Easy Alpines - Alpine Garden Society
... Many alpines, by their very nature, have very long, deeply questing roots. When you have selected your planting site, dig a hole approximately the same diameter as the pot. Knock the plant out of its pot and inspect the roots. You will often find that the roots spiral around at the base. Using your ...
... Many alpines, by their very nature, have very long, deeply questing roots. When you have selected your planting site, dig a hole approximately the same diameter as the pot. Knock the plant out of its pot and inspect the roots. You will often find that the roots spiral around at the base. Using your ...
Common pampas and purple pampas grass
... of native plants along forest and streambank margins, in scrub and secondary forests, and wetlands and coastal areas. ...
... of native plants along forest and streambank margins, in scrub and secondary forests, and wetlands and coastal areas. ...
ten commonly available medicinal plants in malaysia used
... Method: This study was carried out for a general knowledge in which to give information on common medicinal plants in Malaysia used for the treatment of diabetes. Results: There are 10 such very commonly available medicinal plants were found and described in this review which clearly shows the impor ...
... Method: This study was carried out for a general knowledge in which to give information on common medicinal plants in Malaysia used for the treatment of diabetes. Results: There are 10 such very commonly available medicinal plants were found and described in this review which clearly shows the impor ...
11. Soursop - The International Potash Institute
... sugars produced by photosynthesis in the leaves to the other organs, principally the fruit. Potassium can move from the oldest organs, primarily the leaves, to the youngest or to growth. Brownish spots start at the apex and the basal portion of the leaf lamina and gradually merge. In seedlings these ...
... sugars produced by photosynthesis in the leaves to the other organs, principally the fruit. Potassium can move from the oldest organs, primarily the leaves, to the youngest or to growth. Brownish spots start at the apex and the basal portion of the leaf lamina and gradually merge. In seedlings these ...
Untitled
... Angiosperms are plants that have flowers! Some that you might commonly see are roses, tulips, and apple trees. Angiosperms grow their seeds inside of fruits. Flowers are an adaptation that plants use to help them spread their seeds. While angiosperms help spread their seeds using the wind, like gymn ...
... Angiosperms are plants that have flowers! Some that you might commonly see are roses, tulips, and apple trees. Angiosperms grow their seeds inside of fruits. Flowers are an adaptation that plants use to help them spread their seeds. While angiosperms help spread their seeds using the wind, like gymn ...
Dasanthera
... TAXONOMY: the science of describing, naming and classifying plants or animals, following the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature for plants. A taxon (plural: taxa) is any taxonomic entity, of whatever rank. Subgenus Dasanthera (9 species) Bibliographical References: Northwest Penstemons by ...
... TAXONOMY: the science of describing, naming and classifying plants or animals, following the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature for plants. A taxon (plural: taxa) is any taxonomic entity, of whatever rank. Subgenus Dasanthera (9 species) Bibliographical References: Northwest Penstemons by ...
Plants I - Valencia College
... out of water on the shore. This ancestral plant would also have had to nourish and protect the zygote and developing embryo from drying out; it might have done this by retaining the embryo within its body. Such a plant may have given rise to the more highly adapted land plants. All of these plants s ...
... out of water on the shore. This ancestral plant would also have had to nourish and protect the zygote and developing embryo from drying out; it might have done this by retaining the embryo within its body. Such a plant may have given rise to the more highly adapted land plants. All of these plants s ...
How to Look at Oaks
... Quercus is without doubt one of the most important woody genera of the Northern Hemisphere. Historically, oaks have been an important source of fuel, fodder, and building materials throughout their range. Other products include tannins and dyes, and oak bark and leaves were often used for tanning le ...
... Quercus is without doubt one of the most important woody genera of the Northern Hemisphere. Historically, oaks have been an important source of fuel, fodder, and building materials throughout their range. Other products include tannins and dyes, and oak bark and leaves were often used for tanning le ...
10_chapter 2
... The Plant used as a stomachic, aperient and antiseptic. Used for the suppression of lochia. Whole plant used as cataplasm for dyspepsia in children. For earahces, applied warm, moistened with a little castor oil. In Puddokota, juice is applied to itches and other skin diseases. In India, used by tri ...
... The Plant used as a stomachic, aperient and antiseptic. Used for the suppression of lochia. Whole plant used as cataplasm for dyspepsia in children. For earahces, applied warm, moistened with a little castor oil. In Puddokota, juice is applied to itches and other skin diseases. In India, used by tri ...
Noxious Weed Management Pocket Guide
... Growth form: Perennial forb Flower: Heads are urn-shaped, solitary, and composed of disk flowers. Floral bracts are broad, ovoid, entire, and greenish at the base with papery, finely hairy edges. The petals are pink or purple. Seeds: Oval, grayish or ivory, with long white bristles (pappus) at the t ...
