stellar mass that can participate in the fusion reactions f ...
Life Cycle of Stars - Faulkes Telescope Project
... intense region of gravity called a Black Hole, the gravitational pull of these monsters is so intense that anything going over the Event Horizon, even light, cannot escape. ...
... intense region of gravity called a Black Hole, the gravitational pull of these monsters is so intense that anything going over the Event Horizon, even light, cannot escape. ...
Stars - Haag
... But stars actually do move in space, this can be seen by the movement of stars over a time period of thousands of years. This is called Actual Motion ...
... But stars actually do move in space, this can be seen by the movement of stars over a time period of thousands of years. This is called Actual Motion ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size to envelope the Earth. And surprisingly, the larger the mass of the star, the quicker it burns its fuel sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telesc ...
... exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size to envelope the Earth. And surprisingly, the larger the mass of the star, the quicker it burns its fuel sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telesc ...
Astronomy Lecture Notes: Stellar Nomenclature I Introduction
... iii. Examine the Ursa Major handout front and back. b. Stellar Names i. Only the brightest stars have formal names, but all stars have official designations. ii. Many formal names of stars are middle eastern in origin to honor the middle eastern astronomers that carried on work in astronomy after th ...
... iii. Examine the Ursa Major handout front and back. b. Stellar Names i. Only the brightest stars have formal names, but all stars have official designations. ii. Many formal names of stars are middle eastern in origin to honor the middle eastern astronomers that carried on work in astronomy after th ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... What happens to white light as it passes through a prism ? REFRACTS Which color refracts the most and least ? RED What is thought to be at the center of all galaxies ? ____BLACK HOLE______ What is the name of our galaxy ? ____MILKY WAY______ The planets that are closer to the sun have a ...
... What happens to white light as it passes through a prism ? REFRACTS Which color refracts the most and least ? RED What is thought to be at the center of all galaxies ? ____BLACK HOLE______ What is the name of our galaxy ? ____MILKY WAY______ The planets that are closer to the sun have a ...
Maui Stargazing April Observing List DEEP SPACE OBJECTS
... ASTERISMS - In astronomy, an asterism is an informal pattern of stars recognized in the Earth's night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. CONSTELLATIONS - In modern astronomy, a constellation is a specific area of the cel ...
... ASTERISMS - In astronomy, an asterism is an informal pattern of stars recognized in the Earth's night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. CONSTELLATIONS - In modern astronomy, a constellation is a specific area of the cel ...
AST 207 Test 2 Answers 20 October 2010
... star A. Prof. Adams says he discovered a new type of star that is fainter than white dwarfs. Has he discovered a new type of star? Explain. The clues are very much like Walter Adams’ discovery that Sirius B is a white dwarf. However, there is a crucial missing clue. Since Sirius A and B were known t ...
... star A. Prof. Adams says he discovered a new type of star that is fainter than white dwarfs. Has he discovered a new type of star? Explain. The clues are very much like Walter Adams’ discovery that Sirius B is a white dwarf. However, there is a crucial missing clue. Since Sirius A and B were known t ...
H-R Diagram Student
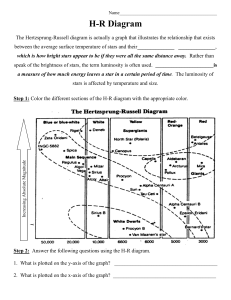
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightne ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightne ...
H-R Diagram - Faculty Website Listing
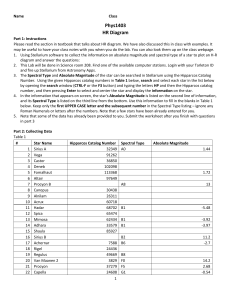
... Please read the section in textbook that talks about HR diagram. We have also discussed this in class with examples. It may be useful to have your class notes with you when you do the lab. You can also look them up on the class webpage. 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on abso ...
... Please read the section in textbook that talks about HR diagram. We have also discussed this in class with examples. It may be useful to have your class notes with you when you do the lab. You can also look them up on the class webpage. 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on abso ...
Consider Average Stars
... measure of how much energy is being generated, how fast the fuel is being consumed, etc. So it’s something we really need to know. Question: How do astronomers describe the brightness of stars? ...
