Stellar Evolution
... where the effective temperature of the Sun is Teff( ) = 5770 K. B. Spectral Classification. 1. The first large-scale classification of stellar spectra was undertaken by Mrs. W.P. Fleming, Antonia Maury, and Annie Jump Cannon in the 1920’s at Harvard College Observatory and became known as the Henry ...
... where the effective temperature of the Sun is Teff( ) = 5770 K. B. Spectral Classification. 1. The first large-scale classification of stellar spectra was undertaken by Mrs. W.P. Fleming, Antonia Maury, and Annie Jump Cannon in the 1920’s at Harvard College Observatory and became known as the Henry ...
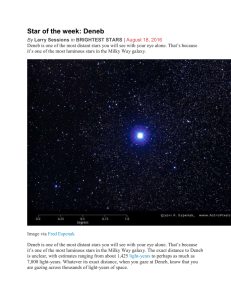
in BRIGHTEST STARS
... the figure of 3,230 light-years, whereas the refined data yield just over 1,400 light-years. At any of these estimates distances, Deneb is one of the farthest stars the unaided human eye can see. It is so far, that the light that reaches the Earth today started on its journey well more than 1,000 ye ...
... the figure of 3,230 light-years, whereas the refined data yield just over 1,400 light-years. At any of these estimates distances, Deneb is one of the farthest stars the unaided human eye can see. It is so far, that the light that reaches the Earth today started on its journey well more than 1,000 ye ...
Cepheid
... Milky Way, different from the spiral nebulae. We now realize that they are ‘dwarf’ galaxies in their own right (but not spirals). ...
... Milky Way, different from the spiral nebulae. We now realize that they are ‘dwarf’ galaxies in their own right (but not spirals). ...
Searching for the oldest, most metal-poor stars in the SkyMapper Survey
... star and to determine the chemical abundance pattern by analysis of the metal absorption lines of the spectra of each star. The nuclear fusion in the core of the star emits light, which is then absorbed by the atoms in the atmosphere of the star, causing an absorption line to appear in the spectrum. ...
... star and to determine the chemical abundance pattern by analysis of the metal absorption lines of the spectra of each star. The nuclear fusion in the core of the star emits light, which is then absorbed by the atoms in the atmosphere of the star, causing an absorption line to appear in the spectrum. ...
Direct Detection of Galactic Halo Dark Matter
... the direction of rotation, whereas W is perpendicular to the galactic disk. The calculations used to derive these velocities take into account the deviation of the velocity of the sun with respect to the average velocity of nearby stars in the Galactic disk. Because our survey was centered around th ...
... the direction of rotation, whereas W is perpendicular to the galactic disk. The calculations used to derive these velocities take into account the deviation of the velocity of the sun with respect to the average velocity of nearby stars in the Galactic disk. Because our survey was centered around th ...
File
... Consider a relatively nearby, single star, that is, a star that is not a member of a binary system and has no known orbiting planets. Listed below are a few properties of this star. Classify each property as either something that we can observe or measure directly (with the aid of a telescope and in ...
... Consider a relatively nearby, single star, that is, a star that is not a member of a binary system and has no known orbiting planets. Listed below are a few properties of this star. Classify each property as either something that we can observe or measure directly (with the aid of a telescope and in ...
Gaps
... Many open questions on HB morphology and hot HB stars nature The origine of blue tails: why hot HB stars loose so much mass? Is there any relation between fast rotation and HB morphology? How is the distribution of stellar rotation along the HB? ...
... Many open questions on HB morphology and hot HB stars nature The origine of blue tails: why hot HB stars loose so much mass? Is there any relation between fast rotation and HB morphology? How is the distribution of stellar rotation along the HB? ...
main sequence stars of a open cluster
... If a larger value is for N1912Vs.fits, the star is a red-colored one. Before going forward, quite Makali`i for a time, then start again Makali`i. 4-4. Photometry Many Stars You will photometry about 100 stars for both N1912Bs.fits and N1912Vs.fits. Adjust the viewing so that you can see faint star ...
... If a larger value is for N1912Vs.fits, the star is a red-colored one. Before going forward, quite Makali`i for a time, then start again Makali`i. 4-4. Photometry Many Stars You will photometry about 100 stars for both N1912Bs.fits and N1912Vs.fits. Adjust the viewing so that you can see faint star ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1
... • Binary stars are pairs of stars that revolve around each other and are held together by gravity. The center of mass, or barycenter, is somewhere between the two stars. • In star systems that have more than two stars, two stars may revolve rapidly around a common barycenter, while a third star revo ...
