Study Guide: Chapter 14 Introduction: Understanding Psychological
... for the development of phobias. 10. List the main symptoms and causes of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and the factors that influence the likelihood of developing PTSD. 11. Describe the main symptoms of obsessive– compulsive disorder (OCD), identifying common obsessions and compulsions in dif ...
... for the development of phobias. 10. List the main symptoms and causes of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and the factors that influence the likelihood of developing PTSD. 11. Describe the main symptoms of obsessive– compulsive disorder (OCD), identifying common obsessions and compulsions in dif ...
Module 29 Notes
... Discuss the benefit and potential dangers of diagnostic labels. Vocabulary: psychological disorder medical model bio-psycho-social model Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fourth edition, text revision (DSM-IV-TR) Philippe Pinel (1745-1826 A. Defining Disorder Psycholog ...
... Discuss the benefit and potential dangers of diagnostic labels. Vocabulary: psychological disorder medical model bio-psycho-social model Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fourth edition, text revision (DSM-IV-TR) Philippe Pinel (1745-1826 A. Defining Disorder Psycholog ...
Personality Disorder
... A longstanding maladaptive pattern of inner experience and behavior dating back to adolescence or adulthood that is manifest in at least two of the following areas: 1. Cognition 2. Affectivity 3. Interpersonal functioning 4. Impulse control ...
... A longstanding maladaptive pattern of inner experience and behavior dating back to adolescence or adulthood that is manifest in at least two of the following areas: 1. Cognition 2. Affectivity 3. Interpersonal functioning 4. Impulse control ...
Chapter 18 - PsychChapter18Psych
... victims are weak and deserving of being taken advantage of. Antisocials tend to lie and steal. Often, they are careless with money and take action without thinking about consequences. They are often agressive and are much more concerned with their own needs than the needs of others. ...
... victims are weak and deserving of being taken advantage of. Antisocials tend to lie and steal. Often, they are careless with money and take action without thinking about consequences. They are often agressive and are much more concerned with their own needs than the needs of others. ...
Clinical Psychology
... She has no friends at school, but seems undisturbed by the fact that she eats lunch by herself and walks alone around the campus. Her grades are erratic; if she likes a class she often receives an A or B, but will do no work at all in those she dislikes. Anne can occasionally be heard talking to her ...
... She has no friends at school, but seems undisturbed by the fact that she eats lunch by herself and walks alone around the campus. Her grades are erratic; if she likes a class she often receives an A or B, but will do no work at all in those she dislikes. Anne can occasionally be heard talking to her ...
Other Disorders
... Doctors discovered the causes of their symptoms as mixed emotions during upraising Kept them for up to 19 days ...
... Doctors discovered the causes of their symptoms as mixed emotions during upraising Kept them for up to 19 days ...
Anxiety Disorders
... • Persistent preoccupation with one’s health despite the fact that genuine symptoms of the disorder are lacking ...
... • Persistent preoccupation with one’s health despite the fact that genuine symptoms of the disorder are lacking ...
Psychological Disorders
... Normal behaviors were interpreted as pathological Doctors rarely responded to questions Many real patients were not fooled ...
... Normal behaviors were interpreted as pathological Doctors rarely responded to questions Many real patients were not fooled ...
Ch 17 Mental Disorders
... symptoms are disorganized thoughts garbled speech, as well as hallucinations and delusions. – 1. Probably not a single disorder. (Rule of thirds) – 2. It is suspected that schizophrenia results mostly from some physical or chemical problem because it appears in late adolescence or early adulthood, a ...
... symptoms are disorganized thoughts garbled speech, as well as hallucinations and delusions. – 1. Probably not a single disorder. (Rule of thirds) – 2. It is suspected that schizophrenia results mostly from some physical or chemical problem because it appears in late adolescence or early adulthood, a ...
Psychological Disorders are - tcouchAPPsych
... People who are declared not guilty by reason of insanity generally spend more time institutionalized than they would have been imprisoned. Being declared insane is not the same as being declared not competent to stand trial – this simply means you are unable to understand the charges against you and ...
... People who are declared not guilty by reason of insanity generally spend more time institutionalized than they would have been imprisoned. Being declared insane is not the same as being declared not competent to stand trial – this simply means you are unable to understand the charges against you and ...
Disorder
... primary personality will appear more than others, but the alternates have their own integrated memories and behaviors. They may or may not know of the existence of the other personalities and can vary in age or gender. Physiology can change with each personality. Ine one case, a female had different ...
... primary personality will appear more than others, but the alternates have their own integrated memories and behaviors. They may or may not know of the existence of the other personalities and can vary in age or gender. Physiology can change with each personality. Ine one case, a female had different ...
(Disorders). - Paul Trapnell
... Disorder is usually manifested in more than one of following areas: ...
... Disorder is usually manifested in more than one of following areas: ...
Psychological
... disorders characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning usually without anxiety, depression, or delusions ...
... disorders characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning usually without anxiety, depression, or delusions ...
