Distance Measurement
... 1 arcsec d = 206265 AU = 1 parsec = 3.26 lightyears 1/10 arcsec d = 10 parsecs = 32.6 lightyears 1 arcsec 50,000 TL coin from 5 kms. So, stellar parallaxes are not visible to the naked eye RUNG 2 ...
... 1 arcsec d = 206265 AU = 1 parsec = 3.26 lightyears 1/10 arcsec d = 10 parsecs = 32.6 lightyears 1 arcsec 50,000 TL coin from 5 kms. So, stellar parallaxes are not visible to the naked eye RUNG 2 ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... Cepheid (Sef-EE-id) variable star – Star’s brightness varies at a constant pattern Brightens and fades in a cycle that can be used to determine how far away it is ...
... Cepheid (Sef-EE-id) variable star – Star’s brightness varies at a constant pattern Brightens and fades in a cycle that can be used to determine how far away it is ...
Stellar Brightness Apparent magnitude
... see into six groups. The brightest stars were in group 1 and called them magnitude 1 stars The stars they could barely see were put into group 6 – magnitude 6 stars The lower the number, the brighter the star ...
... see into six groups. The brightest stars were in group 1 and called them magnitude 1 stars The stars they could barely see were put into group 6 – magnitude 6 stars The lower the number, the brighter the star ...
Unit 11 Vocabulary
... 10. black hole - a place in space where gravity pulls so much that even light can’t get out. The gravity is so strong because matter has been squeezed into a tiny space. 11. Nebula - a cloud of gas and dust in space. Some nebulae are regions where new stars are being formed, while others are the rem ...
... 10. black hole - a place in space where gravity pulls so much that even light can’t get out. The gravity is so strong because matter has been squeezed into a tiny space. 11. Nebula - a cloud of gas and dust in space. Some nebulae are regions where new stars are being formed, while others are the rem ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... 6000 can be seen with the unaided eye Over a trillion stars can be seen with the Hubble Space Telescope Apparent Magnitude: brightness as it appears from Earth Absolute Magnitude: brightness as it appears 32.6 ly away ...
... 6000 can be seen with the unaided eye Over a trillion stars can be seen with the Hubble Space Telescope Apparent Magnitude: brightness as it appears from Earth Absolute Magnitude: brightness as it appears 32.6 ly away ...
Stars
... • They look small because they are a long way away, but in fact many are bigger and brighter than our Sun. • The heat of the star is made in the center by nuclear fusion reactions. • There are lots of different colours and sizes of stars. ...
... • They look small because they are a long way away, but in fact many are bigger and brighter than our Sun. • The heat of the star is made in the center by nuclear fusion reactions. • There are lots of different colours and sizes of stars. ...
Day 15
... couldn’t see it in the available data Mayer looked for a pattern in the measured proper motions of stars ...
... couldn’t see it in the available data Mayer looked for a pattern in the measured proper motions of stars ...
Space Science Unit - World of Teaching
... phase of the star’s life cycle the star is in and other important information about the star. • Most stars are what we consider main sequence (including our sun). They make up 90% of the stars in our sky. These stars are the diagonal strip running through the middle of the chart. ...
... phase of the star’s life cycle the star is in and other important information about the star. • Most stars are what we consider main sequence (including our sun). They make up 90% of the stars in our sky. These stars are the diagonal strip running through the middle of the chart. ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telescope pictures of a developing galactic nebula in our Milky Way Galaxy called NGC 3603. What is the next phase of our sun? ...
... sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telescope pictures of a developing galactic nebula in our Milky Way Galaxy called NGC 3603. What is the next phase of our sun? ...
PHYSICS 015
... For the most massive stars, the Schwarzschild radius is already too big. For example, if you wanted to allow a 10-solar-mass star to settle down as a neutron star, about 10 km in diameter, it already inside its Schwarzschild radius and is doomed to collapse! Stars can’t ‘know’ that they should shed ...
... For the most massive stars, the Schwarzschild radius is already too big. For example, if you wanted to allow a 10-solar-mass star to settle down as a neutron star, about 10 km in diameter, it already inside its Schwarzschild radius and is doomed to collapse! Stars can’t ‘know’ that they should shed ...
Stars Powerpoint
... – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
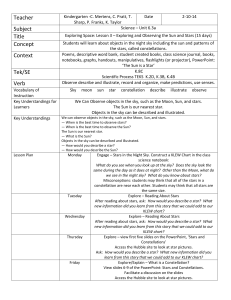
Teacher Subject Title Concept Context Tek/SE Verb
... Students will learn about objects in the night sky including the sun and patterns of the stars, called constellations. Poems, descriptive word bank, student created books, class science journal, books, notebooks, graphs, handouts, manipulatives, flashlights (or projector), PowerPoint: ‘The Sun is a ...
... Students will learn about objects in the night sky including the sun and patterns of the stars, called constellations. Poems, descriptive word bank, student created books, class science journal, books, notebooks, graphs, handouts, manipulatives, flashlights (or projector), PowerPoint: ‘The Sun is a ...
