Personality Disorders (PD)
... – Deceitfulness: Dishonesty and fraudulence – Callousness: Lack of concern for feelings or problems of others; lack of guilt or remorse about the negative or harmful effects of one„s actions on others; aggression; sadism – Hostility: Persistent or frequent angry feelings; anger or irritability in re ...
... – Deceitfulness: Dishonesty and fraudulence – Callousness: Lack of concern for feelings or problems of others; lack of guilt or remorse about the negative or harmful effects of one„s actions on others; aggression; sadism – Hostility: Persistent or frequent angry feelings; anger or irritability in re ...
Psychological Disorders notes
... The Diagnostic Statistical Manual (version 4) is the book that psychologists and psychiatrists use to define (list symptoms) of disorders. Insurance companies won’t cover treatment if not in the DSM. Version 1 said homosexuality was a disorder. Neurotic disorders - a psychological disorder that is u ...
... The Diagnostic Statistical Manual (version 4) is the book that psychologists and psychiatrists use to define (list symptoms) of disorders. Insurance companies won’t cover treatment if not in the DSM. Version 1 said homosexuality was a disorder. Neurotic disorders - a psychological disorder that is u ...
Warm-Up
... Mental Disorders An illness of the mind that can affect the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of a person, preventing him or her from leading a happy, healthful, productive life Each year about 20% of the US population are affected by some form of mental disorder. ...
... Mental Disorders An illness of the mind that can affect the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of a person, preventing him or her from leading a happy, healthful, productive life Each year about 20% of the US population are affected by some form of mental disorder. ...
Personality disorder
... disorders Supporters of new categories answer that it is important to distinguish disorders precisely. Critics point to economics: diagnoses are needed for insurance reasons for therapists to ...
... disorders Supporters of new categories answer that it is important to distinguish disorders precisely. Critics point to economics: diagnoses are needed for insurance reasons for therapists to ...
mental disorders intro and anxiety
... causes a person to suffer is self-defeating or selfdestructive seriously impairs the person’s ability to work or get along with others or endangers others or the community ...
... causes a person to suffer is self-defeating or selfdestructive seriously impairs the person’s ability to work or get along with others or endangers others or the community ...
Multi-impulsive Eating Disorders
... Braun et al, 1994 found that 69% all ED patients had at least one PD Of those with bulimic subtypes, 31% had a Cluster B Personality Disorder – mostly borderline type NONE of the purely restricting anorexic patients had a cluster B personality Disorder Cluster C personality disorders spread ...
... Braun et al, 1994 found that 69% all ED patients had at least one PD Of those with bulimic subtypes, 31% had a Cluster B Personality Disorder – mostly borderline type NONE of the purely restricting anorexic patients had a cluster B personality Disorder Cluster C personality disorders spread ...
PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2 Current
... Rates of DSM-IV Personality Disorders in the Community and in Treatment Settings ...
... Rates of DSM-IV Personality Disorders in the Community and in Treatment Settings ...
Unit 12 PowerPoint Notes - Troup County School System
... • Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. • A person has several rather than one integrated personality. • People with DID commonly have a history of childhood abuse or trauma. ...
... • Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. • A person has several rather than one integrated personality. • People with DID commonly have a history of childhood abuse or trauma. ...
Mental Disorder Notes File
... A person becomes disconnected from their former identity. A) Schizophrenia: severe disturbances in thinking, mood, awareness, behavior. Mind is separated from reality. Ex: irrational fears not based in reality B) Multiple Personality Disorder: switching between two or more separate personalities. Un ...
... A person becomes disconnected from their former identity. A) Schizophrenia: severe disturbances in thinking, mood, awareness, behavior. Mind is separated from reality. Ex: irrational fears not based in reality B) Multiple Personality Disorder: switching between two or more separate personalities. Un ...
Abnormal Psychology
... • Characterized by the presence of two or more distinctive personality systems in the same individual at different times – Each may have distinctive memories and characteristics • Believed to be the result of an individual protecting themselves from extreme stress, shock, or trauma • Used to be know ...
... • Characterized by the presence of two or more distinctive personality systems in the same individual at different times – Each may have distinctive memories and characteristics • Believed to be the result of an individual protecting themselves from extreme stress, shock, or trauma • Used to be know ...
CHAPTER 10 Mental Disorders
... • May occur as the result of psychological causes in which no clear brain damage is involved. • Result from conditions such as stress, emotional conflict, fear, or poor coping skills. ...
... • May occur as the result of psychological causes in which no clear brain damage is involved. • Result from conditions such as stress, emotional conflict, fear, or poor coping skills. ...
Mental Disorders
... Examples of organic brain disorders Degenerative diseases 1)Huntington disease-a genetic disease that consists of abnormal movements, dementia, and psychological problems. 2. Multiple Sclerosis-An immune system disorder that affects the central nervous system (brain & spinal cord). ...
... Examples of organic brain disorders Degenerative diseases 1)Huntington disease-a genetic disease that consists of abnormal movements, dementia, and psychological problems. 2. Multiple Sclerosis-An immune system disorder that affects the central nervous system (brain & spinal cord). ...
