
Age-Dating of Young Stars and Stellar Systems
... % of their lifetime as cool, core-He burning objects in the red part of the HRD. These stars are observationally identified as RSGs, or giants if they undergo core-helium or helium-shell flashes at masses below ∼8 M . I will later return to the importance of RSGs when emphasizing dust obscuration e ...
... % of their lifetime as cool, core-He burning objects in the red part of the HRD. These stars are observationally identified as RSGs, or giants if they undergo core-helium or helium-shell flashes at masses below ∼8 M . I will later return to the importance of RSGs when emphasizing dust obscuration e ...
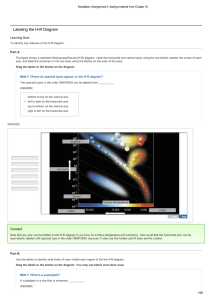
Labeling the HR Diagram - Mastering Physics Answers
... Consider a relatively nearby, single star, that is, a star that is not a member of a binary system and has no known orbiting planets. Listed below are a few properties of this star. Classify each property as either something that we can observe or measure directly (with the aid of a telescope and in ...
... Consider a relatively nearby, single star, that is, a star that is not a member of a binary system and has no known orbiting planets. Listed below are a few properties of this star. Classify each property as either something that we can observe or measure directly (with the aid of a telescope and in ...
Using Parallax to Measure the Distance of Stars
... distances, with radar being useful nearby (for example, the Moon), and the Hubble Law being useful at the farthest distances. In this exercise, we investigate the use of the trigonometric or measured parallax method to determine distances. Even when observed with the largest telescopes, stars are st ...
... distances, with radar being useful nearby (for example, the Moon), and the Hubble Law being useful at the farthest distances. In this exercise, we investigate the use of the trigonometric or measured parallax method to determine distances. Even when observed with the largest telescopes, stars are st ...
Cosmic variance in [O/Fe] in the Galactic disk
... based on their distance to the plane, age, kinematics, or chemical compositions. The kinematic properties of both disks overlap, and the available distances are not very accurate. On the other hand, the intrinsic uncertainties in the determination of abundances by the ASPCAP pipeline are very small, ...
... based on their distance to the plane, age, kinematics, or chemical compositions. The kinematic properties of both disks overlap, and the available distances are not very accurate. On the other hand, the intrinsic uncertainties in the determination of abundances by the ASPCAP pipeline are very small, ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... luminosities. These are white dwarfs, stars with radii similar to the Earth. These are dead and compact stars which have stopped energy production by nuclear fusion and are slowly becoming colder and colder. In the lectures on stellar evolution we will come back to why stars are not randomly distrib ...
... luminosities. These are white dwarfs, stars with radii similar to the Earth. These are dead and compact stars which have stopped energy production by nuclear fusion and are slowly becoming colder and colder. In the lectures on stellar evolution we will come back to why stars are not randomly distrib ...
An introduction to photometry and photometric measurements Henry
... The wavelength range, depth, and image quality for all data presently reduced and included in the version 2.0 optical / IR catalog are given in Table 2 and plotted in Figure 3. The depth quoted is for a 5 ! measurement in a 300 aperture of an isolated point source at the median seeing given in Table ...
... The wavelength range, depth, and image quality for all data presently reduced and included in the version 2.0 optical / IR catalog are given in Table 2 and plotted in Figure 3. The depth quoted is for a 5 ! measurement in a 300 aperture of an isolated point source at the median seeing given in Table ...
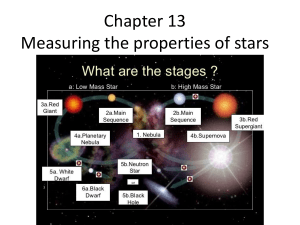
Chapter 13 Measuring the properties of stars
... The spectrum of a star shows the 656 nm absorption line shifted to 654 nm. Which of the following can we conclude about this star? A. The star is approaching us with an approximate speed of 1,800 km/sec. B. The star is receding with an approximate speed of ...
... The spectrum of a star shows the 656 nm absorption line shifted to 654 nm. Which of the following can we conclude about this star? A. The star is approaching us with an approximate speed of 1,800 km/sec. B. The star is receding with an approximate speed of ...
classifying stars
... brighter to us on earth because they are much closer than others, astronomers call this apparent magnitude (HOW BRIGHT A STAR APPEARS.) However, if astronomers could take two stars and place them exactly the same distance from earth, they could tell which one really is brighter... unfortunately, thi ...
... brighter to us on earth because they are much closer than others, astronomers call this apparent magnitude (HOW BRIGHT A STAR APPEARS.) However, if astronomers could take two stars and place them exactly the same distance from earth, they could tell which one really is brighter... unfortunately, thi ...