... • Binary stars are pairs of stars that revolve around each other and are held together by gravity. The center of mass, or barycenter, is somewhere between the two stars. • In star systems that have more than two stars, two stars may revolve rapidly around a common barycenter, while a third star revo ...
No. 2 - Society for Astronomical Sciences
... resulting apsidal motion can be used to anchor theories of stellar structure and orbit circularization, but it might contain a troubling discrepancy compared to the predictions of general relativity. This article reports on new times of minima and their implications. The times of minima are based on ...
... resulting apsidal motion can be used to anchor theories of stellar structure and orbit circularization, but it might contain a troubling discrepancy compared to the predictions of general relativity. This article reports on new times of minima and their implications. The times of minima are based on ...
Stars - Emera Astronomy Center
... visit. The Cosmic Classroom is one more way that the Jordan Planetarium extends its resources to help the front line teacher and support the teaching of astronomy and space science in Maine schools. The lessons in this Cosmic Classroom have been edited and selected for the range of ages/grades that ...
... visit. The Cosmic Classroom is one more way that the Jordan Planetarium extends its resources to help the front line teacher and support the teaching of astronomy and space science in Maine schools. The lessons in this Cosmic Classroom have been edited and selected for the range of ages/grades that ...
sections 7-8 instructor notes
... The effective wavelengths of the filters are determined both by the shape of the incident stellar continuum and the amount of interstellar and atmospheric reddening, which are difficult to model. The redward shift in λeff caused by atmospheric extinction or large reddening is less of a problem for ...
... The effective wavelengths of the filters are determined both by the shape of the incident stellar continuum and the amount of interstellar and atmospheric reddening, which are difficult to model. The redward shift in λeff caused by atmospheric extinction or large reddening is less of a problem for ...
Carbon Stars - The OzSky Star Safari
... Interesting Features of Carbon Stars • The brightest carbon stars are evolved cool giant stars with shells or clouds of carbon dust. • Typical surface temperatures range from 2,000 to 3,000oK. • Most classical carbon stars are long‐period irregular or semi‐regular variable stars. • Colors are m ...
... Interesting Features of Carbon Stars • The brightest carbon stars are evolved cool giant stars with shells or clouds of carbon dust. • Typical surface temperatures range from 2,000 to 3,000oK. • Most classical carbon stars are long‐period irregular or semi‐regular variable stars. • Colors are m ...
An Overview of the Gaia
... • Chemical abundances for several elements down to V~1213 (few 106 stars) • Extinction (DIB at 862.0 nm) down to V~13 (e.g. Munari et al. 2008) • ~ 40 transits will identify a large number of new spectroscopic binaries with periods < 15 yr (CU4, CU6, CU8) ...
... • Chemical abundances for several elements down to V~1213 (few 106 stars) • Extinction (DIB at 862.0 nm) down to V~13 (e.g. Munari et al. 2008) • ~ 40 transits will identify a large number of new spectroscopic binaries with periods < 15 yr (CU4, CU6, CU8) ...
There are 88 constellations in the sky around the Earth. 12 are the
... Principal stars are Hamal (Alpha ), magnitude 2.0 and Sheratan (Beta), magnitude 2.6. Mesartim (Gamma) is a nice optical double star, magnitudes 4.6 & 4.7, easily resolved with a small telescope. (Magnitude is a measure of how bright a star is – a magnitude 2 star is 2 ½ times fainter than a magnitu ...
... Principal stars are Hamal (Alpha ), magnitude 2.0 and Sheratan (Beta), magnitude 2.6. Mesartim (Gamma) is a nice optical double star, magnitudes 4.6 & 4.7, easily resolved with a small telescope. (Magnitude is a measure of how bright a star is – a magnitude 2 star is 2 ½ times fainter than a magnitu ...
A search for debris disks in the Herschel
... approach by comparing the properties of the most likely candidate disks to those of the known population. Methods. We use a photometric selection technique to identify main sequence stars in the SDSS DR7 catalogue and a Bayesian Likelihood Ratio method to identify H-ATLAS catalogue sources associate ...
... approach by comparing the properties of the most likely candidate disks to those of the known population. Methods. We use a photometric selection technique to identify main sequence stars in the SDSS DR7 catalogue and a Bayesian Likelihood Ratio method to identify H-ATLAS catalogue sources associate ...
