Mental and Emotional Illness
... Post Traumatic Stress Disorder • Withdrawal or depression after a distressing experience such as physical abuse, natural disaster, accident, or witnessing violence. ...
... Post Traumatic Stress Disorder • Withdrawal or depression after a distressing experience such as physical abuse, natural disaster, accident, or witnessing violence. ...
BEHAVIORAL HEALTH PROBLEMS OF FARM PEOPLE DIFFER
... pattern that is consistent across various situations and over time. For example, some people tend to be gregarious and seemingly “talk all the time” wherever they are and with whomever they interact. Personality disorders are enduring behavior patterns that seriously and regularly disrupt personal, ...
... pattern that is consistent across various situations and over time. For example, some people tend to be gregarious and seemingly “talk all the time” wherever they are and with whomever they interact. Personality disorders are enduring behavior patterns that seriously and regularly disrupt personal, ...
Section III - American Psychiatric Association
... Some proposed conditions had clear merit but ultimately were judged to need further research before they might be considered as formal disorders. Inclusion of conditions in Section III was contingent on the amount of empirical evidence available on a diagnosis, diagnostic reliability or validity, a ...
... Some proposed conditions had clear merit but ultimately were judged to need further research before they might be considered as formal disorders. Inclusion of conditions in Section III was contingent on the amount of empirical evidence available on a diagnosis, diagnostic reliability or validity, a ...
psychology - TeacherWeb
... • Dopamine – brain chemical that causes speech and thoughts; if too much it can lead to schizophrenia ...
... • Dopamine – brain chemical that causes speech and thoughts; if too much it can lead to schizophrenia ...
Jeopardy IV
... A pattern of disregard for, and violation of, the rights of others; Typically have no regard for right or wrong ...
... A pattern of disregard for, and violation of, the rights of others; Typically have no regard for right or wrong ...
2. Personality Disorders
... • Study of chemical changes to a gene that influence its expression • (without altering DNA sequence) ...
... • Study of chemical changes to a gene that influence its expression • (without altering DNA sequence) ...
Key terms - Ms. Paras
... psychological disorders. • Recognize the use of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) published by the American Psychiatric Association as the primary reference for making diagnostic judgments. • Evaluate the strengths and limitations of various approaches to explaining psy ...
... psychological disorders. • Recognize the use of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) published by the American Psychiatric Association as the primary reference for making diagnostic judgments. • Evaluate the strengths and limitations of various approaches to explaining psy ...
Personality Disorders
... developed improperly from the start. If you had a personality disorder, you probably wouldn’t know it. You may know that you have trouble forming stable relationships. Your work and personal life would probably suffer. But you would probably think it is other people, not you, who are the problem. If ...
... developed improperly from the start. If you had a personality disorder, you probably wouldn’t know it. You may know that you have trouble forming stable relationships. Your work and personal life would probably suffer. But you would probably think it is other people, not you, who are the problem. If ...
Personality Disorders
... Think of: The core construction of a person’s world Experiences and Behaviors remarkably outside the norm (for culture). Causes significant distress or impairment Starts in adolescence/early adulthood Pervasive across settings Not GMC or Substance ...
... Think of: The core construction of a person’s world Experiences and Behaviors remarkably outside the norm (for culture). Causes significant distress or impairment Starts in adolescence/early adulthood Pervasive across settings Not GMC or Substance ...
Overheads – Abnormal Psychology
... Often due to stress, but can occur in the absence of stress Detachment or separation from your body & watching yourself with a sense of detachment ...
... Often due to stress, but can occur in the absence of stress Detachment or separation from your body & watching yourself with a sense of detachment ...
Abnormal Psychology A look at
... Vol. 3 stopped listing homosexuality as a disorder Vol. 4 changes term from manic depressive to bipolar disorder. ...
... Vol. 3 stopped listing homosexuality as a disorder Vol. 4 changes term from manic depressive to bipolar disorder. ...
A mental or emotional condition that makes it difficult for
... Disturbance in a person’s mood…such as a depressive mood or a bipolar (split personality) mood. A disorder involving extreme moods. ...
