Chapter 17 - Disorders
... ADD/ADHD – Attention Deficit Hyper Activity Disorder. Up to 3-5% affected Controversial. * Ritalin treatment or “Super-structured” day. * 80% boys * Long-term – relationship issues, delinquency, stigma. Autism – failed communication patterns, social interactions, and emotional response. A wide range ...
... ADD/ADHD – Attention Deficit Hyper Activity Disorder. Up to 3-5% affected Controversial. * Ritalin treatment or “Super-structured” day. * 80% boys * Long-term – relationship issues, delinquency, stigma. Autism – failed communication patterns, social interactions, and emotional response. A wide range ...
Abnormal Psychology
... What is the DSM-IV? How is the DSM-IV used by psychologists? Why the DSM-IV only bases diagnoses on observable patterns of behavior? self-fulfilling prophecies What is the difference between neurotic disorders and psychotic disorders? The negative effects of diagnostic labels The relationship betwee ...
... What is the DSM-IV? How is the DSM-IV used by psychologists? Why the DSM-IV only bases diagnoses on observable patterns of behavior? self-fulfilling prophecies What is the difference between neurotic disorders and psychotic disorders? The negative effects of diagnostic labels The relationship betwee ...
Personality Disorders
... Difficulty making friends A need for instant gratification Poor impulse control Alcohol or substance abuse ...
... Difficulty making friends A need for instant gratification Poor impulse control Alcohol or substance abuse ...
personality disorders histrionic personality disorder
... HISTRIONIC PERSONALITY DISORDER What it is: ...
... HISTRIONIC PERSONALITY DISORDER What it is: ...
PSYC+103+Ch
... Bipolar disorder: one or more manic episodes with periods of depression Cyclothymic disorder: milder, chronic form of bipolar Etiology Genetic vulnerability Neurochemical factors Cognitive factors Interpersonal roots Precipitating stress ...
... Bipolar disorder: one or more manic episodes with periods of depression Cyclothymic disorder: milder, chronic form of bipolar Etiology Genetic vulnerability Neurochemical factors Cognitive factors Interpersonal roots Precipitating stress ...
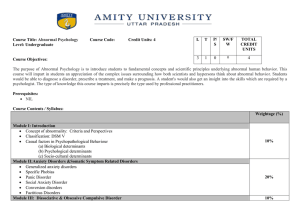
L T P/S SW/FW TOTAL CREDIT UNITS 3 1 0 0 4 Course Title
... Describe the diagnostic criteria, symptoms, course, incidence, prevalence, etiology, prognosis, and correlates of major mental disorders. Evaluate biological, social, learning, and developmental influences on psychopathology. Apply diagnostic criteria and case formulations to the assessment and diag ...
... Describe the diagnostic criteria, symptoms, course, incidence, prevalence, etiology, prognosis, and correlates of major mental disorders. Evaluate biological, social, learning, and developmental influences on psychopathology. Apply diagnostic criteria and case formulations to the assessment and diag ...
Dissociative Disorders
... Personality Disorders • Personality disorders are evident in up to 15 percent of the general population • 10 personality disorders divided into 3 clusters: – Related to anxiety – With odd and eccentric behaviors – With dramatic or impulsive behaviors ...
... Personality Disorders • Personality disorders are evident in up to 15 percent of the general population • 10 personality disorders divided into 3 clusters: – Related to anxiety – With odd and eccentric behaviors – With dramatic or impulsive behaviors ...
histrionic personality disorder
... The cause of this disorder is unknown. Both genes and early childhood events are thought to contribute. It occurs more often in women than in men, although it may be diagnosed more often in women because attentionseeking and sexual forwardness are less socially acceptable for women. Histrionic perso ...
... The cause of this disorder is unknown. Both genes and early childhood events are thought to contribute. It occurs more often in women than in men, although it may be diagnosed more often in women because attentionseeking and sexual forwardness are less socially acceptable for women. Histrionic perso ...
Understanding Borderline Personality Disorder
... ◦ Over-developed or hypervigilance in some personality characteristics common in most, if not all people. For example: ...
... ◦ Over-developed or hypervigilance in some personality characteristics common in most, if not all people. For example: ...
Unit XII: Abnormal Behavior
... Operation Beautiful website is to end negative self-talk or “Fat Talk.” ...
... Operation Beautiful website is to end negative self-talk or “Fat Talk.” ...
Mental Disorders
... Mental Disorders An illness of the mind that can affect the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of a person. It can prevent them from leading a healthy life. ...