Astronomy 114 - Department of Astronomy
... Magnitude scale Greek astronomer Hipparchus divided stars into six classes or magnitudes (2nd century BC) 1st magnitude is brightest, 6th magnitude is faintest Sensitivity of human eye is logarithmic Magnitude difference of 1 corresponds log(1000) 3 to −2.5 log(F1 /F2 ) ...
... Magnitude scale Greek astronomer Hipparchus divided stars into six classes or magnitudes (2nd century BC) 1st magnitude is brightest, 6th magnitude is faintest Sensitivity of human eye is logarithmic Magnitude difference of 1 corresponds log(1000) 3 to −2.5 log(F1 /F2 ) ...
Project 5: Globular cluster
... by gravity. Globular clusters orbit around the Milky Way galaxy core like satellites. The number of stars in a globular cluster varies from a few thousand up to a million stars for the more massive ones. There are ~150 known globular clusters that orbit our own Milky Way galaxy cor ...
... by gravity. Globular clusters orbit around the Milky Way galaxy core like satellites. The number of stars in a globular cluster varies from a few thousand up to a million stars for the more massive ones. There are ~150 known globular clusters that orbit our own Milky Way galaxy cor ...
Recent science results from VLTI commissioning
... (from North to East). The points distribution reveals an extremely oblate shape with an aspect ratio 2a/2b = 1.56±0.05. ...
... (from North to East). The points distribution reveals an extremely oblate shape with an aspect ratio 2a/2b = 1.56±0.05. ...
Chapter 19 Stars Galaxies and the Universe
... brightness of the stars with their naked eyes. They called the brightest stars they could see first-magnitude stars, and the dimmest stars, sixth-magnitude stars. When telescopes were developed, scientists discovered this system had flaws. They could see more stars with the telescope than with the n ...
... brightness of the stars with their naked eyes. They called the brightest stars they could see first-magnitude stars, and the dimmest stars, sixth-magnitude stars. When telescopes were developed, scientists discovered this system had flaws. They could see more stars with the telescope than with the n ...
Rotation Periods and Relative Ages of Solar-Type Stars
... focus attention on detecting rotation periods. This is an ongoing project in which each of its 1200 LMS stars is scheduled for several observations per week. Three measurements of that same star are typically made per night. Data presented here were obtained either from spectrophotometers on the 60- ...
... focus attention on detecting rotation periods. This is an ongoing project in which each of its 1200 LMS stars is scheduled for several observations per week. Three measurements of that same star are typically made per night. Data presented here were obtained either from spectrophotometers on the 60- ...
Neon abundances - UCL Astrophysics Group
... spectroscopy, stellar observations and analyses such as those of Auer & Mihalas, is comparable with that of C, N and O. It is also interesting because its atomic structure resembles that of He, with a very high first ionization potential (of about 22 eV). Consequently, all of its resonance lines and ...
... spectroscopy, stellar observations and analyses such as those of Auer & Mihalas, is comparable with that of C, N and O. It is also interesting because its atomic structure resembles that of He, with a very high first ionization potential (of about 22 eV). Consequently, all of its resonance lines and ...
A search for a new class of pulsating DA white dwarf stars in the DB
... dramatically in recent years as a consequence of the data available from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS; York et al. 2000). While the SDSS is primarily an extragalactic project, its uniform, relatively deep (23 mag) wide-field data set is of significant use for stellar astronomy, in particular f ...
... dramatically in recent years as a consequence of the data available from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS; York et al. 2000). While the SDSS is primarily an extragalactic project, its uniform, relatively deep (23 mag) wide-field data set is of significant use for stellar astronomy, in particular f ...
On the nature and detectability of Type Ib/c supernova progenitors
... YWL21) end their lives while they are filling their Rochelobes during Case ABB or BB mass transfer (i.e., mass transfer from the He star during/after the carbon-oxygen core contraction phase; see Yoon et al. 2010 for more details). For comparison, the evolutionary track of a single, pure helium star ...
... YWL21) end their lives while they are filling their Rochelobes during Case ABB or BB mass transfer (i.e., mass transfer from the He star during/after the carbon-oxygen core contraction phase; see Yoon et al. 2010 for more details). For comparison, the evolutionary track of a single, pure helium star ...
CHAPTER 7—ATOMS AND STARLIGHT
... ____ 21. The table below lists the spectral types for each of five stars. Which star in this table would have the have the strongest hydrogen lines? Star Name For Cet 35 Ari Tri Per ...
... ____ 21. The table below lists the spectral types for each of five stars. Which star in this table would have the have the strongest hydrogen lines? Star Name For Cet 35 Ari Tri Per ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.