... Growth form: Perennial forb Flower: Heads are urn-shaped, solitary, and composed of disk flowers. Floral bracts are broad, ovoid, entire, and greenish at the base with papery, finely hairy edges. The petals are pink or purple. Seeds: Oval, grayish or ivory, with long white bristles (pappus) at the t ...
Plant Flexbook - jl041.k12.sd.us
... of the non-woody parts of a plant, including roots, stems, and leaves. Each type of tissue contains one or more kinds of cells that are specialized to perform particular functions. Dermal tissue covers the outside of a plant’s body. In the non-woody parts of a plant, dermal tissue forms a “skin” cal ...
... of the non-woody parts of a plant, including roots, stems, and leaves. Each type of tissue contains one or more kinds of cells that are specialized to perform particular functions. Dermal tissue covers the outside of a plant’s body. In the non-woody parts of a plant, dermal tissue forms a “skin” cal ...
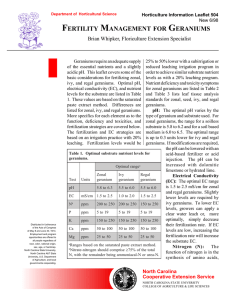
fertility management for geraniums
... element and uptake is by the root tips. Excess levels of Ca can reduce the uptake of K, Mg, and B. A fertilization rate of 50 to 100 ppm Ca should be used, remembering to maintain the K : Ca : Mg fertilizer ratio of 4 : 2 : 1. Ca can be supplied from your irrigation water (if adequate levels exist), ...
... element and uptake is by the root tips. Excess levels of Ca can reduce the uptake of K, Mg, and B. A fertilization rate of 50 to 100 ppm Ca should be used, remembering to maintain the K : Ca : Mg fertilizer ratio of 4 : 2 : 1. Ca can be supplied from your irrigation water (if adequate levels exist), ...
Phenology of Adhatoda vasica a multifarious useful medicinal plant
... growth, leaves fall (if it is deciduous), flushing of new leaves, flowering and then fruiting has been studied. Five sites have been selected from in and around Bhopal MP and the study was done and founded that the flowering starts in the month of October around the second week and is sparse. The no ...
... growth, leaves fall (if it is deciduous), flushing of new leaves, flowering and then fruiting has been studied. Five sites have been selected from in and around Bhopal MP and the study was done and founded that the flowering starts in the month of October around the second week and is sparse. The no ...
List of Climbers - OOTY Flower Show
... flowers. It is vigorous and of rapid growth, leaves large round form, glabrous flowers 7-10 in long, green marked with dark purple, hairy inside, with 2 long lips, one of which has a much expanded limb. Blooms during May-July. Propagated from cutting taken from well matured wood. Useful for covering ...
... flowers. It is vigorous and of rapid growth, leaves large round form, glabrous flowers 7-10 in long, green marked with dark purple, hairy inside, with 2 long lips, one of which has a much expanded limb. Blooms during May-July. Propagated from cutting taken from well matured wood. Useful for covering ...
183KB - NZQA
... allows plants to have the extra energy required for parts of the life cycle that may need extra energy, for example producing flowers for reproduction. The starch can also be converted back into glucose when extra energy is needed for plant growth, for example in the spring. Therefore we can say tha ...
... allows plants to have the extra energy required for parts of the life cycle that may need extra energy, for example producing flowers for reproduction. The starch can also be converted back into glucose when extra energy is needed for plant growth, for example in the spring. Therefore we can say tha ...
Bio3460-9 Photosynthesis
... The rice section shows vascular bundles with few chloroplasts and large numbers of mesophyll cells between the vascular bundles typical for C3 species. The sorghum leaf section shows chloroplasts in bundle sheath and only two or three mesophyll cells in between the vascular tissue typical of a C4 sp ...
... The rice section shows vascular bundles with few chloroplasts and large numbers of mesophyll cells between the vascular bundles typical for C3 species. The sorghum leaf section shows chloroplasts in bundle sheath and only two or three mesophyll cells in between the vascular tissue typical of a C4 sp ...
76KB - NZQA
... allows plants to have the extra energy required for parts of the life cycle that may need extra energy, for example producing flowers for reproduction. The starch can also be converted back into glucose when extra energy is needed for plant growth, for example in the spring. Therefore we can say tha ...
... allows plants to have the extra energy required for parts of the life cycle that may need extra energy, for example producing flowers for reproduction. The starch can also be converted back into glucose when extra energy is needed for plant growth, for example in the spring. Therefore we can say tha ...
Lab 5 Plants 1
... plants is for the dominant gametophyte to become smaller and less conspicuous and for the sporophyte to become large and dominant. The reproduction of many land plants (Divisions Bryophyta, Hepatophyta, Anthocerophyta, Lycophyta, Sphenophyta, and Pterophyta) still involves a flagellated sperm that ...
... plants is for the dominant gametophyte to become smaller and less conspicuous and for the sporophyte to become large and dominant. The reproduction of many land plants (Divisions Bryophyta, Hepatophyta, Anthocerophyta, Lycophyta, Sphenophyta, and Pterophyta) still involves a flagellated sperm that ...
Plants I
... plants is for the dominant gametophyte to become smaller and less conspicuous and for the sporophyte to become large and dominant. The reproduction of many land plants (Divisions Bryophyta, Hepatophyta, Anthocerophyta, Lycophyta, Sphenophyta, and Pterophyta) still involves a flagellated sperm that ...
... plants is for the dominant gametophyte to become smaller and less conspicuous and for the sporophyte to become large and dominant. The reproduction of many land plants (Divisions Bryophyta, Hepatophyta, Anthocerophyta, Lycophyta, Sphenophyta, and Pterophyta) still involves a flagellated sperm that ...
Seedless Vascular Plants
... made their appearance in the fossil record during the Devonian period and expanded during the Carboniferous. The dominant stage of the lifecycle of a fern is the sporophyte, which consists of large compound leaves called fronds. Fronds fulfill a double role; they are photosynthetic organs that also ...
... made their appearance in the fossil record during the Devonian period and expanded during the Carboniferous. The dominant stage of the lifecycle of a fern is the sporophyte, which consists of large compound leaves called fronds. Fronds fulfill a double role; they are photosynthetic organs that also ...
““lVle-m6’i%iiidum
... resin, fatty materials, extractive matter, gum, starch, glucose and traces of tanine; carbonic, salisilicate, clorhydric, sulphuric and phosphoric acids; soda, potash, magnesia, limestone and iron. Common Uses: Brewed for several stomach ailments; it causes salivation, increases urination and probab ...
... resin, fatty materials, extractive matter, gum, starch, glucose and traces of tanine; carbonic, salisilicate, clorhydric, sulphuric and phosphoric acids; soda, potash, magnesia, limestone and iron. Common Uses: Brewed for several stomach ailments; it causes salivation, increases urination and probab ...
Biology 2 – Study Guide # 2
... Know the three different tissue systems and their components (ground, vascular, epidermis)? Know the types of cells and tissues that make up each one (parenchyma, sclerenchyma, sclerids, fibers, collenchyma, xylem, tracheids, vessel elements, phloem, sieve tube members, companion cells, pith). Know ...
... Know the three different tissue systems and their components (ground, vascular, epidermis)? Know the types of cells and tissues that make up each one (parenchyma, sclerenchyma, sclerids, fibers, collenchyma, xylem, tracheids, vessel elements, phloem, sieve tube members, companion cells, pith). Know ...
ACANT H- ACEAE
... Acanthaceae… Lamiales with •swelling above nodes •opposite leaves •cystoliths •mismatched anthers •jaculators ...
... Acanthaceae… Lamiales with •swelling above nodes •opposite leaves •cystoliths •mismatched anthers •jaculators ...
What Are the Parts of a Plant? / What Are the Functions of Different
... The gas found in the air that has no colour, taste or smell, and is necessary for life ...
... The gas found in the air that has no colour, taste or smell, and is necessary for life ...
Morphological and Anatomical Characteristics of Selected Dicot
... time. These plants are characteristics of desert and semi desert regions. Xerophytes are the plants which are able to survive in an environment with a limited supply of water as compared to hydrophytes and mesophytes. These plants develop certain structural, anatomical and physiological adaptations ...
... time. These plants are characteristics of desert and semi desert regions. Xerophytes are the plants which are able to survive in an environment with a limited supply of water as compared to hydrophytes and mesophytes. These plants develop certain structural, anatomical and physiological adaptations ...
Leaf

A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively.Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases) and other features. In most plant species, leaves are broad and flat. Such species are referred to as broad-leaved plants. Many gymnosperm species have thin needle-like leaves that can be advantageous in cold climates frequented by snow and frost. Leaves can also have other shapes and forms such as the scales in certain species of conifers. Some leaves are not above ground (such as bulb scales). Succulent plants often have thick juicy leaves, but some leaves are without major photosynthetic function and may be dead at maturity, as in some cataphylls, and spines). Furthermore, several kinds of leaf-like structures found in vascular plants are not totally homologous with them. Examples include flattened plant stems (called phylloclades and cladodes), and phyllodes (flattened leaf stems), both of which differ from leaves in their structure and origin. Many structures of non-vascular plants, and even of some lichens, which are not plants at all (in the sense of being members of the kingdom Plantae), look and function much like leaves. The primary site of photosynthesis in most leaves (palisade mesophyll) almost always occurs on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus palisade occurs on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral.