- Cezar Giosan`s Website
... Weill Medical College of Cornell University, Dept of Psychiatry Assistant Professor of Psychology Worked with populations in high-risk occupations (e.g., disaster relief workers, military personnel). Statistical analyses of various research projects. Research on psychological consequences of t ...
... Weill Medical College of Cornell University, Dept of Psychiatry Assistant Professor of Psychology Worked with populations in high-risk occupations (e.g., disaster relief workers, military personnel). Statistical analyses of various research projects. Research on psychological consequences of t ...
Midterm Examination Stress and Coping – PSY 325 Siena Heights
... A. Membership in formal and informal groups and organizations B. Family and friends C. Membership in informal groups and organizations D. Family, friends, and coworkers ...
... A. Membership in formal and informal groups and organizations B. Family and friends C. Membership in informal groups and organizations D. Family, friends, and coworkers ...
Chapter 16 Notes
... iv. Some people have episodes separated by long intervals of normal behavior, others have no normal behavior and just alternate between the two d. Seasonal Affective Disorder i. In winter these people develop a deep depression ii. Spirits only lift with the coming of spring iii. Tend to sleep and ea ...
... iv. Some people have episodes separated by long intervals of normal behavior, others have no normal behavior and just alternate between the two d. Seasonal Affective Disorder i. In winter these people develop a deep depression ii. Spirits only lift with the coming of spring iii. Tend to sleep and ea ...
Psychological Disorders ppt - kyle
... B. Symptoms of Psychological Disorders • Note: Just because someone may exhibit some of these symptoms it does NOT necessarily mean that they definitely have a psychological disorder! • It is EXTREMELY difficult to diagnose someone with a psychological disorder ...
... B. Symptoms of Psychological Disorders • Note: Just because someone may exhibit some of these symptoms it does NOT necessarily mean that they definitely have a psychological disorder! • It is EXTREMELY difficult to diagnose someone with a psychological disorder ...
Clinical Psychology
... • The person has some permanent personality characteristics which often deviate from social norms and can cause distress to others, for example, a psychopath may display superficial charm and pathological lying ...
... • The person has some permanent personality characteristics which often deviate from social norms and can cause distress to others, for example, a psychopath may display superficial charm and pathological lying ...
Dissociative dis
... clouding of consciousness, somatic conversion symptoms, confusion, stress, loss of personal identity, echolalia, and echopraxia. Individuals also give approximate answers to simple questions. For example, "How many legs are on a cat?", to which the subject may respond '3?'. The syndrome may occur in ...
... clouding of consciousness, somatic conversion symptoms, confusion, stress, loss of personal identity, echolalia, and echopraxia. Individuals also give approximate answers to simple questions. For example, "How many legs are on a cat?", to which the subject may respond '3?'. The syndrome may occur in ...
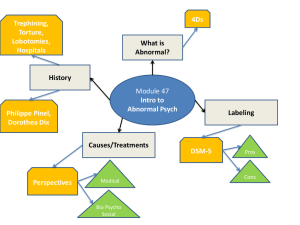
abnormal defining and labeling disorders
... • French physician who worked to reform the treatment of people with mental disorders • Encouraged more humane treatment ...
... • French physician who worked to reform the treatment of people with mental disorders • Encouraged more humane treatment ...
Unit 8, Abnormal Psychology
... leads to the growth of an individual and a new positive view on life. ...
... leads to the growth of an individual and a new positive view on life. ...
Terms in Psychiatry - Northwest Technology Center
... •Ability to function at school, home or work is affected •Individuals are referred to as addicts ...
... •Ability to function at school, home or work is affected •Individuals are referred to as addicts ...
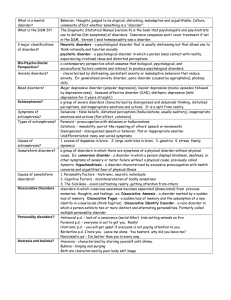
Psychological Disorders notes
... Major depressive disorder (unipolar depression), bipolar depression (mainic episodes followed by depressive ones), Seasonal affective disorder (SAD), disthymic depression (mild depression for 2 years straight.) a group of severe disorders characterized by disorganized and delusional thinking, distur ...
... Major depressive disorder (unipolar depression), bipolar depression (mainic episodes followed by depressive ones), Seasonal affective disorder (SAD), disthymic depression (mild depression for 2 years straight.) a group of severe disorders characterized by disorganized and delusional thinking, distur ...
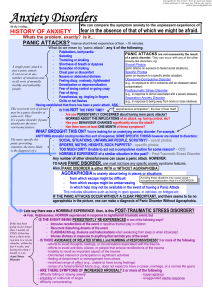
Anxiety Disorders - Deranged Physiology
... Target the distorted threat appraisal process (e.g., through repeated exposure or through techniques focusing on information processing without repeated exposure) in an effort to desensitize the patient to trauma-related triggers. • May speed recovery and prevent PTSD when therapy is given 2 to 3 we ...
... Target the distorted threat appraisal process (e.g., through repeated exposure or through techniques focusing on information processing without repeated exposure) in an effort to desensitize the patient to trauma-related triggers. • May speed recovery and prevent PTSD when therapy is given 2 to 3 we ...
Chapter 5: Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... – Dissociative amnesia and fugue usually begin in adulthood – Both conditions show rapid onset and dissipation – Both conditions occur most often in females • Causes – Little is known, but trauma and stress seem heavily involved • Treatment – Persons with dissociative amnesia and fugue usually get b ...
... – Dissociative amnesia and fugue usually begin in adulthood – Both conditions show rapid onset and dissipation – Both conditions occur most often in females • Causes – Little is known, but trauma and stress seem heavily involved • Treatment – Persons with dissociative amnesia and fugue usually get b ...
Abnormal Psychology - North Cobb High School Class Websites
... of a car wreck who has no memory what happened before the accident • anterograde amnesia happens when a person can recall only small parts of events that took place after an event; a survivor of a car wreck who has no memory what happened after the accident ...
... of a car wreck who has no memory what happened before the accident • anterograde amnesia happens when a person can recall only small parts of events that took place after an event; a survivor of a car wreck who has no memory what happened after the accident ...
Psychological Disorders notes 16-1 objectives 1-4
... disease from another. Treatment: Treating a disorder in a psychiatric hospital. Prognosis: Forecast about the disorder. ...
... disease from another. Treatment: Treating a disorder in a psychiatric hospital. Prognosis: Forecast about the disorder. ...
File
... Questions to Consider See textbook for objectives! 1. Describe contemporary and historical conceptions of what constitutes psychological disorders. 2. Recognize the use of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manula of Mental Disorders (DSM) published by the American Psychiatric Associaiton as the primary ...
... Questions to Consider See textbook for objectives! 1. Describe contemporary and historical conceptions of what constitutes psychological disorders. 2. Recognize the use of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manula of Mental Disorders (DSM) published by the American Psychiatric Associaiton as the primary ...
Ch. 18: Psychological Disorders Sec. 1: Understanding
... Psychological disorders are illnesses that an individual experiences as episodes. In contrast, personality disorders are enduring traits that are major components of the ...
... Psychological disorders are illnesses that an individual experiences as episodes. In contrast, personality disorders are enduring traits that are major components of the ...
Abnormal Psychology
... and some get irritable). • Engage in risky behavior during the manic episode. ...
... and some get irritable). • Engage in risky behavior during the manic episode. ...
Abnormal Psychology - AP Psychology Community
... and some get irritable). • Engage in risky behavior during the manic episode. ...
... and some get irritable). • Engage in risky behavior during the manic episode. ...
Dissociative Disorders
... b. Each personality maintains its own identity, name, and distinctive behavior pattern. c. The diagnosis of this disorder is controversial. Even research showing different brain wave patterns for personalities is now suspect since others have shown an ability to produce different brain waves on ...
... b. Each personality maintains its own identity, name, and distinctive behavior pattern. c. The diagnosis of this disorder is controversial. Even research showing different brain wave patterns for personalities is now suspect since others have shown an ability to produce different brain waves on ...
Overheads – Abnormal Psychology
... Issue: could they tell right from wrong of have ability to control their actions? Severely psychotic or severely mentally retarded persons = insane. Rarely a successful defense. ...
... Issue: could they tell right from wrong of have ability to control their actions? Severely psychotic or severely mentally retarded persons = insane. Rarely a successful defense. ...
Abnormal Psychology cracking Mac
... Compulsions- repetitive behaviors that are time consuming and maladaptive Example – germs and washing hands (lots of time and thought associated) ...
... Compulsions- repetitive behaviors that are time consuming and maladaptive Example – germs and washing hands (lots of time and thought associated) ...