Evidence-Based Screening Instruments for Co
... prevalence rates of behavioral health and related disorders in justice settings ...
... prevalence rates of behavioral health and related disorders in justice settings ...
NIMH Co-Occurring Disorders Curriculum
... prevalence rates of behavioral health and related disorders in justice settings ...
... prevalence rates of behavioral health and related disorders in justice settings ...
Ch. 18 S. 2
... • Stress Disorders – Stress disorders include posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and acute stress disorder. The two disorders have similar symptoms, but they differ in how quickly they occur after the traumatic event that triggers the disorder. They also differ in how long they last. Post-traumat ...
... • Stress Disorders – Stress disorders include posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and acute stress disorder. The two disorders have similar symptoms, but they differ in how quickly they occur after the traumatic event that triggers the disorder. They also differ in how long they last. Post-traumat ...
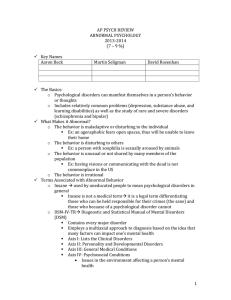
UNIT THREE - STRESS MANAGEMENT
... a situation. Cognitive therapy aims to change unwanted or maladaptive thoughts and beliefs. Behaviourists believe that undesirable behaviours have been learned, therefore behavioural therapy aims to reverse the learning process in order to produce a new set of more desirable behaviours. CBT links th ...
... a situation. Cognitive therapy aims to change unwanted or maladaptive thoughts and beliefs. Behaviourists believe that undesirable behaviours have been learned, therefore behavioural therapy aims to reverse the learning process in order to produce a new set of more desirable behaviours. CBT links th ...
Chapter 15 pt. 1: Perspectives on Psychological Disorders and Anxiety
... individual genes, brain structures and chemistry) ...
... individual genes, brain structures and chemistry) ...
psychological disorders
... “Negative emotions contribute to physical illness, and physical abnormalities contribute to negative emotions. We are mind embodied.” - David Myers ...
... “Negative emotions contribute to physical illness, and physical abnormalities contribute to negative emotions. We are mind embodied.” - David Myers ...
dissociative disorders - NAMI Southern Arizona
... later recall what happened during their dissociation, but others may not be able to remember significant parts of what occurred, sometimes for even a time before they dissociated. There is an association between traumatic events and the process of dissociation. It may be that dissociation is a way t ...
... later recall what happened during their dissociation, but others may not be able to remember significant parts of what occurred, sometimes for even a time before they dissociated. There is an association between traumatic events and the process of dissociation. It may be that dissociation is a way t ...
Somatisation medical students
... pains and am frequently sick.’ ‘There’s a big question mark on the reason for this illness. I went through several medical exams but the doctors can’t quite seem to find a reason. I hit balls for half an hour and then have to stop because I’m just too tired.’ ...
... pains and am frequently sick.’ ‘There’s a big question mark on the reason for this illness. I went through several medical exams but the doctors can’t quite seem to find a reason. I hit balls for half an hour and then have to stop because I’m just too tired.’ ...
Psychology Class- XII Sample Question Paper – 2017 Time – 3
... Somatoform disorders are conditions in which there are physical symptoms in the absence of physical disease. The individual has psychological difficulties and complains of physical symptoms for which there are no biological cause. It includes the following: Pain disorder: Hypochondriasis : Somatisat ...
... Somatoform disorders are conditions in which there are physical symptoms in the absence of physical disease. The individual has psychological difficulties and complains of physical symptoms for which there are no biological cause. It includes the following: Pain disorder: Hypochondriasis : Somatisat ...
Abnormal Psych2014 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... Depressed episodes are those described in unipolar depression Manic episodes include heightened sense of self confidence, anxiety, inflated sense of well-being, and engage in risky behaviors Some can experience mania without depression o Dysthymic disorder Symptoms similar to major depressio ...
... Depressed episodes are those described in unipolar depression Manic episodes include heightened sense of self confidence, anxiety, inflated sense of well-being, and engage in risky behaviors Some can experience mania without depression o Dysthymic disorder Symptoms similar to major depressio ...
Psychology Chapter 19: Group Interaction
... aa. Loneliness of old age c. An effort to end the torment of unacceptable feelings d. To punish themselves for wrongs they committed e. To punish others f. Many times there is no explanation iv. More than 30,000 Americans end their lives by suicide a. 1 every 20 minutes v. More women than men attemp ...
... aa. Loneliness of old age c. An effort to end the torment of unacceptable feelings d. To punish themselves for wrongs they committed e. To punish others f. Many times there is no explanation iv. More than 30,000 Americans end their lives by suicide a. 1 every 20 minutes v. More women than men attemp ...
Somatoform Disorders Somatoform Disorders Hypochondriasis
... Involves dissociative symptoms and sudden changes in personality Symptoms and personality changes are often attributed to possession by a spirit Symptoms must be considered undesirable/pathological by the culture ...