... measure of how much energy is being generated, how fast the fuel is being consumed, etc. So it’s something we really need to know. Question: How do astronomers describe the brightness of stars? ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... place as a star evolves. Most stars are on the Main Sequence because that is where stars spend most of their lives, burning hydrogen to helium through nuclear reactions. As stars live out their lives, changes in the structure of the star are reflected in changes in stars temperatures, sizes and lumi ...
... place as a star evolves. Most stars are on the Main Sequence because that is where stars spend most of their lives, burning hydrogen to helium through nuclear reactions. As stars live out their lives, changes in the structure of the star are reflected in changes in stars temperatures, sizes and lumi ...
Stars
... Life Cycle of Stars • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the univ ...
... Life Cycle of Stars • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the univ ...
Study Guide: Use your notes and handouts to
... 13. For each characteristic below, mark S – Spiral, E – Elliptical, I – Irregular for the types of galaxy it describes. For some of these characteristics, there are more than one answer. _________ Older stars reside primarily in this galaxy _________ Contains stars, gas and dust _________Younger and ...
... 13. For each characteristic below, mark S – Spiral, E – Elliptical, I – Irregular for the types of galaxy it describes. For some of these characteristics, there are more than one answer. _________ Older stars reside primarily in this galaxy _________ Contains stars, gas and dust _________Younger and ...
No Slide Title
... of an object due to the movement of the observer. Remember looking at your finger through the left and then right eye? One parsec is the distance an object must be in order to have a parallax of one arc second. One parsec = 3.3 light years Alpha Centauri is the closest star. Most stars are too dista ...
... of an object due to the movement of the observer. Remember looking at your finger through the left and then right eye? One parsec is the distance an object must be in order to have a parallax of one arc second. One parsec = 3.3 light years Alpha Centauri is the closest star. Most stars are too dista ...
Weekly Homework Questions #3, Sep. 14, 2010
... Aldebaran, the brightest star in the constellation of Taurus, which will also be visible this fall? How much brighter or fainter is it? (a) Fomalhaut is 0.36 magnitudes brighter than Aldebaran (b) Fomalhaut is 1.45 magnitudes fainter than Aldebaran (c) Fomalhaut is 2.07 magnitudes brighter than Alde ...
... Aldebaran, the brightest star in the constellation of Taurus, which will also be visible this fall? How much brighter or fainter is it? (a) Fomalhaut is 0.36 magnitudes brighter than Aldebaran (b) Fomalhaut is 1.45 magnitudes fainter than Aldebaran (c) Fomalhaut is 2.07 magnitudes brighter than Alde ...
20.1 Notes
... own gravity and rebounds with a shock wave that violently blows the stars outer layers from the core. This huge, bright explosion is called a Type II _________________________. If the core that remains after a supernova has a mass of 1.4 – 3 solar masses it becomes a _______________ star, a very den ...
... own gravity and rebounds with a shock wave that violently blows the stars outer layers from the core. This huge, bright explosion is called a Type II _________________________. If the core that remains after a supernova has a mass of 1.4 – 3 solar masses it becomes a _______________ star, a very den ...
The Life Cycle of a Star Webquest:
... 15. What is the scientific name for the twinkling of stars? ___________________________ 16. Why do stars twinkle? ____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 17. Why don’t planets twinkle? ________ ...
... 15. What is the scientific name for the twinkling of stars? ___________________________ 16. Why do stars twinkle? ____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 17. Why don’t planets twinkle? ________ ...
Astro 1 & 100 Levine Homework Stars Name:____________________________
... 1. Rank these stars in order of luminosity, from brightest to dimmest : Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Dimmest Or, all have the same luminosity ______________ 2. Rank these stars in order of apparent brightness, from brightest to dimmest: Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ __ ...
... 1. Rank these stars in order of luminosity, from brightest to dimmest : Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Dimmest Or, all have the same luminosity ______________ 2. Rank these stars in order of apparent brightness, from brightest to dimmest: Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ __ ...
Stars
... Life span of a star depends on its size and mass. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... Life span of a star depends on its size and mass. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
The Hubble Space Telescope
... and debris from the disk eventually nuclear fusion occurs and a STAR is BORN Heat and radiation create a stellar wind sweeping away lose matter, but some debris remains eventually clumping together to become ...
... and debris from the disk eventually nuclear fusion occurs and a STAR is BORN Heat and radiation create a stellar wind sweeping away lose matter, but some debris remains eventually clumping together to become ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.