... Disturbance in a person’s mood…such as a depressive mood or a bipolar (split personality) mood. A disorder involving extreme moods. ...
Am J Psychiatry 167:487
... personality disorder, or both. They studied 433 patients from four sites over a 6-year period: 73 with depression alone, 119 with personality disorder alone (and no history of previous depression), and 241 with both depression and personality disorder. The patients with personality disorders had one ...
... personality disorder, or both. They studied 433 patients from four sites over a 6-year period: 73 with depression alone, 119 with personality disorder alone (and no history of previous depression), and 241 with both depression and personality disorder. The patients with personality disorders had one ...
Personality Disorders - Cornwall Partnership NHS Foundation Trust
... with everything seeming to go wrong all at once. Core symptoms are: • Strong emotional responses – emotions feel particularly strong, are hard to understand or explain. This often means people are more sensitive to how they perceive they are being treated. • Self-harming – the overwhelming feeling ...
... with everything seeming to go wrong all at once. Core symptoms are: • Strong emotional responses – emotions feel particularly strong, are hard to understand or explain. This often means people are more sensitive to how they perceive they are being treated. • Self-harming – the overwhelming feeling ...
chapter 16 review
... Major depressive disorder Mania Bipolar disorder Schizophrenia Delusions Personality disorders Antisocial personality disorder ...
... Major depressive disorder Mania Bipolar disorder Schizophrenia Delusions Personality disorders Antisocial personality disorder ...
Module 49 Dissociative and Personality Disorders Outline
... a. characterized by a need for social isolation, odd behavior and thinking, and often unconventional beliefs such as being convinced of having extra sensory abilities. b. Some people believe that schizotypal personality disorder is a mild form of schizophrenia. 16. Avoidant personality disorder a. c ...
... a. characterized by a need for social isolation, odd behavior and thinking, and often unconventional beliefs such as being convinced of having extra sensory abilities. b. Some people believe that schizotypal personality disorder is a mild form of schizophrenia. 16. Avoidant personality disorder a. c ...
Module 69 - Personality Disorders
... Personality Disorders • Disruptive, inflexible, enduring pattern of thoughts, emotions, behaviors, and interpersonal functioning that are stable over time and across situations, – deviate from the expectations of the individual’s culture ...
... Personality Disorders • Disruptive, inflexible, enduring pattern of thoughts, emotions, behaviors, and interpersonal functioning that are stable over time and across situations, – deviate from the expectations of the individual’s culture ...
Personality Disorders - Nightingale Hospital London
... Classically a personality disorder is diagnosed in an individual who exhibits characteristics and behaviours which cause them to have difficulties within their relationships and functioning in their cultural milieu. The disorders are persistent and cause distress to both the individual and society. ...
... Classically a personality disorder is diagnosed in an individual who exhibits characteristics and behaviours which cause them to have difficulties within their relationships and functioning in their cultural milieu. The disorders are persistent and cause distress to both the individual and society. ...
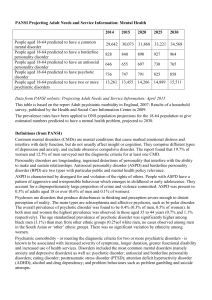
Mental Health Projections: PANSI 2015
... interfere with daily function, but do not usually affect insight or cognition. They comprise different types of depression and anxiety, and include obsessive compulsive disorder. The report found that 19.7% of women and 12.5% of men surveyed met the diagnostic criteria for at least one CMD. Personal ...
... interfere with daily function, but do not usually affect insight or cognition. They comprise different types of depression and anxiety, and include obsessive compulsive disorder. The report found that 19.7% of women and 12.5% of men surveyed met the diagnostic criteria for at least one CMD. Personal ...
Chapter 13 Notes (Part 2)
... o _______________________________________ Personality Disorder: person has an exaggerated sense of self-importance and needs constant admiration Believe they are extraordinary, need constant attention and admiration, display sense of entitlement, and tend to exploit others o ______________________ ...
... o _______________________________________ Personality Disorder: person has an exaggerated sense of self-importance and needs constant admiration Believe they are extraordinary, need constant attention and admiration, display sense of entitlement, and tend to exploit others o ______________________ ...