Introduction to Psychological Disorders, Summary Notes
... abnormal in someone that we are told is mentally ill. These labels cause you to act differently around that person thereby eliciting behaviors that proves that this label is appropriate. For example if someone in class convinces others that you are a mean person, people may avoid you or treat you co ...
... abnormal in someone that we are told is mentally ill. These labels cause you to act differently around that person thereby eliciting behaviors that proves that this label is appropriate. For example if someone in class convinces others that you are a mean person, people may avoid you or treat you co ...
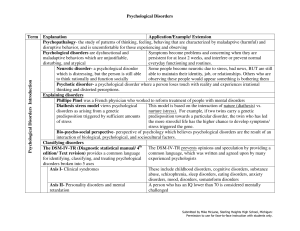
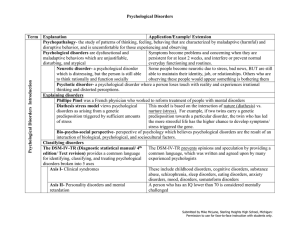
Psychological Disorders Term Explanation Application
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
13A-Psychdisorder-table - Miami Beach Senior High School
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
Mental health
... “Is unable on account of mental disorder to conduct a defence at any stage of the proceeding before a verdict is rendered or to instruct counsel to do so, and in particular, unable on account of mental disorder to a) understand the nature or object of the proceedings b) understand the possible conse ...
... “Is unable on account of mental disorder to conduct a defence at any stage of the proceeding before a verdict is rendered or to instruct counsel to do so, and in particular, unable on account of mental disorder to a) understand the nature or object of the proceedings b) understand the possible conse ...
7. PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT THEORIES OF 7.1 WHAT IS
... disorders, anyway? A personality disorder is a chronic and pervasive mental disorder that affects thoughts, behaviors and interpersonal functioning. The DSMIV currently lists 10 different personality disorders, including borderline, antisocial and avoidant personality disorder. You can learn more ab ...
... disorders, anyway? A personality disorder is a chronic and pervasive mental disorder that affects thoughts, behaviors and interpersonal functioning. The DSMIV currently lists 10 different personality disorders, including borderline, antisocial and avoidant personality disorder. You can learn more ab ...
File - Alphonse Asylum
... Each recipe must include symptoms as ingredients (i.e. 2 lbs. of hallucinations, 1 part delusions of grandeur, etc.) with appropriate 'measurement' amounts. Include directions for how to combine the ingredients to 'make' the recipe . Your front cover must have your “chef name” and your real na ...
... Each recipe must include symptoms as ingredients (i.e. 2 lbs. of hallucinations, 1 part delusions of grandeur, etc.) with appropriate 'measurement' amounts. Include directions for how to combine the ingredients to 'make' the recipe . Your front cover must have your “chef name” and your real na ...
Use of the Millon Clinical Multiaxial Inventory in the psychological
... sexual abuse in the past year, and 37% reported abuse at some point in their lifetime (Dearwater et al., 1998). The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders — Fourth Edition (DSM-IV) (American Psychiatric Association, 1994) does not contain an Axis I clinical syndrome specific to domest ...
... sexual abuse in the past year, and 37% reported abuse at some point in their lifetime (Dearwater et al., 1998). The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders — Fourth Edition (DSM-IV) (American Psychiatric Association, 1994) does not contain an Axis I clinical syndrome specific to domest ...
Chapter Summary/Lecture Organizer I. STUDYING
... B. Personality Disorders - Personality disorders involve inflexible, maladaptive personality traits. The best known type is the antisocial personality, characterized by egocentrism, lack of conscience, impulsivity, and superficial charm. Some research has suggested this disorder may be related to de ...
... B. Personality Disorders - Personality disorders involve inflexible, maladaptive personality traits. The best known type is the antisocial personality, characterized by egocentrism, lack of conscience, impulsivity, and superficial charm. Some research has suggested this disorder may be related to de ...
Substance-Related and Addictive Disorders
... DSM-5 will not include caffeine use disorder, although research shows that as little as two to three cups of coffee can trigger a withdrawal effect marked by tiredness or sleepiness. There is sufficient evidence to support this as a condition, however it is not yet clear to what extent it is a clini ...
... DSM-5 will not include caffeine use disorder, although research shows that as little as two to three cups of coffee can trigger a withdrawal effect marked by tiredness or sleepiness. There is sufficient evidence to support this as a condition, however it is not yet clear to what extent it is a clini ...
Chapter 14: Psychological Disorders
... the behaviors, internal states, and motivations of both ourselves and other people. Clarkin (2006) “Personality disorders are long-standing ways of behaving that are not so much severe mental disorders as dysfunctional styles of living” (Bernstein 628) ...
... the behaviors, internal states, and motivations of both ourselves and other people. Clarkin (2006) “Personality disorders are long-standing ways of behaving that are not so much severe mental disorders as dysfunctional styles of living” (Bernstein 628) ...