15% of the population has a personality disorder
... They set unreasonably high standards for themselves and others and, fearing a mistake, may be afraid to make decisions. They may have trouble expressing affection and their relationships are often stiff and superficial. They may exhibit extreme emotional outbursts to intimidate others and may become ...
... They set unreasonably high standards for themselves and others and, fearing a mistake, may be afraid to make decisions. They may have trouble expressing affection and their relationships are often stiff and superficial. They may exhibit extreme emotional outbursts to intimidate others and may become ...
Antecedents of Personality Disorders in Young
... Shea and others; Klein and Mannuzza; Johnson and others; Quinton and others). However, developmental variables, with the exception of quality of the family environment, did not contribute to the predictability of poor functioning over and above the effect of having a personality disorder. Subjects w ...
... Shea and others; Klein and Mannuzza; Johnson and others; Quinton and others). However, developmental variables, with the exception of quality of the family environment, did not contribute to the predictability of poor functioning over and above the effect of having a personality disorder. Subjects w ...
DisordersMultipleChoice - Homework due date to be
... has not developed bipolar disorder may be that a. her self-actualization has not been blocked. b. she has not yet had any unresolved unconscious conflicts c. no life events have yet provoked the disorder d. there is no genetic tendency in the first place 10. _____ Repeatedly washing one’s hands is t ...
... has not developed bipolar disorder may be that a. her self-actualization has not been blocked. b. she has not yet had any unresolved unconscious conflicts c. no life events have yet provoked the disorder d. there is no genetic tendency in the first place 10. _____ Repeatedly washing one’s hands is t ...
Psychological Disorders
... can be very subjective… – Rosenhan (1973) study Mentally healthy confederates were admitted with schizophrenia into psychiatric hospitals They then behaved normally in the hospitals, but their normal behavior was interpreted as pathological based on previous diagnosis ...
... can be very subjective… – Rosenhan (1973) study Mentally healthy confederates were admitted with schizophrenia into psychiatric hospitals They then behaved normally in the hospitals, but their normal behavior was interpreted as pathological based on previous diagnosis ...
Behavioral Perspective Quiz
... she leaves her desk she will not have the opportunity to talk and gossip with her classmates, so she stays in her desk and is repeatedly shocked. One day the student actually does some work. She doesn’t turn around and doesn’t talk to her friends for 5 whole minutes. She then notices that the shocks ...
... she leaves her desk she will not have the opportunity to talk and gossip with her classmates, so she stays in her desk and is repeatedly shocked. One day the student actually does some work. She doesn’t turn around and doesn’t talk to her friends for 5 whole minutes. She then notices that the shocks ...
ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Tourette syndrome* Comorbid
... NOTE: Insurance compensation for services for patients with TS is complicated by the diagnosis being in ICD-9’s 290-319 series (mental disorders), which may trigger use of mental health benefit rules rather than those for medical benefits. This despite clear evidence confirming it as a neurological ...
... NOTE: Insurance compensation for services for patients with TS is complicated by the diagnosis being in ICD-9’s 290-319 series (mental disorders), which may trigger use of mental health benefit rules rather than those for medical benefits. This despite clear evidence confirming it as a neurological ...
psychological disorders Psych
... Genain sisters suffer from schizophrenia. Two more than others, thus there are contributing environmental factors. ...
... Genain sisters suffer from schizophrenia. Two more than others, thus there are contributing environmental factors. ...
the clinician`s dilemma: core conflictual relationship themes
... begin to get insight into the relationship between symptoms (the response of self, such as depression or anxiety) and their interpersonal concomitants - the expected, perceived, or actual responses from others. We know that the accounts of relationships given to us by our clients can be distorted (t ...
... begin to get insight into the relationship between symptoms (the response of self, such as depression or anxiety) and their interpersonal concomitants - the expected, perceived, or actual responses from others. We know that the accounts of relationships given to us by our clients can be distorted (t ...