The DBV stars: Progress and problems
... DBV stars, and we are at a crossroads with the 1995 May run,with PG 13513-489 as the primary target. We obtained the largest telescopes possible in the northern hemisphere for this faint DBV; if we cannot get satisfactory results here, then we may have to wait until we obtain more sensitivity from o ...
... DBV stars, and we are at a crossroads with the 1995 May run,with PG 13513-489 as the primary target. We obtained the largest telescopes possible in the northern hemisphere for this faint DBV; if we cannot get satisfactory results here, then we may have to wait until we obtain more sensitivity from o ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... During the Hayashi track phases newly-formed stars are thoroughly mixed, since convection is the most efficient way of releasing energy from the object. At some stage (earlier for massive stars) the contracting star slows its contraction as the mode of energy escape changes from convective transpor ...
... During the Hayashi track phases newly-formed stars are thoroughly mixed, since convection is the most efficient way of releasing energy from the object. At some stage (earlier for massive stars) the contracting star slows its contraction as the mode of energy escape changes from convective transpor ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... During the Hayashi track phases newly-formed stars are thoroughly mixed, since convection is the most efficient way of releasing energy from the object. At some stage (earlier for massive stars) the contracting star slows its contraction as the mode of energy escape changes from convective transpor ...
... During the Hayashi track phases newly-formed stars are thoroughly mixed, since convection is the most efficient way of releasing energy from the object. At some stage (earlier for massive stars) the contracting star slows its contraction as the mode of energy escape changes from convective transpor ...
ASTRO-114--Lecture 38-
... and look up at the stars. And after a little practice, they could pick a star and tell what its magnitude was. Because you only had six numbers to choose from and usually you could tell whether it was first, ‘cause they were very bright, or whether it was sixth, because you could hardly see them, an ...
... and look up at the stars. And after a little practice, they could pick a star and tell what its magnitude was. Because you only had six numbers to choose from and usually you could tell whether it was first, ‘cause they were very bright, or whether it was sixth, because you could hardly see them, an ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... dwarfs, stars with radii similar to the Earth. These are dead and compact stars which have stopped energy production by nuclear fusion and are slowly becoming colder and colder. In the lectures on stellar evolution we will come back to why stars are not randomly distributed in a HR-diagram and why t ...
... dwarfs, stars with radii similar to the Earth. These are dead and compact stars which have stopped energy production by nuclear fusion and are slowly becoming colder and colder. In the lectures on stellar evolution we will come back to why stars are not randomly distributed in a HR-diagram and why t ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... dwarfs, stars with radii similar to the Earth. These are dead and compact stars which have stopped energy production by nuclear fusion and are slowly becoming colder and colder. In the lectures on stellar evolution we will come back to why stars are not randomly distributed in a HR-diagram and why t ...
... dwarfs, stars with radii similar to the Earth. These are dead and compact stars which have stopped energy production by nuclear fusion and are slowly becoming colder and colder. In the lectures on stellar evolution we will come back to why stars are not randomly distributed in a HR-diagram and why t ...
The HERMES GALAH survey: overview
... clumps represent stars that have some degree of common motion, and they are usually called stellar moving groups. The stars of the moving groups are all around us: they are seen as concentrations in velocity but not in position. Some of these groups are the debris of old disrupted star clusters in t ...
... clumps represent stars that have some degree of common motion, and they are usually called stellar moving groups. The stars of the moving groups are all around us: they are seen as concentrations in velocity but not in position. Some of these groups are the debris of old disrupted star clusters in t ...
Document
... • At least four supernovae have been observed in our Milky Way galaxy during the last thousand years, in 1006, 1054, 1572, and 1064. Another supernova called Supernova 1987A was observed to explode in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a companion galaxy to the Milky Way, in 1987. ...
... • At least four supernovae have been observed in our Milky Way galaxy during the last thousand years, in 1006, 1054, 1572, and 1064. Another supernova called Supernova 1987A was observed to explode in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a companion galaxy to the Milky Way, in 1987. ...
Geoscience Astronomy Formative on Stellar Evolution and
... A rapidly spinning neutron star that emits bursts of radio and optical energy is a a. supernova c. black hole b. red giant d. pulsar Pulsars emanate from a. Black holes c. White dwarfs b. Neutron stars d. Electron degenerate cores The most massive stars will collapse into a. Neutron stars c. White d ...
... A rapidly spinning neutron star that emits bursts of radio and optical energy is a a. supernova c. black hole b. red giant d. pulsar Pulsars emanate from a. Black holes c. White dwarfs b. Neutron stars d. Electron degenerate cores The most massive stars will collapse into a. Neutron stars c. White d ...
New Mass Loss Measurements from Astrospheric Lyα Absorption
... predicted by the mass-loss/activity relation defined by the less active stars, with the y Boo example being particularly relevant since the stars in this binary are easily the most solar-like of those in this high-activity regime. Thus, the location of y Boo is shown in Figure 3b in order to infer w ...
