Chapter 8 Lesson 4
... Understanding Mental Disorders • Feeling anxious, sad or fearful is natural. • If feelings continue for long period of time and make people feel out of control or unable to deal with life may signal mental disorder • Sometimes it has a physical cause, injury to brain, effects of drug use, genentics ...
... Understanding Mental Disorders • Feeling anxious, sad or fearful is natural. • If feelings continue for long period of time and make people feel out of control or unable to deal with life may signal mental disorder • Sometimes it has a physical cause, injury to brain, effects of drug use, genentics ...
Psychological Disorders Review Sheet (Chapter 15)
... emptying of mental hospitals brought about by the introduction of anti-psychotic drugs. Unintended result: Lead to many people with severe mental illness becoming homeless. ...
... emptying of mental hospitals brought about by the introduction of anti-psychotic drugs. Unintended result: Lead to many people with severe mental illness becoming homeless. ...
Module 36 Chapter 110 Essentials of Understanding
... Antisocial (Sociopath) – lacks feelings of guilt or remorse (make a good con artists) Borderline – Difficulty developing sense of self – Overly dependent on others Narcissistic – Exaggerated sense of self-importance – lacks empathy for others ...
... Antisocial (Sociopath) – lacks feelings of guilt or remorse (make a good con artists) Borderline – Difficulty developing sense of self – Overly dependent on others Narcissistic – Exaggerated sense of self-importance – lacks empathy for others ...
Personality Disorders - lakshya education hub
... violation of, the rights of others Borderline PD – is a pattern of instability in interpersonal relationships, self-image, and affects, and marked impulsivity Histrionic PD – is a pattern of excessive emotionality and attention seeking Narcissistic PD – is a pattern of grandiosity, need for admirati ...
... violation of, the rights of others Borderline PD – is a pattern of instability in interpersonal relationships, self-image, and affects, and marked impulsivity Histrionic PD – is a pattern of excessive emotionality and attention seeking Narcissistic PD – is a pattern of grandiosity, need for admirati ...
Abnormal Psychology
... A “harmful dysfunction” in which behavior is judged to be atypical, disturbing, maladaptive and unjustifiable. ...
... A “harmful dysfunction” in which behavior is judged to be atypical, disturbing, maladaptive and unjustifiable. ...
Psychological Disorders
... conditions, but in which no known organic or physiological basis for the symptoms can be found. ...
... conditions, but in which no known organic or physiological basis for the symptoms can be found. ...
Personality Disorders
... Personality: an enduring pattern of inner experiences, emotional responses, attitudes and behaviors in an individual Takes ...
... Personality: an enduring pattern of inner experiences, emotional responses, attitudes and behaviors in an individual Takes ...
Introduction to Psychology
... Psychological Disorders Medical Model Concept that diseases have physical causes Assumes “mental” illnesses diagnosed on basis of symptoms, treated & possibly cured through therapy, may include treatment in psychiatric hospital ...
... Psychological Disorders Medical Model Concept that diseases have physical causes Assumes “mental” illnesses diagnosed on basis of symptoms, treated & possibly cured through therapy, may include treatment in psychiatric hospital ...
Abnormal test review -Know which collections of symptoms are
... For example: chemical imbalances in the brain are thought to be contributing factors in several disorders such as depression, schizophrenia, bipolar, OCD ...
... For example: chemical imbalances in the brain are thought to be contributing factors in several disorders such as depression, schizophrenia, bipolar, OCD ...
Describe dissociative disorders in general several
... analysis used to create Hans Eysenck's trait theory of personality? (two to five sentences) Briefly, in terms of human behavior, how would you define or explain latent learning? (Two to five sentences) Dissociative disorders are psychological phenomena in which there is a breakdown in an individual’ ...
... analysis used to create Hans Eysenck's trait theory of personality? (two to five sentences) Briefly, in terms of human behavior, how would you define or explain latent learning? (Two to five sentences) Dissociative disorders are psychological phenomena in which there is a breakdown in an individual’ ...
Sharleen Yuan
... The statistics on sanity are that one out of every four Americans is suffering from some form of mental illness. Think of your three best friends. If they're okay, then it's you. ~Rita Mae Brown ...
... The statistics on sanity are that one out of every four Americans is suffering from some form of mental illness. Think of your three best friends. If they're okay, then it's you. ~Rita Mae Brown ...
Chapter 14 Powerpoint
... and then using unhealthy methods to avoid weight gain • Purging – vomiting or misuse of laxatives • Binge may be triggered by a stress in life, then the person is not able to stop, they have no self control ...
... and then using unhealthy methods to avoid weight gain • Purging – vomiting or misuse of laxatives • Binge may be triggered by a stress in life, then the person is not able to stop, they have no self control ...
Abnormal Psychology - North Cobb High School Class Websites
... depression. • Involves periods of depression and manic episodes. • Manic episodes involve feelings of high energy (but they tend to differ a lot…some get confident and some get irritable). • Engage in risky behavior during the manic episode. ...
