FREE Sample Here
... common knowledge before time became quantified on clocks and city lights blocked our nightly view of the sky. Most people today no longer have an understanding of the basic appearance or motions of the sky. The three Window on Science (WOS) discussions in this chapter present very important concepts ...
... common knowledge before time became quantified on clocks and city lights blocked our nightly view of the sky. Most people today no longer have an understanding of the basic appearance or motions of the sky. The three Window on Science (WOS) discussions in this chapter present very important concepts ...
chapter 2 - Test Bank 1
... common knowledge before time became quantified on clocks and city lights blocked our nightly view of the sky. Most people today no longer have an understanding of the basic appearance or motions of the sky. The three Window on Science (WOS) discussions in this chapter present very important concepts ...
... common knowledge before time became quantified on clocks and city lights blocked our nightly view of the sky. Most people today no longer have an understanding of the basic appearance or motions of the sky. The three Window on Science (WOS) discussions in this chapter present very important concepts ...
Surveying the Stars
... •Apparent positions of the nearest stars shift by only about an arcsecond as Earth orbits the Sun, and the shift is smaller for more distant stars. •These very small angles explain why the Greeks were unable to detect parallax with their naked eyes. •This inability helped delay the acceptance of the ...
... •Apparent positions of the nearest stars shift by only about an arcsecond as Earth orbits the Sun, and the shift is smaller for more distant stars. •These very small angles explain why the Greeks were unable to detect parallax with their naked eyes. •This inability helped delay the acceptance of the ...
ASTR1102-002 Potentially useful facts and mathematical relations
... parallax of 0.15 arcsec/yr. Which star is moving through space with the faster speed? a. Star “A” is moving faster than star “B”. b. Star “B” is moving faster than star “A”. c. The stars are moving through space at the same speed. d. None of the above. (Briefly explain.) ANS: ...
... parallax of 0.15 arcsec/yr. Which star is moving through space with the faster speed? a. Star “A” is moving faster than star “B”. b. Star “B” is moving faster than star “A”. c. The stars are moving through space at the same speed. d. None of the above. (Briefly explain.) ANS: ...
Magnitude Scales and Photometric Systems
... the primary standards. Later lists comprising more stars and fainter stars but based on the primary standards are called secondary standards. However, in the case of all photometric systems, recently published secondary standards effectively redefine the standard system because they tend to be more ...
... the primary standards. Later lists comprising more stars and fainter stars but based on the primary standards are called secondary standards. However, in the case of all photometric systems, recently published secondary standards effectively redefine the standard system because they tend to be more ...
SEEING STARS! SEEING STARS!
... name means. They can then draw the shape of the star pattern for their sign, and draw it to scale. The following website could help with this: www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/.../stars/comstellations.shtml ...
... name means. They can then draw the shape of the star pattern for their sign, and draw it to scale. The following website could help with this: www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/.../stars/comstellations.shtml ...
Publications 2003 - Département d`Astrophysique, Géophysique et
... challenge for current evolution scenarios in close binaries and it is also a puzzle how a massive binary with such a large eccentricity could have formed in the first place. Both the primary and the secondary exhibit line-profile variations. A period analysis performed on the radial velocity variati ...
... challenge for current evolution scenarios in close binaries and it is also a puzzle how a massive binary with such a large eccentricity could have formed in the first place. Both the primary and the secondary exhibit line-profile variations. A period analysis performed on the radial velocity variati ...
IAU-Perraut-2013 - Putting A Stars into Context
... IAU Conference « Putting A Stars into Context” Moscow, 2013 June 3rd ...
... IAU Conference « Putting A Stars into Context” Moscow, 2013 June 3rd ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Outline
... In 1911, Ejnar Hertzsprung investigated the relationship between luminosity and colors of stars in within clusters. ...
... In 1911, Ejnar Hertzsprung investigated the relationship between luminosity and colors of stars in within clusters. ...
The star Epsilon UMa, or more commonly known as Alioth
... Alpha-CV type stars are divided into three main groups depending on which spectral lines are most dominant. These three types of spectral lines are silicon, manganese, or as in Alioth’s case, chromium-strontium lines.8 These stars usually lack the more common elements that are found in stars and hav ...
... Alpha-CV type stars are divided into three main groups depending on which spectral lines are most dominant. These three types of spectral lines are silicon, manganese, or as in Alioth’s case, chromium-strontium lines.8 These stars usually lack the more common elements that are found in stars and hav ...
star - Cloudfront.net
... the region of space around them. 2. Although the stars that make up a pattern appear to be close together, they are not all the same distance from Earth. ...
... the region of space around them. 2. Although the stars that make up a pattern appear to be close together, they are not all the same distance from Earth. ...
5. cosmic distance ladder ii: standard candles
... easily calculated. However, some special types of variable and exploding stars do have known, standard luminosities. Consequently, if you can identify a star as being one of these special types, you know its luminosity. Then you only have to measure its brightness to be able to compute its distance. ...