... predicted by the mass-loss/activity relation defined by the less active stars, with the y Boo example being particularly relevant since the stars in this binary are easily the most solar-like of those in this high-activity regime. Thus, the location of y Boo is shown in Figure 3b in order to infer w ...
arXiv:1705.00964v1 [astro-ph.GA] 2 May 2017
... J1819+3845 might be related to the foreground, bright star Vega. We therefore examined whether ionized gas associated with foreground stars provides a good explanation for the IDV phenomenon. Although we continue to monitor PKS1322-110, it will be some time before that data set rivals the coverage o ...
... J1819+3845 might be related to the foreground, bright star Vega. We therefore examined whether ionized gas associated with foreground stars provides a good explanation for the IDV phenomenon. Although we continue to monitor PKS1322-110, it will be some time before that data set rivals the coverage o ...
ASTRONOMY 113 Laboratory Lab 5: Spectral Classification of the
... Some of the most beautiful objects in the sky are star clusters, groups of stars ranging in number from a few hundreds of stars ("open clusters") to a few million stars ("globular star clusters"). All of the stars in these clusters are bound to each other by gravity. Star clusters are also valuable ...
... Some of the most beautiful objects in the sky are star clusters, groups of stars ranging in number from a few hundreds of stars ("open clusters") to a few million stars ("globular star clusters"). All of the stars in these clusters are bound to each other by gravity. Star clusters are also valuable ...
Science Grade 08 Unit 11 Exemplar Lesson 02: Classifying Stars
... A star’s life cycle depends on its mass. 5. Ask students to open their notebooks to the Handout: Galaxies and Stars Questions (previously distributed and affixed). 6. Project the Teacher Resource: PowerPoint: Galaxies and Stars, and discuss slides 7–9 with students. Instruct students to watch for un ...
... A star’s life cycle depends on its mass. 5. Ask students to open their notebooks to the Handout: Galaxies and Stars Questions (previously distributed and affixed). 6. Project the Teacher Resource: PowerPoint: Galaxies and Stars, and discuss slides 7–9 with students. Instruct students to watch for un ...
THE N/O RATIO IN EARLY B-TYPE MAIN SEQUENCE STARS AS
... include carbon, may contain systematic errors for stars with Teff > 18500 K because of neglected overionization of CII ions. The ratio N/O is studied in the atmospheres of 46 early main-sequence B stars. These values of N/O are examined as functions of the effective temperature, age, rotation speed, ...
... include carbon, may contain systematic errors for stars with Teff > 18500 K because of neglected overionization of CII ions. The ratio N/O is studied in the atmospheres of 46 early main-sequence B stars. These values of N/O are examined as functions of the effective temperature, age, rotation speed, ...
Hertzsprung–Russell diagram - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
... The original diagram displayed the spectral type of stars on the horizontal axis and the absolute visual magnitude on the vertical axis. The spectral type is not a numerical quantity, but the sequence of spectral types is a monotonic series ordered by stellar surface temperature. Modern observationa ...
... The original diagram displayed the spectral type of stars on the horizontal axis and the absolute visual magnitude on the vertical axis. The spectral type is not a numerical quantity, but the sequence of spectral types is a monotonic series ordered by stellar surface temperature. Modern observationa ...
STC-Scripting Guide for Celestia
... to create, you can skip them. Stars are obviously emitting light, otherwise we wouldn’t be able to see them, but they do not only have different luminosities, but also different colors. The color of a star depends on its composition and its surface temperature, similar to glowing iron. When iron is ...
... to create, you can skip them. Stars are obviously emitting light, otherwise we wouldn’t be able to see them, but they do not only have different luminosities, but also different colors. The color of a star depends on its composition and its surface temperature, similar to glowing iron. When iron is ...
Export To Word
... Collect all of the completed work and other materials from each group (H-R Diagram, Response Letter, Guiding Questions, Data Chart 1). These will be graded by the teacher at a later time (note: do not grade the H-R Diagram until the students have completed the full MEA parts 1 and 2). Using the ...
... Collect all of the completed work and other materials from each group (H-R Diagram, Response Letter, Guiding Questions, Data Chart 1). These will be graded by the teacher at a later time (note: do not grade the H-R Diagram until the students have completed the full MEA parts 1 and 2). Using the ...
Star catalogue

A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient peoples, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from NASA's Astronomical Data Center.Completeness and accuracy is described by the weakest apparent magnitude V (largest number) and the accuracy of the positions.

![Cosmic variance in [O/Fe] in the Galactic disk](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014331057_1-996ec6eddf93071c5e835624d4620c7e-300x300.png)










![arXiv:1705.00964v1 [astro-ph.GA] 2 May 2017](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/013011793_1-8f89fb3e8b5cd5cf78613aebb3c8e2a5-300x300.png)