... depression. • Involves periods of depression and manic episodes. • Manic episodes involve feelings of high energy (but they tend to differ a lot…some get confident and some get irritable). • Engage in risky behavior during the manic episode. ...
Personality Disorders in the Elderly
... • Schizotypal Personality Disorder – Strikingly odd, even to laypersons – Magical-thinking, peculiar ideas, ideas of reference, illusions and derealization are part of the schizotypal patient’s everyday world ...
... • Schizotypal Personality Disorder – Strikingly odd, even to laypersons – Magical-thinking, peculiar ideas, ideas of reference, illusions and derealization are part of the schizotypal patient’s everyday world ...
Ch12worksheetAPpsyMentalDisorders
... and not feel bad about it, some people call me a “psychopath,” _________________; Look at me, look at me, look at me, _______________; I will cut myself it you try to leave me, ___________ Cluster C of personality disorders Anxious-fearful: I NEED someone, I am a needy person, ___________________; I ...
... and not feel bad about it, some people call me a “psychopath,” _________________; Look at me, look at me, look at me, _______________; I will cut myself it you try to leave me, ___________ Cluster C of personality disorders Anxious-fearful: I NEED someone, I am a needy person, ___________________; I ...
Psychological Disorders
... Know the 5 types and delusional disorders and their characteristics (erotomanic, grandiose, etc) List the characteristics of schizophrenia Know the 4 types of schizophrenia Define Mood Disorder Define Depressive and bipolar disorders Define moderate mood disorder What are the symptoms of dysthymic d ...
... Know the 5 types and delusional disorders and their characteristics (erotomanic, grandiose, etc) List the characteristics of schizophrenia Know the 4 types of schizophrenia Define Mood Disorder Define Depressive and bipolar disorders Define moderate mood disorder What are the symptoms of dysthymic d ...
Genetics of Schizophrenia
... 4. persistent preoccupation with parts of objects (B) Delays or abnormal functioning in at least one of the following areas, with onset prior to age 3 years: (1) social interaction (2) language as used in social communication (3) symbolic or imaginative play (C) The disturbance is not better account ...
... 4. persistent preoccupation with parts of objects (B) Delays or abnormal functioning in at least one of the following areas, with onset prior to age 3 years: (1) social interaction (2) language as used in social communication (3) symbolic or imaginative play (C) The disturbance is not better account ...
Slide 1
... multiple organ systems, coupled with negative work-ups, is typical of patients with somatization disorder. Often such patients present not with a long list of symptoms but one or two at a time, making diagnosis that is based on a single interview challenging. Obtaining collateral information from si ...
... multiple organ systems, coupled with negative work-ups, is typical of patients with somatization disorder. Often such patients present not with a long list of symptoms but one or two at a time, making diagnosis that is based on a single interview challenging. Obtaining collateral information from si ...
Personality Disorders
... Personality disorder - - DSM - long term, stable pattern of unusual and inflexible personality traits that lead to functional impairment or distress ...
... Personality disorder - - DSM - long term, stable pattern of unusual and inflexible personality traits that lead to functional impairment or distress ...
a PowerPoint presentation of Module 51
... This is most clearly attributable to: A. cultural ideals of beauty that increasingly encourage thinness. B. increasing levels of childhood sexual abuse. C. the onset of adolescence at increasingly younger ages. D. the decreasing emphasis on maintaining stable marriages. ...
... This is most clearly attributable to: A. cultural ideals of beauty that increasingly encourage thinness. B. increasing levels of childhood sexual abuse. C. the onset of adolescence at increasingly younger ages. D. the decreasing emphasis on maintaining stable marriages. ...
Affective and Personality Disorders
... • Who needs admission? – Risk of suicide/homicide – Lacks capacity to cooperate with treatment ...
... • Who needs admission? – Risk of suicide/homicide – Lacks capacity to cooperate with treatment ...
Personality Disorders - American Psychiatric Association
... Personality disorders are associated with ways of thinking and feeling about oneself and others that significantly and adversely affect how an individual functions in many aspects of life. They fall within 10 distinct types: paranoid personality disorder, schizoid personality disorder, schizotypal p ...
... Personality disorders are associated with ways of thinking and feeling about oneself and others that significantly and adversely affect how an individual functions in many aspects of life. They fall within 10 distinct types: paranoid personality disorder, schizoid personality disorder, schizotypal p ...
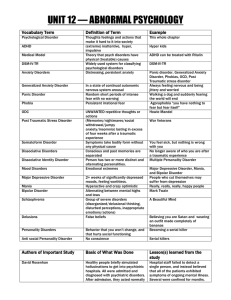
unit 12 — abnormal psychology
... Behavior that you won’t change, and that hurts social functioning No conscience ...
... Behavior that you won’t change, and that hurts social functioning No conscience ...