Biology 202
... specialized for food storage Leaves ¥ Blade – main photosynthetic structure ¥ Petiole – attaches the blade to the stem at the node – Monocots generally lack petioles – instead the blade wraps the stem in a sheath Leaf Veins ¥ Monocots – major veins are parallel ¥ Dicots – major veins are multi-branc ...
... specialized for food storage Leaves ¥ Blade – main photosynthetic structure ¥ Petiole – attaches the blade to the stem at the node – Monocots generally lack petioles – instead the blade wraps the stem in a sheath Leaf Veins ¥ Monocots – major veins are parallel ¥ Dicots – major veins are multi-branc ...
FOSSIL PLANTS AND EVOLUTION
... and Jurassic times, as shown by their characteristic leaves, but we have as yet little certain knowledge of their reproductive structures. Prof. Harris (1951) has furnished good evidence for thinking that the simple or forking linear leaves known as Solenites or Czekanowskia, and previously thought ...
... and Jurassic times, as shown by their characteristic leaves, but we have as yet little certain knowledge of their reproductive structures. Prof. Harris (1951) has furnished good evidence for thinking that the simple or forking linear leaves known as Solenites or Czekanowskia, and previously thought ...
Multiflora Rose (Rosa multiflora)
... Chemical: The most effective way to control multiflora rose is to cut the stems down as close to the ground as possible, then apply concentrated herbicide to the stump. Triclopyr (Garlon® 4, Brush-B-Gon®) is the most effective herbicide for cutstump or basal bark application to multiflora rose, but ...
... Chemical: The most effective way to control multiflora rose is to cut the stems down as close to the ground as possible, then apply concentrated herbicide to the stump. Triclopyr (Garlon® 4, Brush-B-Gon®) is the most effective herbicide for cutstump or basal bark application to multiflora rose, but ...
PDF - CLIMBERS - University of Michigan
... Asteroideae. Also in this tribe are the genera Ageratum, Carphephorous, Eupatorium, Garberia, Iva, and Liatris. The flowers of the tribe are usually disks with short lobes (occasionally long), ...
... Asteroideae. Also in this tribe are the genera Ageratum, Carphephorous, Eupatorium, Garberia, Iva, and Liatris. The flowers of the tribe are usually disks with short lobes (occasionally long), ...
Biological Diversity 5
... material in, out, and within the organism. Adaptations to this include the circulatory systems of animals, and the specialized conducting tissues xylem and phloem in plants. Some multicellular algae and bryophytes also have specialized conducting cells. 5. Reproduction. Organisms in water can relea ...
... material in, out, and within the organism. Adaptations to this include the circulatory systems of animals, and the specialized conducting tissues xylem and phloem in plants. Some multicellular algae and bryophytes also have specialized conducting cells. 5. Reproduction. Organisms in water can relea ...
Plant growth and development
... Roots typically originate from the lower portion of a plant or cutting. They have a root cap, but lack nodes and never bear leaves or flowers directly. Their principal functions are to absorb nutrients and moisture, anchor the plant in the soil, support the stem and store food. In some plants, roots ...
... Roots typically originate from the lower portion of a plant or cutting. They have a root cap, but lack nodes and never bear leaves or flowers directly. Their principal functions are to absorb nutrients and moisture, anchor the plant in the soil, support the stem and store food. In some plants, roots ...
Multiflora
... Corolla: 8-20 mm (5/16-3/4”) long, mostly cream or very pale yellowish, with or without red or maroon guide lines, the tube not much expanded in the throat, the upper lip shorter than the lower. Anther sacs: Spreading widely to opposite, the sacs opening flat, smooth, 0.5-0.9 mm long and mostly incl ...
... Corolla: 8-20 mm (5/16-3/4”) long, mostly cream or very pale yellowish, with or without red or maroon guide lines, the tube not much expanded in the throat, the upper lip shorter than the lower. Anther sacs: Spreading widely to opposite, the sacs opening flat, smooth, 0.5-0.9 mm long and mostly incl ...
Chapter 23
... A growing plant produces new cells in areas called meristems. Meristems are regions of actively dividing cells. Meristematic cells are differently shaped parenchyma cells with large nuclei. There are several types of meristems; two types are shown in Figure 23.6 on page 609. Apical meristems are fou ...
... A growing plant produces new cells in areas called meristems. Meristems are regions of actively dividing cells. Meristematic cells are differently shaped parenchyma cells with large nuclei. There are several types of meristems; two types are shown in Figure 23.6 on page 609. Apical meristems are fou ...