Mental Illness intro (Bipolar / mood Disorder
... What causes Mental Disorders? Many believe the some mental disorders such as phobias develop from traumatic or stressful situations such as a death, an accident or an abusive event. Other disorders can be inherited and yet other disorders can result from an injury or a physical disorder that effect ...
... What causes Mental Disorders? Many believe the some mental disorders such as phobias develop from traumatic or stressful situations such as a death, an accident or an abusive event. Other disorders can be inherited and yet other disorders can result from an injury or a physical disorder that effect ...
Unit I
... A personality disorder is a pattern of perceiving, reacting, and relating to other people and events that is relatively inflexible and that impairs a person’s ability to function socially Personality traits become rigid and dysfunctional Personality disorders are chronic and maladaptive, impacting a ...
... A personality disorder is a pattern of perceiving, reacting, and relating to other people and events that is relatively inflexible and that impairs a person’s ability to function socially Personality traits become rigid and dysfunctional Personality disorders are chronic and maladaptive, impacting a ...
Narcissistic Personality Disorder
... Specific personality disorders are diagnosed based on DSM-IV-TR criteria. The general criteria in DSM-IV-TR emphasize the need to consider whether other mental or physical disorders (eg, depression, substance abuse, hyperthyroidism) can account for the patient's patterns of behavior. Patients' e ...
... Specific personality disorders are diagnosed based on DSM-IV-TR criteria. The general criteria in DSM-IV-TR emphasize the need to consider whether other mental or physical disorders (eg, depression, substance abuse, hyperthyroidism) can account for the patient's patterns of behavior. Patients' e ...
Dissociative Identity Disorder
... A. The presence of two or more distinct identities or personality states. B. At least two of this identites or personalities states recurrently take control of person’s C. Inability to recall important personal information that is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness ...
... A. The presence of two or more distinct identities or personality states. B. At least two of this identites or personalities states recurrently take control of person’s C. Inability to recall important personal information that is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness ...
Document
... Enduring pattern of inner experience or behavior that deviates from expectations of culture, manifested in two or more of the following: - cognition (perception of self, others) affectivity (intensity, range of emotions) interpersonal functioning impulse control ...
... Enduring pattern of inner experience or behavior that deviates from expectations of culture, manifested in two or more of the following: - cognition (perception of self, others) affectivity (intensity, range of emotions) interpersonal functioning impulse control ...
Mental Disorders
... • Puberty, body changes, and media cause some teens to put pressure on themselves to look a certain way • Common among girls but affect boys, too ...
... • Puberty, body changes, and media cause some teens to put pressure on themselves to look a certain way • Common among girls but affect boys, too ...
AP Psych 15 sq AP Psych-Psychological Disorders-SQ
... 11. What evidence is there to support the notion that early traumas create a risk factor for later depression? 12. What specific attributes cause depression according to learned helplessness theory? 13. How are cultural factors related to prevalence, manifestations, and gender differences in depress ...
... 11. What evidence is there to support the notion that early traumas create a risk factor for later depression? 12. What specific attributes cause depression according to learned helplessness theory? 13. How are cultural factors related to prevalence, manifestations, and gender differences in depress ...
Psychology 11
... 4. What are somatoform disorders? Give some examples. 5. What is schizophrenia? 6. List and describe the major symptoms present in schizophrenia. 7. Differentiate between the four major types of schizophrenia, outlining the main characteristics of each: a) paranoid schizophrenia; b) catatonic schizo ...
... 4. What are somatoform disorders? Give some examples. 5. What is schizophrenia? 6. List and describe the major symptoms present in schizophrenia. 7. Differentiate between the four major types of schizophrenia, outlining the main characteristics of each: a) paranoid schizophrenia; b) catatonic schizo ...
Chapter 14- Psychological disorders
... Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM IV) 1952- First edition 1994- 4th edition 2000- 4th revised 2013- Planned release for 5th edition Five axis criteria for diagnostic classification of psych. disorders Axis 1- Principal diagnosis - 16 categories Axis 2- Personality or developmental disorders Axi ...
... Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM IV) 1952- First edition 1994- 4th edition 2000- 4th revised 2013- Planned release for 5th edition Five axis criteria for diagnostic classification of psych. disorders Axis 1- Principal diagnosis - 16 categories Axis 2- Personality or developmental disorders Axi ...
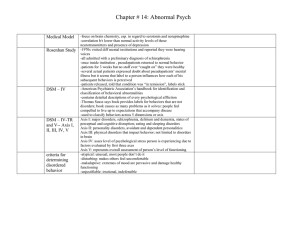
Medical Model - Biloxi Public Schools
... illness but it seems that label to a person influences how each of his subsequent behaviors is perceived -patients released, told that condition was “in remission”, labels stick -American Psychiatric Association’s handbook for identification and classification of behavioral abnormalities -contains d ...
... illness but it seems that label to a person influences how each of his subsequent behaviors is perceived -patients released, told that condition was “in remission”, labels stick -American Psychiatric Association’s handbook for identification and classification of behavioral abnormalities -contains d ...