... Mental Disorders An illness of the mind that can affect the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of a person. It can prevent them from leading a healthy life. ...
Borderline Personality Disorder
... of co-occurring disorders, such as depression, anxiety disorders, substance abuse and eating disorders, along with self-harm, suicidal behaviors and completed suicides. Other illnesses that often occur with BPD include diabetes, high blood pressure, chronic back pain, arthritis and fibromyalgia. The ...
... of co-occurring disorders, such as depression, anxiety disorders, substance abuse and eating disorders, along with self-harm, suicidal behaviors and completed suicides. Other illnesses that often occur with BPD include diabetes, high blood pressure, chronic back pain, arthritis and fibromyalgia. The ...
Semi-final written exam in Psychiatry
... interviewing techniques7.Clinical examination of the psychiatric patient3.Brain Behaviour8.Typical signs and symptoms in psychiatry9.Classification in psychiatry and psychiatric rating scales10.Delirium, dementia and amnestic and other cognitive disorders and mental disorders due to a general medica ...
... interviewing techniques7.Clinical examination of the psychiatric patient3.Brain Behaviour8.Typical signs and symptoms in psychiatry9.Classification in psychiatry and psychiatric rating scales10.Delirium, dementia and amnestic and other cognitive disorders and mental disorders due to a general medica ...
PSYCHOLOGY (9th Edition) David Myers
... Understanding Antisocial Personality Disorder Like mood disorders and schizophrenia, antisocial personality disorder has biological and psychological reasons. Youngsters, before committing a crime, respond with lower levels of stress hormones than others do at their age. ...
... Understanding Antisocial Personality Disorder Like mood disorders and schizophrenia, antisocial personality disorder has biological and psychological reasons. Youngsters, before committing a crime, respond with lower levels of stress hormones than others do at their age. ...
2. Personality Disorders
... Inflexible, enduring patterns of behavior that create impairment in functioning or subjective distress ...
... Inflexible, enduring patterns of behavior that create impairment in functioning or subjective distress ...
Abnormal Psychology Overview
... Differential Diagnosis- How to distinguish this disorder from others ...
... Differential Diagnosis- How to distinguish this disorder from others ...
Personality Disorders - Wiki-cik
... Not delusional (as in paranoid schizophrenia) Unlikely to seek treatment ...
... Not delusional (as in paranoid schizophrenia) Unlikely to seek treatment ...
PARANOID PERSONALITY DISORDER
... Rigid ways of relating to others Excessive concern with order, rules, schedules and lists Perfectionism, often so pronounced that you can't complete tasks because your standards are impossible to meet Inability to throw out even broken, worthless objects Inability to share responsibility w ...
... Rigid ways of relating to others Excessive concern with order, rules, schedules and lists Perfectionism, often so pronounced that you can't complete tasks because your standards are impossible to meet Inability to throw out even broken, worthless objects Inability to share responsibility w ...
DSM-IV-TR
... Antisocial Personality Disorder There is a pervasive pattern of disregard for and violation of the rights of others occurring since age 15 years, as indicated by three (or more) of the following: 1. failure to conform to social norms with respect to lawful behaviors as indicated by repeatedly perfor ...
... Antisocial Personality Disorder There is a pervasive pattern of disregard for and violation of the rights of others occurring since age 15 years, as indicated by three (or more) of the following: 1. failure to conform to social norms with respect to lawful behaviors as indicated by repeatedly perfor ...
Interrater and Test-Retest Reliability
... Schizotypal Personality Disorder - have the interpersonal difficulties of the schizoid personality and excessive social anxiety that does not diminish with familiarity. They have some symptoms that define schizophrenia, including odd beliefs or magical thinking, and recurrent illusions. They may h ...
... Schizotypal Personality Disorder - have the interpersonal difficulties of the schizoid personality and excessive social anxiety that does not diminish with familiarity. They have some symptoms that define schizophrenia, including odd beliefs or magical thinking, and recurrent illusions. They may h ...
Document
... Borderline personality disorder - troubled relationships - high risk activities, poor self esteem, - lash out at those they need the most ...
... Borderline personality disorder - troubled relationships - high risk activities, poor self esteem, - lash out at those they need the most ...
chpt 10
... An illness of the mind that can affect the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of a person, preventing him or her from leading a happy, healthful, and productive life. ...
... An illness of the mind that can affect the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of a person, preventing him or her from leading a happy, healthful, and productive life. ...