Stars and Their Characteristics
... • Luminosity (apparent magnitude)- brightness of a star at its current distance from Earth – depends on its size and temperature – Bigger stars tend to be brighter – Bluer stars tend to be brighter ...
... • Luminosity (apparent magnitude)- brightness of a star at its current distance from Earth – depends on its size and temperature – Bigger stars tend to be brighter – Bluer stars tend to be brighter ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telescope pictures of a developing galactic nebula in our Milky Way Galaxy called NGC 3603. What is the next phase of our sun? ...
... sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telescope pictures of a developing galactic nebula in our Milky Way Galaxy called NGC 3603. What is the next phase of our sun? ...
Galactic Address/Stars/Constellations
... What is a star? • A star is an object in space that produces its own light and heat through nuclear ...
... What is a star? • A star is an object in space that produces its own light and heat through nuclear ...
Basic Observations of Stars
... Distances are Hard to Measure This took centuries of hard work following Galileo’s first use of an astronomical telescope, around 1600. Success came only in 1837 (as we will learn in the next few presentations). ...
... Distances are Hard to Measure This took centuries of hard work following Galileo’s first use of an astronomical telescope, around 1600. Success came only in 1837 (as we will learn in the next few presentations). ...
Lecture 10: Stars
... & Read Chap 15.1: Properties of Stars & Overview read for recitation Chap S3: Spacetime & Gravity (Black Holes) & First Mid-Term Exam in class today (9:50am) -- 50 minutes & Observatory #3 was last night & Homework #4 due on in class on Tues & Fiske Planetarium next Thur (20 Feb) on “Black Hol ...
... & Read Chap 15.1: Properties of Stars & Overview read for recitation Chap S3: Spacetime & Gravity (Black Holes) & First Mid-Term Exam in class today (9:50am) -- 50 minutes & Observatory #3 was last night & Homework #4 due on in class on Tues & Fiske Planetarium next Thur (20 Feb) on “Black Hol ...
the life cycle of stars
... BLACK HOLE • A volume of space in which gravity is SO GREAT that nothing can escape, not even light, although objects can fall in • If the core of a supernova has a mass of more than about two Suns, its own gravity will squash it further, into a black hole. ...
... BLACK HOLE • A volume of space in which gravity is SO GREAT that nothing can escape, not even light, although objects can fall in • If the core of a supernova has a mass of more than about two Suns, its own gravity will squash it further, into a black hole. ...
Space Science Unit
... phase of the star’s life cycle the star is in and other important information about the star. • Most stars are what we consider main sequence (including our sun). They make up 90% of the stars in our sky. These stars are the diagonal strip running through the middle of the chart. ...
... phase of the star’s life cycle the star is in and other important information about the star. • Most stars are what we consider main sequence (including our sun). They make up 90% of the stars in our sky. These stars are the diagonal strip running through the middle of the chart. ...
Lecture 19 The Milky Way Galaxy
... - The galaxy is rotating: our solar system takes 225 – 250 million years to orbit the galactic center ...
... - The galaxy is rotating: our solar system takes 225 – 250 million years to orbit the galactic center ...
Classifying Stars (pages 753–754) Key Concept: Characteristics
... from Earth does not look very bright. But the sun looks very bright because it is so close to Earth. ...
... from Earth does not look very bright. But the sun looks very bright because it is so close to Earth. ...
Lecture 6: Properties of Stars The Constellations The Constellations
... o Greek astronomer Hipparchos made first known catalogue of stars in ~130-160 BC, which was added to by Ptolomy in ~150 AD. o Hipparcus grouped stars into six magnitude groups, with 1st magnitude being brightest and 6th the faintest. o In 19th century, it was shown that stars of a given magnitude ...
... o Greek astronomer Hipparchos made first known catalogue of stars in ~130-160 BC, which was added to by Ptolomy in ~150 AD. o Hipparcus grouped stars into six magnitude groups, with 1st magnitude being brightest and 6th the faintest. o In 19th century, it was shown that stars of a given magnitude ...
Figure 10-6 The same star field shown in Figure
... Hipparchus misjudged the magnitudes of some of the brighter stars, however. When the magnitude scale was extended and expressed by a mathematical formula, it developed that the brighter stars are brighter than those of the first magnitude; indeed they are even brighter than those of zero magnitude. ...
... Hipparchus misjudged the magnitudes of some of the brighter stars, however. When the magnitude scale was extended and expressed by a mathematical formula, it developed that the brighter stars are brighter than those of the first magnitude; indeed they are even brighter than those of zero magnitude. ...
Stars and Galaxies – Notes
... Many stars are found in multiple-star systems. Alpha Centauri is in a multiple star system. It is made up of three stars called a triple star system. Over half of the stars in the sky have at least one companion star. Most of these stars are doublestar systems in which two stars revolve around each ...
... Many stars are found in multiple-star systems. Alpha Centauri is in a multiple star system. It is made up of three stars called a triple star system. Over half of the stars in the sky have at least one companion star. Most of these stars are doublestar systems in which two stars revolve around each ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.