Chapter 23: Plant Structure and Function
... A growing plant produces new cells in areas called meristems. Meristems are regions of actively dividing cells. Meristematic cells are differently shaped parenchyma cells with large nuclei. There are several types of meristems; two types are shown in Figure 23.6 on page 609. Apical meristems are fou ...
... A growing plant produces new cells in areas called meristems. Meristems are regions of actively dividing cells. Meristematic cells are differently shaped parenchyma cells with large nuclei. There are several types of meristems; two types are shown in Figure 23.6 on page 609. Apical meristems are fou ...
Chapter 23: Plant Structure and Function
... A growing plant produces new cells in areas called meristems. Meristems are regions of actively dividing cells. Meristematic cells are differently shaped parenchyma cells with large nuclei. There are several types of meristems; two types are shown in Figure 23.6 on page 609. Apical meristems are fou ...
... A growing plant produces new cells in areas called meristems. Meristems are regions of actively dividing cells. Meristematic cells are differently shaped parenchyma cells with large nuclei. There are several types of meristems; two types are shown in Figure 23.6 on page 609. Apical meristems are fou ...
enz resp photo test marker
... at 500 and 1300 ppm CO2 the curve is the same shape but with different maximum rates / each higher light intensity requires a higher CO2 concentration to reach maximum rate; maximum rate of photosynthesis from 280 to 500 ppm / increases 5 to 6 times while 500 to 1300 ppm increases 1.5 times; ...
... at 500 and 1300 ppm CO2 the curve is the same shape but with different maximum rates / each higher light intensity requires a higher CO2 concentration to reach maximum rate; maximum rate of photosynthesis from 280 to 500 ppm / increases 5 to 6 times while 500 to 1300 ppm increases 1.5 times; ...
Teaching Parts Of Plants
... • Compare various kinds of leaves. • Classify leaves by similar characteristics. • Identify leaf characteristics. • Arrange items on a chart. • Explain categories for classification. Activity procedures Prepare (teacher) • Copy Kinds of Leaves p. 14 for each student. • Gather leaves of different sha ...
... • Compare various kinds of leaves. • Classify leaves by similar characteristics. • Identify leaf characteristics. • Arrange items on a chart. • Explain categories for classification. Activity procedures Prepare (teacher) • Copy Kinds of Leaves p. 14 for each student. • Gather leaves of different sha ...
Native Plants for the Edges of Walkways and Driveways
... Woodland phlox, Phlox divaricata. Long-flowering, useful where there is some shade Woodland creeping phlox, Phlox stolonifera, similar to the above, but with rounded leaves Dwarf Iris, Iris cristata, very pretty when blooming in spring, leaves may look ratty in summer Pasque flower, Pulsatilla paten ...
... Woodland phlox, Phlox divaricata. Long-flowering, useful where there is some shade Woodland creeping phlox, Phlox stolonifera, similar to the above, but with rounded leaves Dwarf Iris, Iris cristata, very pretty when blooming in spring, leaves may look ratty in summer Pasque flower, Pulsatilla paten ...
316 Vegetative Propagation
... • Roots grow from the buried stem. Model Agricultural Core Curriculum: Supplement University of California, Davis ...
... • Roots grow from the buried stem. Model Agricultural Core Curriculum: Supplement University of California, Davis ...
Surviving in the Wild: 19 Common Edible Plants
... Grain heads with pink, purplish, or black spurs Three-leaved growth pattern ...
... Grain heads with pink, purplish, or black spurs Three-leaved growth pattern ...
Exploring Plant Parts
... Information on the KLEW chart can be found at: What is a plant? Plants are living organisms that do not move, usually have http://www.nsta.org/publications/news/story.aspx?id=51519 chlorophyll (or green coloring somewhere), and produce their own food. What are the parts of plants? Plants have many p ...
... Information on the KLEW chart can be found at: What is a plant? Plants are living organisms that do not move, usually have http://www.nsta.org/publications/news/story.aspx?id=51519 chlorophyll (or green coloring somewhere), and produce their own food. What are the parts of plants? Plants have many p ...
Making a Forsythe Pot - University of Minnesota Extension
... Making a forsythe pot for rooting houseplant cuttings is an easy, educational, and not-tooexpensive project; one that can be enjoyed by people of all ages. Although many cuttings will root in water, better results can be obtained by starting cuttings in moist vermiculite. Plants that are somewhat di ...