... Involves dissociative symptoms and sudden changes in personality Symptoms and personality changes are often attributed to possession by a spirit Symptoms must be considered undesirable/pathological by the culture ...
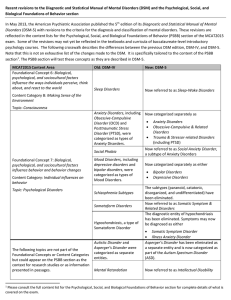
Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental
... Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) and the Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior section In May 2013, the American Psychiatric Association published the 5th edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorder ...
... Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) and the Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior section In May 2013, the American Psychiatric Association published the 5th edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorder ...
Anxiety, Somatoform, and Dissociative Disorders Homework
... Te person spends a lot of time looking for signs of serious illness. He or she thinks any minor pain is a sign of fatal illness. In spite of medical reports showing nothing wrong, a hypochondriac will continue to believe a disease exists. Like conversion, hypochondriasis is a physical expression of ...
... Te person spends a lot of time looking for signs of serious illness. He or she thinks any minor pain is a sign of fatal illness. In spite of medical reports showing nothing wrong, a hypochondriac will continue to believe a disease exists. Like conversion, hypochondriasis is a physical expression of ...
Slide 1
... Focus on assets rather than deficiencies Increasing each client’s sense of self-worth and competence Reinforcing evidence of personal growth Normalizing the difficulty of change ...
... Focus on assets rather than deficiencies Increasing each client’s sense of self-worth and competence Reinforcing evidence of personal growth Normalizing the difficulty of change ...
Exam 5 Study Guide sp11
... CHAPTER 14: Psychological Disorders -‐ Define “disorder” as psychologists and psychiatrists do. -‐ How has the medical model changed how we approach psychological disorders? -‐ The DSM o Know its full name ...
... CHAPTER 14: Psychological Disorders -‐ Define “disorder” as psychologists and psychiatrists do. -‐ How has the medical model changed how we approach psychological disorders? -‐ The DSM o Know its full name ...
"Abnormal" Psychology
... Abnormal is... Any behavior that differs much from the average Any behavior that leads to distress (pain), disability (impaired functioning), or an increased risk of death, pain, or loss of freedom (DSM definition) ...
... Abnormal is... Any behavior that differs much from the average Any behavior that leads to distress (pain), disability (impaired functioning), or an increased risk of death, pain, or loss of freedom (DSM definition) ...
View Presentation
... • Diagnosed in school-aged children, mostly male • 15 percent of school-aged population in the United States have been diagnosed • Increasing numbers of children diagnosed with ADHD may be a reflection of changing social expectations, rather than an increase in the frequency of this neurological con ...
... • Diagnosed in school-aged children, mostly male • 15 percent of school-aged population in the United States have been diagnosed • Increasing numbers of children diagnosed with ADHD may be a reflection of changing social expectations, rather than an increase in the frequency of this neurological con ...
Mental Disorders
... Fear of taking risks, gullible, hyper-sensitive, avoids all things that include social interaction. ...
... Fear of taking risks, gullible, hyper-sensitive, avoids all things that include social interaction. ...
Common Symptoms and Diagnostic Features
... Cycling mood changes, manic symptoms: inflated self- esteem or grandiosity, decreased need for sleep, more talkative than usual, flights of ideas, thoughts racing, distractibility, dangerous activities (i.e., shopping sprees, sexual indiscretions etc.) What does it look like on campus? Stay up a ...
... Cycling mood changes, manic symptoms: inflated self- esteem or grandiosity, decreased need for sleep, more talkative than usual, flights of ideas, thoughts racing, distractibility, dangerous activities (i.e., shopping sprees, sexual indiscretions etc.) What does it look like on campus? Stay up a ...
Chapter 11 -Social Psychology – The study of how people think
... months and in which the individual is unable to specify the reasons for the anxiety. -Panic Disorder – Anxiety disorder in which the individual experiences recurrent, sudden onsets of intense terror, often without warning and no specific cause. -Phobic Disorder (Phobia) – Anxiety disorder characteri ...
... months and in which the individual is unable to specify the reasons for the anxiety. -Panic Disorder – Anxiety disorder in which the individual experiences recurrent, sudden onsets of intense terror, often without warning and no specific cause. -Phobic Disorder (Phobia) – Anxiety disorder characteri ...
What is Anxiety?
... GAD is a particularly difficult disorder to live with as it is constantly on the sufferer’s mind – there is no respite as the anxiety is not tied to a specific situation or event. It can cause problems with sleep, ability to focus upon school work, as well as impacting on close relationships. Post-t ...
... GAD is a particularly difficult disorder to live with as it is constantly on the sufferer’s mind – there is no respite as the anxiety is not tied to a specific situation or event. It can cause problems with sleep, ability to focus upon school work, as well as impacting on close relationships. Post-t ...