1-Development of the Spinal Cord & Vertebral Column 2015+++
... Development of the Vertebral Column The vertebral column develops from the ...
... Development of the Vertebral Column The vertebral column develops from the ...
Here - Statistical Analysis of Neuronal Data
... And yet, these models have not incorporated information about the spatial interrelationships between recording sites despite the fact that MI is a highly spatially distributed cortical area with heterogeneous response properties. We hypothesized that consideration of spatial information in simultane ...
... And yet, these models have not incorporated information about the spatial interrelationships between recording sites despite the fact that MI is a highly spatially distributed cortical area with heterogeneous response properties. We hypothesized that consideration of spatial information in simultane ...
FREE Sample Here
... motor nerves exit the vertebral column between each vertebral bone resulting in 31 discrete nerve segments. The area that is innervated by each of the 31 spinal nerves is called a dermatome. The motor cortex and somatosensory cortex respectively located in the frontal and parietal lobes are organize ...
... motor nerves exit the vertebral column between each vertebral bone resulting in 31 discrete nerve segments. The area that is innervated by each of the 31 spinal nerves is called a dermatome. The motor cortex and somatosensory cortex respectively located in the frontal and parietal lobes are organize ...
Consciousness Operates Beyond the Timescale
... the equivalent of 20/400 vision – about the same as a severely nearsighted person – in a narrow field. Although the relatively small electrode array produces tunnel vision, the patient is also able to navigate in unfamiliar environments including the New York City subway system. One other patient wh ...
... the equivalent of 20/400 vision – about the same as a severely nearsighted person – in a narrow field. Although the relatively small electrode array produces tunnel vision, the patient is also able to navigate in unfamiliar environments including the New York City subway system. One other patient wh ...
Evidence for parasympathetic innervation of white adipose tissue
... only sympathetic but also parasympathetic innervation (5). Using microsurgery, transneuronal retrograde tracing, and hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamps, we demonstrated that parasympathetic innervation of fat tissue has an anabolic effect and stimulated fat growth. In a follow-up paper on body fat d ...
... only sympathetic but also parasympathetic innervation (5). Using microsurgery, transneuronal retrograde tracing, and hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamps, we demonstrated that parasympathetic innervation of fat tissue has an anabolic effect and stimulated fat growth. In a follow-up paper on body fat d ...
12 - Dr. Jerry Cronin
... • Visual association area – Surrounds primary visual cortex – Uses past visual experiences to interpret visual stimuli (e.g., color, form, and movement) • E.g., ability to recognize faces ...
... • Visual association area – Surrounds primary visual cortex – Uses past visual experiences to interpret visual stimuli (e.g., color, form, and movement) • E.g., ability to recognize faces ...
The dual-pathway model of auditory signal
... tral stream, is crucial for identifying objects, and the occipitoparietal pathway, or dorsal stream, is crucial for judging spatial locations and/or spatial relations among objects guiding movements in the space[3,5]. Specifically, neurons in the areas of the ventral stream selectively respond to sh ...
... tral stream, is crucial for identifying objects, and the occipitoparietal pathway, or dorsal stream, is crucial for judging spatial locations and/or spatial relations among objects guiding movements in the space[3,5]. Specifically, neurons in the areas of the ventral stream selectively respond to sh ...
An optical neural interface: in vivo control of rodent
... outputs 20 mW of power at 473 nm, and is coupled to a lightweight, flexible multimode optical fiber, ∼200 µm in diameter. To capitalize on the unique advantages of this system, we specifically targeted ChR2 to excitatory cells in vivo with the CaMKIIα promoter. Under these conditions, the intensity ...
... outputs 20 mW of power at 473 nm, and is coupled to a lightweight, flexible multimode optical fiber, ∼200 µm in diameter. To capitalize on the unique advantages of this system, we specifically targeted ChR2 to excitatory cells in vivo with the CaMKIIα promoter. Under these conditions, the intensity ...
An optical neural interface: in vivo control of
... outputs 20 mW of power at 473 nm, and is coupled to a lightweight, flexible multimode optical fiber, ∼200 µm in diameter. To capitalize on the unique advantages of this system, we specifically targeted ChR2 to excitatory cells in vivo with the CaMKIIα promoter. Under these conditions, the intensity ...
... outputs 20 mW of power at 473 nm, and is coupled to a lightweight, flexible multimode optical fiber, ∼200 µm in diameter. To capitalize on the unique advantages of this system, we specifically targeted ChR2 to excitatory cells in vivo with the CaMKIIα promoter. Under these conditions, the intensity ...
The Different Neural Correlates of Action and Functional Knowledge
... fMRI Data Acquisition Anatomical T1-weighted and functional T2*-weighted MR images were acquired with a 3 Tesla Philips Intera scanner (Philips Medical Systems, Best, the Netherlands), using an 8-channel Sense head coil (sense reduction factor = 2). Functional images were acquired using a T2*weighte ...
... fMRI Data Acquisition Anatomical T1-weighted and functional T2*-weighted MR images were acquired with a 3 Tesla Philips Intera scanner (Philips Medical Systems, Best, the Netherlands), using an 8-channel Sense head coil (sense reduction factor = 2). Functional images were acquired using a T2*weighte ...
Cortex - Anatomy and Physiology
... • Visual association area – Surrounds primary visual cortex – Uses past visual experiences to interpret visual stimuli (e.g., color, form, and movement) • E.g., ability to recognize faces ...
... • Visual association area – Surrounds primary visual cortex – Uses past visual experiences to interpret visual stimuli (e.g., color, form, and movement) • E.g., ability to recognize faces ...
600 Kb PDF
... Proprioceptive feedback was provided for each movement within the virtual world as well as for the effects of those movements from collisions with walls or barriers. Feedback into the neuronal network was accomplished by inducing neural activity near one of five possible electrodes using custom hard ...
... Proprioceptive feedback was provided for each movement within the virtual world as well as for the effects of those movements from collisions with walls or barriers. Feedback into the neuronal network was accomplished by inducing neural activity near one of five possible electrodes using custom hard ...
Lecture #6 Notes
... on both the sensory and the motor side—consist of several neurons linked by synapses to form a chain with synapses. (The stretch reflex is an exception to this rule.) Part of your job is to learn where the synapses are located along each pathway we talk about. 4. The thalamus is a major center for r ...
... on both the sensory and the motor side—consist of several neurons linked by synapses to form a chain with synapses. (The stretch reflex is an exception to this rule.) Part of your job is to learn where the synapses are located along each pathway we talk about. 4. The thalamus is a major center for r ...
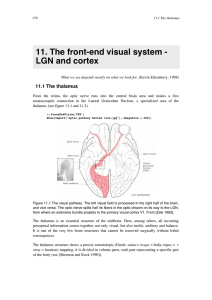
11. The front-end visual system - LGN and cortex
... One speculative option is that they may be modeled as processing some (polynomial?) function of the neighboring derivative cells, and thus be involved in complex differential features (see also [Alonso1998a]). As Ohzawa states: "Complex cell receptive fields are not that interesting when measured wi ...
... One speculative option is that they may be modeled as processing some (polynomial?) function of the neighboring derivative cells, and thus be involved in complex differential features (see also [Alonso1998a]). As Ohzawa states: "Complex cell receptive fields are not that interesting when measured wi ...
Visual Prostheses: Current Progress and Challenges
... surgical challenge. As to epi-retinal versus sub-retinal, the epiretinal approach is easier form a surgical point of view but the mechanical anchoring of the implant to the epi-retinal surface is difficult[2]. This can be partially alleviated by placing the device subretinally[3], though the surgery ...
... surgical challenge. As to epi-retinal versus sub-retinal, the epiretinal approach is easier form a surgical point of view but the mechanical anchoring of the implant to the epi-retinal surface is difficult[2]. This can be partially alleviated by placing the device subretinally[3], though the surgery ...
PDF
... Serial reconstructions or tangential sections, parallel to the pia and layer 1, reveal that what appear to be columns in cross section have a variety of shapes and sizes. Ocular dominance columns, one of the textbook examples of columnar organization, are actually slab-like domains; and column width ...
... Serial reconstructions or tangential sections, parallel to the pia and layer 1, reveal that what appear to be columns in cross section have a variety of shapes and sizes. Ocular dominance columns, one of the textbook examples of columnar organization, are actually slab-like domains; and column width ...
Ch03.pps
... what it can do. This lecture will show that the brain plays an important part in everything we think and do. © West Educational Publishing ...
... what it can do. This lecture will show that the brain plays an important part in everything we think and do. © West Educational Publishing ...
Executive function
... forty years, however, have established links between performance of certain paradigms which putatively make demands upon executive processes and the operation of prefrontal cortex, as assessed by human lesion studies, functional neuroimaging, and other methods (such as electrophysiology). There are ...
... forty years, however, have established links between performance of certain paradigms which putatively make demands upon executive processes and the operation of prefrontal cortex, as assessed by human lesion studies, functional neuroimaging, and other methods (such as electrophysiology). There are ...
Segregation and convergence of specialised pathways in
... The experiments reported here reveal no further divergence between these channels: both types of V4 subcompartment make rather similar patterns of connection with further visual areas and subcortical structures. In contrast to V4, area V5 receives input from the thick stripes of V2. V4 and V5 are we ...
... The experiments reported here reveal no further divergence between these channels: both types of V4 subcompartment make rather similar patterns of connection with further visual areas and subcortical structures. In contrast to V4, area V5 receives input from the thick stripes of V2. V4 and V5 are we ...
The Neural Control of Speech
... Since 1992, our laboratory has developed and refined a neural network model that provides a quantitative account of the interactions between motor, somatosensory, and auditory cortical areas that underlie speech motor control. Because a central aspect of the model concerns how the brain transforms ...
... Since 1992, our laboratory has developed and refined a neural network model that provides a quantitative account of the interactions between motor, somatosensory, and auditory cortical areas that underlie speech motor control. Because a central aspect of the model concerns how the brain transforms ...
Structural divisions and functional fields in the human cerebral cortex 1
... Microstructural parcellation of the human cerebral cortex should be made on multiple criteria based on quantitative measurements of microstructural variables, such as neuron densities, neurotransmitter receptor densities, enzyme densities, etc. Because of the inter-individual variations of extent an ...
... Microstructural parcellation of the human cerebral cortex should be made on multiple criteria based on quantitative measurements of microstructural variables, such as neuron densities, neurotransmitter receptor densities, enzyme densities, etc. Because of the inter-individual variations of extent an ...
thalamus
... Afferents: Visual from the optic tract Projects to primary visual cortex in occipital cortex ( Area 17). ...
... Afferents: Visual from the optic tract Projects to primary visual cortex in occipital cortex ( Area 17). ...
Analogy = Computer
... B. Cerebrum (cerebral hemispheres): 1) Cerebral cortex: • Contains 3 types of functional areas • Contralateral control (e.g., left hemisphere controls right body) ...
... B. Cerebrum (cerebral hemispheres): 1) Cerebral cortex: • Contains 3 types of functional areas • Contralateral control (e.g., left hemisphere controls right body) ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... Extrapyrimidal System- all portions of the brain and brain stem that contribute to motor control but are not part of the direct scorticospinal-pyramidal system a. Include the basal ganglia, reticular formation, and the vestibular nuclei ...
... Extrapyrimidal System- all portions of the brain and brain stem that contribute to motor control but are not part of the direct scorticospinal-pyramidal system a. Include the basal ganglia, reticular formation, and the vestibular nuclei ...
asgn2d -- CEREBRAL CORTEX:
... Q5.. The brain can tell the difference between a touch on the cheek and a touch on the hand because A. different places on the somatosensory ("touch") area become active B. it relates touch to vision which tells where the touch was C. it feels the touch at different places D. anatomical or labeled l ...
... Q5.. The brain can tell the difference between a touch on the cheek and a touch on the hand because A. different places on the somatosensory ("touch") area become active B. it relates touch to vision which tells where the touch was C. it feels the touch at different places D. anatomical or labeled l ...
Cortical cooling
Neuroscientists generate various studies to help explain many of the complex connections and functions of the brain. Most studies utilize animal models that have varying degrees of comparison to the human brain; for example, small rodents are less comparable than non-human primates. One of the most definitive ways of determining which sections of the brain contribute to certain behavior or function is to deactivate a section of the brain and observe what behavior is altered. Investigators have a wide range of options for deactivating neural tissue, and one of the more recently developed methods being used is deactivation through cooling. Cortical cooling refers to the cooling methods restricted to the cerebral cortex, where most higher brain processes occur. Below is a list of current cooling methods, their advantages and limitations, and some studies that have used cooling to elucidate neural functions.