... Making a forsythe pot for rooting houseplant cuttings is an easy, educational, and not-tooexpensive project; one that can be enjoyed by people of all ages. Although many cuttings will root in water, better results can be obtained by starting cuttings in moist vermiculite. Plants that are somewhat di ...
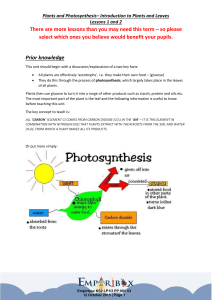
There are more lessons than you may need this term
... Plants and Photosynthesis– Introduction to Plants and Leaves Lessons 1 and 2 Timetables are provided to suggest a weekly outline in order to ensure children have plants, seedlings etc. to observe in lessons. This is only a guide and you may wish to alter it as you ...
... Plants and Photosynthesis– Introduction to Plants and Leaves Lessons 1 and 2 Timetables are provided to suggest a weekly outline in order to ensure children have plants, seedlings etc. to observe in lessons. This is only a guide and you may wish to alter it as you ...
Making a Forsythe Pot - University of Minnesota Extension
... Making a forsythe pot for rooting houseplant cuttings is an easy, educational, and not-tooexpensive project; one that can be enjoyed by people of all ages. Although many cuttings will root in water, better results can be obtained by starting cuttings in moist vermiculite. Plants that are somewhat di ...
... Making a forsythe pot for rooting houseplant cuttings is an easy, educational, and not-tooexpensive project; one that can be enjoyed by people of all ages. Although many cuttings will root in water, better results can be obtained by starting cuttings in moist vermiculite. Plants that are somewhat di ...
EDIBLE PLANTS OF NEW ENGLAND - Herbaceous
... salads, steamed, sauteed, or simmered; flower clusters dense, bristly; seeds winnowed and made into high-protein flour. Caution: amaranth absorbs nitrates and pesticides; avoid plants growing in overly fertilized or polluted soil. Arrowheads/Duck-Potatoes/Wapato (Sagittaria spp.) Water-plantain fami ...
... salads, steamed, sauteed, or simmered; flower clusters dense, bristly; seeds winnowed and made into high-protein flour. Caution: amaranth absorbs nitrates and pesticides; avoid plants growing in overly fertilized or polluted soil. Arrowheads/Duck-Potatoes/Wapato (Sagittaria spp.) Water-plantain fami ...
CHAPTER 35: PLANT STRUCTURE, GROWTH, AND
... main vertical root that stores sugars and starches that plants will consume during flowering and fruit production. Root hairs, which are extensions of epidermal cells, are located near the tips of roots, where the absorption of water and minerals primarily occur, and increase the surface area of the ...
... main vertical root that stores sugars and starches that plants will consume during flowering and fruit production. Root hairs, which are extensions of epidermal cells, are located near the tips of roots, where the absorption of water and minerals primarily occur, and increase the surface area of the ...
Lakhmir Singh`s Science For Class 7
... omissions or damages arising out of the use of the information contained in this publication. Further, the appearance of the personal name, location, place and incidence, if any; in the illustrations used herein is purely coincidental and work of imagination. Thus the same should in no manner be ter ...
... omissions or damages arising out of the use of the information contained in this publication. Further, the appearance of the personal name, location, place and incidence, if any; in the illustrations used herein is purely coincidental and work of imagination. Thus the same should in no manner be ter ...
Plant Yacon 120(04004) Primary essential character No Characters
... 2:Almost none 3:Very little 4:Little 5:Intermediate 6:Some 7:Much 8:Very much ...
... 2:Almost none 3:Very little 4:Little 5:Intermediate 6:Some 7:Much 8:Very much ...
Leaf

A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively.Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases) and other features. In most plant species, leaves are broad and flat. Such species are referred to as broad-leaved plants. Many gymnosperm species have thin needle-like leaves that can be advantageous in cold climates frequented by snow and frost. Leaves can also have other shapes and forms such as the scales in certain species of conifers. Some leaves are not above ground (such as bulb scales). Succulent plants often have thick juicy leaves, but some leaves are without major photosynthetic function and may be dead at maturity, as in some cataphylls, and spines). Furthermore, several kinds of leaf-like structures found in vascular plants are not totally homologous with them. Examples include flattened plant stems (called phylloclades and cladodes), and phyllodes (flattened leaf stems), both of which differ from leaves in their structure and origin. Many structures of non-vascular plants, and even of some lichens, which are not plants at all (in the sense of being members of the kingdom Plantae), look and function much like leaves. The primary site of photosynthesis in most leaves (palisade mesophyll) almost always occurs on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus palisade occurs on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral.