Psychopharmacology of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder.1998
... there is limited information about posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), since the drug treatment of this disorder has been admixed with the literature on the treatment of anxiety, panic disorder, depression, and borderline personality disorder (all of which include trauma survivors). As those of us ...
... there is limited information about posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), since the drug treatment of this disorder has been admixed with the literature on the treatment of anxiety, panic disorder, depression, and borderline personality disorder (all of which include trauma survivors). As those of us ...
Silent Killers-NATASHA Stewart 05.04.16
... ▪ There are at least three different types of stress, all of which carry physical and mental health risks: ...
... ▪ There are at least three different types of stress, all of which carry physical and mental health risks: ...
Stress Management - University Counseling Services @ Truman
... http://ucs.truman.edu ucs@truman.edu/how was it ...
... http://ucs.truman.edu ucs@truman.edu/how was it ...
Anxiety, Somatoform, Dissociative Disorders and Stress
... During the movie you will be trying to identify what behaviors Mr. Udall shows that are part of his obsessive compulsive disorder and which behaviors are part of his personality and if there are any other behaviors which might indicate ...
... During the movie you will be trying to identify what behaviors Mr. Udall shows that are part of his obsessive compulsive disorder and which behaviors are part of his personality and if there are any other behaviors which might indicate ...
Anxiety and Mood Disorders
... Classical conditioning model e.g., dog = CS, bite = UCS problems: often no memory of a traumatic experience traumatic experience may not produce phobia ...
... Classical conditioning model e.g., dog = CS, bite = UCS problems: often no memory of a traumatic experience traumatic experience may not produce phobia ...
Disorders and treatment – KEY TERMS 1. Hallucinations 2
... In this portion of the course, students examine the nature of common challenges to adaptive functioning. This section emphasizes formal conventions that guide psychologists’ judgments about diagnosis and problem severity. AP students in psychology should be able to do the following: • Describe conte ...
... In this portion of the course, students examine the nature of common challenges to adaptive functioning. This section emphasizes formal conventions that guide psychologists’ judgments about diagnosis and problem severity. AP students in psychology should be able to do the following: • Describe conte ...
Somatoform Disorders
... • Pain that causes clinically significant distress or impairment in functioning • There may have been clear physical reasons for the pain initially, but psychological factors play a major role in maintaining it. • The pain is real & it hurts regardless of the cause • Whatever its cause, the pain has ...
... • Pain that causes clinically significant distress or impairment in functioning • There may have been clear physical reasons for the pain initially, but psychological factors play a major role in maintaining it. • The pain is real & it hurts regardless of the cause • Whatever its cause, the pain has ...
Mental and Emotional Problems
... Anorexia nervosa- extreme fear of gaining weight. They tend to starve themselves and exercise excessively. They maybe thin but they see themselves as fat. ...
... Anorexia nervosa- extreme fear of gaining weight. They tend to starve themselves and exercise excessively. They maybe thin but they see themselves as fat. ...
has
... _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
... _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
Disorder therapy ppt - Fort Bend ISD / Homepage
... chest pain, choking and other frightening sensations. ...
... chest pain, choking and other frightening sensations. ...
Methods and Ethics of Psychology
... Phobic Disorders - marked, persistent, and excessive fear and avoidance of specific objects, activities, or situations ...
... Phobic Disorders - marked, persistent, and excessive fear and avoidance of specific objects, activities, or situations ...
Chapter 5
... over time) • 15% of all Teens will display some signs of depression • Most common mental health concerns ...
... over time) • 15% of all Teens will display some signs of depression • Most common mental health concerns ...
How Mental Illness and Addiction Influence Each Other
... Neuro-chemical deficiencies have been linked to mental illnesses Some of these deficiencies are found in dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine ...
... Neuro-chemical deficiencies have been linked to mental illnesses Some of these deficiencies are found in dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine ...
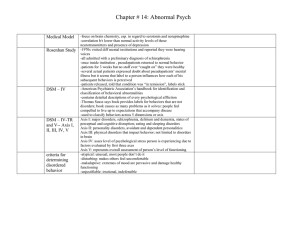
Medical Model - Biloxi Public Schools
... maladaptive and does not want to have them but cannot control them -caused by exposure to trauma (ex: war or violence) which leads to recurring thoughts and anxiety linked to trauma -decreased ability to function, detachment from reality -restlessness, irritability, sleep impairment, loss of concent ...
... maladaptive and does not want to have them but cannot control them -caused by exposure to trauma (ex: war or violence) which leads to recurring thoughts and anxiety linked to trauma -decreased ability to function, detachment from reality -restlessness, irritability, sleep impairment, loss of concent ...
Chapter 10: Mental Disorders What Are Mental Disorders?
... Illnesses of the mind that can affect the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of a person, preventing him or her from leading a happy, healthful, and productive life. People who suffer from mental disorders are often identified by their inability to cope in healthful ways with life’s changes, dema ...
... Illnesses of the mind that can affect the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of a person, preventing him or her from leading a happy, healthful, and productive life. People who suffer from mental disorders are often identified by their inability to cope in healthful ways with life’s changes, dema ...
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
... purging. Weight is often normal. Binge Eating Disorder: compulsive overeating without attempting to purge ...
... purging. Weight is often normal. Binge Eating Disorder: compulsive overeating without attempting to purge ...
Review Documents #8: Chapter 16
... Four diagnostic criteria (UMAD): Time period for clinical diagnosis: __________ (that symptoms must be consistently present) Neurotic: Psychotic: ...
... Four diagnostic criteria (UMAD): Time period for clinical diagnosis: __________ (that symptoms must be consistently present) Neurotic: Psychotic: ...
Psychological Disorders
... Very rare; .5% - 1% suffer from this disorder Characterized by a loss of contact with reality Can develop gradually or very quickly Worsens over time Very difficult to treat 20% with schizophrenia will attempt suicide; 10% of ...
... Very rare; .5% - 1% suffer from this disorder Characterized by a loss of contact with reality Can develop gradually or very quickly Worsens over time Very difficult to treat 20% with schizophrenia will attempt suicide; 10% of ...
Referral Criteria for Specialist CAMHS What we do The core
... • Severe or debilitating Anxiety panic attacks • Separation anxiety which severely impacts on the child’s functioning • Phobias including phobic anxiety Depression • Physical symptoms – poor sleep/appetite/ libido ...
... • Severe or debilitating Anxiety panic attacks • Separation anxiety which severely impacts on the child’s functioning • Phobias including phobic anxiety Depression • Physical symptoms – poor sleep/appetite/ libido ...
acute and postraumatic stress disorders, dissociative disorders, and
... SOMATOFORM DISORDERS Diagnosis of Somatoform Disorders Conversion Disorder ...
... SOMATOFORM DISORDERS Diagnosis of Somatoform Disorders Conversion Disorder ...
to open a document about Dissociation
... There is a retrospective gap in memory, which is usually related to traumatic, extremely stressful events, and is more likely to occur in wartime, or as a result of a natural disaster or other forms of severe trauma. 2. Dissociative Fugue: "Sudden, unexpected travel away from home, or one's customar ...
... There is a retrospective gap in memory, which is usually related to traumatic, extremely stressful events, and is more likely to occur in wartime, or as a result of a natural disaster or other forms of severe trauma. 2. Dissociative Fugue: "Sudden, unexpected travel away from home, or one's customar ...