... easily calculated. However, some special types of variable and exploding stars do have known, standard luminosities. Consequently, if you can identify a star as being one of these special types, you know its luminosity. Then you only have to measure its brightness to be able to compute its distance. ...
Learning Objectives
... easily calculated. However, some special types of variable and exploding stars do have known, standard luminosities. Consequently, if you can identify a star as being one of these special types, you know its luminosity. Then you only have to measure its brightness to be able to compute its distance. ...
... easily calculated. However, some special types of variable and exploding stars do have known, standard luminosities. Consequently, if you can identify a star as being one of these special types, you know its luminosity. Then you only have to measure its brightness to be able to compute its distance. ...
Visual Measurements of the Multiple Star
... pattern of (1) calibration of the eyepiece, (2) collecting Pulkowa. The principle instrument was an equatorial separation and position angle measurements on a refractor with a 15-inch objective lens. This was the “known “ double star (a system that has been exten- largest refractor in the world at t ...
... pattern of (1) calibration of the eyepiece, (2) collecting Pulkowa. The principle instrument was an equatorial separation and position angle measurements on a refractor with a 15-inch objective lens. This was the “known “ double star (a system that has been exten- largest refractor in the world at t ...
Application Exercise: Distances to Stars Using Measured Parallax
... Law being useful at the farthest distance (e.g., galaxies far, far away). In this exercise, we investigate the use of the measured parallax method to determine distances to nearby stars, those within about 650 light years from the Sun. Even when observed with the largest telescopes, stars are still ...
... Law being useful at the farthest distance (e.g., galaxies far, far away). In this exercise, we investigate the use of the measured parallax method to determine distances to nearby stars, those within about 650 light years from the Sun. Even when observed with the largest telescopes, stars are still ...
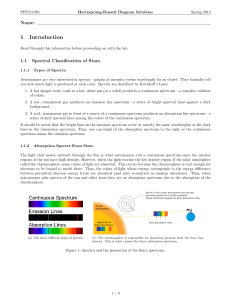
1 Introduction - High Point University
... 3. Check show luminosity classes and show isoradius lines (if they are not already checked). The green region (Dwarfs (V)) is known as the main sequence and contains all stars that are fusing hydrogen into helium as their primary energy source. Over 90% of all stars fall in this region on the H-R di ...
... 3. Check show luminosity classes and show isoradius lines (if they are not already checked). The green region (Dwarfs (V)) is known as the main sequence and contains all stars that are fusing hydrogen into helium as their primary energy source. Over 90% of all stars fall in this region on the H-R di ...
Review 3 (11-18-10)
... we can tell how large it is. Binary stars allow us to determine stellar masses ...
... we can tell how large it is. Binary stars allow us to determine stellar masses ...
... 3. THE RR LYRAE STARS IN M15 In Clement’s (2002) data base of variables stars, a total of 158 variable stars are known, from which approximately 104 are RR Lyrae type stars. In this work, 33 known RR Lyrae stars, identified in Figs. 1 and 2 and listed in Table 4, have been studied. For all the stars ...
August 2014 Saguaro Skies
... pretty bright, very slight green color. Filter brings out some detail in the outer part. Brightest part is elongated NE/SW, faint part is elongated NW/SE. WOW! 9 stars involved including central star. Next is the relatively nearby M57, another magnificent planetary nebula. It is considerably smaller ...
... pretty bright, very slight green color. Filter brings out some detail in the outer part. Brightest part is elongated NE/SW, faint part is elongated NW/SE. WOW! 9 stars involved including central star. Next is the relatively nearby M57, another magnificent planetary nebula. It is considerably smaller ...
Notes - Bill Wolf
... Astronomy with one of its worst attributes: the magnitude scales. He sought to classify the stars by their brightness with a number scale. The first group of stars to become visible at night were called magnitude one, the next group to become visible were the magnitude two stars, and so on up to mag ...
... Astronomy with one of its worst attributes: the magnitude scales. He sought to classify the stars by their brightness with a number scale. The first group of stars to become visible at night were called magnitude one, the next group to become visible were the magnitude two stars, and so on up to mag ...
Star Formation in Bok Globules - European Southern Observatory
... luminous band of the Milky Way are a number of smalI, isolated compact clouds, wh ich often exhibit a large degree of regularity. These objects are today known as Bok globules, after the Dutch-American astronomer Bart Bok, who more than 30 years aga singled out the globules as a group of special int ...
... luminous band of the Milky Way are a number of smalI, isolated compact clouds, wh ich often exhibit a large degree of regularity. These objects are today known as Bok globules, after the Dutch-American astronomer Bart Bok, who more than 30 years aga singled out the globules as a group of special int ...
star
... With the invention of the telescope, astronomers could measure the positions of stars with much greater accuracy. • The closer a star is to Earth, the greater is its parallax. • Astronomers have measured the parallax of many nearby stars and determined their distances from Earth. ...
... With the invention of the telescope, astronomers could measure the positions of stars with much greater accuracy. • The closer a star is to Earth, the greater is its parallax. • Astronomers have measured the parallax of many nearby stars and determined their distances from Earth. ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.