Psychological Disorders
... DSM-IV: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edition Multiaxial (multidimensional) system of diagnosis • Axis I - the clinical syndrome for which a patient seeks treatment • Axis II - an enduring personality disorder that may contribute to axis I • Axis III – medical condition ...
... DSM-IV: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edition Multiaxial (multidimensional) system of diagnosis • Axis I - the clinical syndrome for which a patient seeks treatment • Axis II - an enduring personality disorder that may contribute to axis I • Axis III – medical condition ...
Psychological Disorders - Eric Sweetwood's PTHS Psychology
... • MULTIPLE PERSONALITY is a rare but striking dissociative disorder in which two or more distinct personalities exist within one individual. Each personality has its own characteristics, memories, desires and relationships. Each identity speaks, writes and acts in a very different way. Personalities ...
... • MULTIPLE PERSONALITY is a rare but striking dissociative disorder in which two or more distinct personalities exist within one individual. Each personality has its own characteristics, memories, desires and relationships. Each identity speaks, writes and acts in a very different way. Personalities ...
Treating the Difficult Patient
... Antisocial Personality Disorder Other Personality Disorders (Cluster B traits) ...
... Antisocial Personality Disorder Other Personality Disorders (Cluster B traits) ...
Mental Disorders
... and tasks of the real world. • Suffer discomfort more or less continuously – extreme anxiety, endless worry, or long periods of depression (something wrong with their life more than the average person) • May behave in a bizarre fashion – continuously misinterprets what is going on and what others ar ...
... and tasks of the real world. • Suffer discomfort more or less continuously – extreme anxiety, endless worry, or long periods of depression (something wrong with their life more than the average person) • May behave in a bizarre fashion – continuously misinterprets what is going on and what others ar ...
Obsessive Compulsive and Related Disorders - DSM-5
... often fill up or clutter active living areas of the home or workplace to the extent that their intended use is no longer possible. Symptoms of the disorder cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational or other important areas of functioning including maintaining an env ...
... often fill up or clutter active living areas of the home or workplace to the extent that their intended use is no longer possible. Symptoms of the disorder cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational or other important areas of functioning including maintaining an env ...
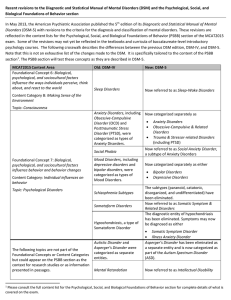
Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental
... In May 2013, the American Psychiatric Association published the 5th edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐5) with revisions to the criteria for the diagnosis and classification of mental disorders. These revisions are reflected in the content lists for the Psych ...
... In May 2013, the American Psychiatric Association published the 5th edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐5) with revisions to the criteria for the diagnosis and classification of mental disorders. These revisions are reflected in the content lists for the Psych ...
Chapter 16
... societal norms or the usual minimum standards for social conduct, culturally specific. 2. Mood disorder is a major disturbance in mood or emotion, such as depression or mania or bipolarity. 3. Schizophrenia means having a split personality 4. Everyone who experiences the same traumatic event will ex ...
... societal norms or the usual minimum standards for social conduct, culturally specific. 2. Mood disorder is a major disturbance in mood or emotion, such as depression or mania or bipolarity. 3. Schizophrenia means having a split personality 4. Everyone who experiences the same traumatic event will ex ...
Personality Disorders
... • Must rule out another personality disorder such as Schzoid Personality Disorder (Schzoids do not want relationships; Avoidants want them but are frightened of them) • Must rule out phobias (agoraphobics, people who have simple phobias, and people with social phobias, will have the same avoidant me ...
... • Must rule out another personality disorder such as Schzoid Personality Disorder (Schzoids do not want relationships; Avoidants want them but are frightened of them) • Must rule out phobias (agoraphobics, people who have simple phobias, and people with social phobias, will have the same avoidant me ...
Do Now
... • Clinical Syndromes • Major disorders: anxiety, depression, substance abuse, schizophrenia , learning disabilities ...
... • Clinical Syndromes • Major disorders: anxiety, depression, substance abuse, schizophrenia , learning disabilities ...
Chapter 9 (Personality Disorders)
... traits as an adolescent is associated with increased risk for the later development of other mental disorders • Sometimes, PDs represent the beginning stages of the onset of a ...
... traits as an adolescent is associated with increased risk for the later development of other mental disorders • Sometimes, PDs represent the beginning stages of the onset of a ...
Psychological DisordersClickers
... explanatory style, learns that she earned a poor grade on her psychology exam. Which attribution is most likely to help her cope without becoming depressed? A. “I’ll always be a poor student.” B. “The teacher gave a particularly hard exam this time.” C. “Of course my grade is bad, since I can’t do a ...
... explanatory style, learns that she earned a poor grade on her psychology exam. Which attribution is most likely to help her cope without becoming depressed? A. “I’ll always be a poor student.” B. “The teacher gave a particularly hard exam this time.” C. “Of course my grade is bad, since I can’t do a ...
"Everybody Hurts" by REM
... • Eventually the medical model came to dominate understandings of mental illness. • The medical model assumes that diseases have physical causes that can be diagnosed based on their symptoms and be treated and in ...
... • Eventually the medical model came to dominate understandings of mental illness. • The medical model assumes that diseases have physical causes that can be diagnosed based on their symptoms and be treated and in ...
Personality Disorders - Life Christian Counseling Network
... • Must rule out another personality disorder such as Schzoid Personality Disorder (Schzoids do not want relationships; Avoidants want them but are frightened of them) • Must rule out phobias (agoraphobics, people who have simple phobias, and people with social phobias, will have the same avoidant me ...
... • Must rule out another personality disorder such as Schzoid Personality Disorder (Schzoids do not want relationships; Avoidants want them but are frightened of them) • Must rule out phobias (agoraphobics, people who have simple phobias, and people with social phobias, will have the same avoidant me ...
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS AND TREATMENT
... DSM-5 Major Diagnostic Catagories 1.2.1 Neurodevelopmental disorders 1.2.2 Schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders 1.2.3 Bipolar and related disorders 1.2.4 Depressive disorders 1.2.5 Anxiety disorders 1.2.6 Obsessive-compulsive and related disorders 1.2.7 Trauma- and stressor-related ...
... DSM-5 Major Diagnostic Catagories 1.2.1 Neurodevelopmental disorders 1.2.2 Schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders 1.2.3 Bipolar and related disorders 1.2.4 Depressive disorders 1.2.5 Anxiety disorders 1.2.6 Obsessive-compulsive and related disorders 1.2.7 Trauma- and stressor-related ...
Dissociative Disorders
... their surroundings and their own bodies. 2. In those persons with dissociative disorders the dissociative experiences are more extreme and frequent, and the symptoms severely disrupt everyday functioning. 3. The learning perspective views dissociation as rewarding and thus highly reinforcing. ...
... their surroundings and their own bodies. 2. In those persons with dissociative disorders the dissociative experiences are more extreme and frequent, and the symptoms severely disrupt everyday functioning. 3. The learning perspective views dissociation as rewarding and thus highly reinforcing. ...
DSM-IV AND IDEA - Seattle University School of Law
... experts differently when DSM-IV diagnosis is raised in ...
... experts differently when DSM-IV diagnosis is raised in ...
Dissociative Disorders
... Extreme and rare, involves flight from home and the assumption of a new identity, with amnesia for past identity and events. A. Sudden, unexpected travel away from home or one’s customary place of work, with inability to recall one’s past B. Confusion about personal identity or assumption of a new i ...
... Extreme and rare, involves flight from home and the assumption of a new identity, with amnesia for past identity and events. A. Sudden, unexpected travel away from home or one’s customary place of work, with inability to recall one’s past B. Confusion about personal identity or assumption of a new i ...