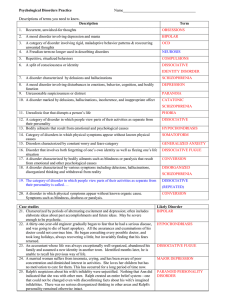
WC-Hyd-M021 - WordPress.com
... A number of psychologists claim that Smith exhibited many of the symptoms of histrionic personality disorder. The public watched as she displayed excessive emotions, abused drugs, had promiscuous sex, and always had to be the center of attention. Famous People with Personality Disorders ...
... A number of psychologists claim that Smith exhibited many of the symptoms of histrionic personality disorder. The public watched as she displayed excessive emotions, abused drugs, had promiscuous sex, and always had to be the center of attention. Famous People with Personality Disorders ...
Specific Learning Disorder - American Psychiatric Association
... symptoms, such as difficulty in reading, are just symptoms. And in many cases, one symptom points to a larger set of problems. These problems can have long-term impact on a person’s ability to function because so many activities of daily living require a mastery of number facts, written words, and w ...
... symptoms, such as difficulty in reading, are just symptoms. And in many cases, one symptom points to a larger set of problems. These problems can have long-term impact on a person’s ability to function because so many activities of daily living require a mastery of number facts, written words, and w ...
Ch. 16 - Psychological Disorders
... What is the effect of labeling psychological disorders? It biases your perception of the patient’s behavior After you know the diagnosis (label) even normal behavior is seen as a symptom of that diagnosis. ...
... What is the effect of labeling psychological disorders? It biases your perception of the patient’s behavior After you know the diagnosis (label) even normal behavior is seen as a symptom of that diagnosis. ...
Ch.16-Psych. Disorders
... What is the effect of labeling psychological disorders? It biases your perception of the patient’s behavior After you know the diagnosis (label) even normal behavior is seen as a symptom of that diagnosis. ...
... What is the effect of labeling psychological disorders? It biases your perception of the patient’s behavior After you know the diagnosis (label) even normal behavior is seen as a symptom of that diagnosis. ...
Chapter 14, Psych Disorders
... everyday life. • Estimates suggest that almost one third of adults in the U.S. have experienced some type of psychological disorder. ...
... everyday life. • Estimates suggest that almost one third of adults in the U.S. have experienced some type of psychological disorder. ...
dysfunctionalbehavio..
... Normal: behavior that is aligned with what society says is appropriate. Abnormal: behavior that is not socially acceptable and is personally distressful. Both of these definitions are accurate, due to the fact that society defines what the norm is and those who do not follow it are considered abno ...
... Normal: behavior that is aligned with what society says is appropriate. Abnormal: behavior that is not socially acceptable and is personally distressful. Both of these definitions are accurate, due to the fact that society defines what the norm is and those who do not follow it are considered abno ...
The DSM-V
... • Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) is a system that contains the the American Psychiatric Association (APA) criteria for mental disorders. • orginated in 1952, currently on fifth edition. • Has 17 different classes of disorders. ...
... • Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) is a system that contains the the American Psychiatric Association (APA) criteria for mental disorders. • orginated in 1952, currently on fifth edition. • Has 17 different classes of disorders. ...
DSM-IV-TR in Action Powerpoint
... Numerous clarifications and changes to almost all diagnoses in this category ...
... Numerous clarifications and changes to almost all diagnoses in this category ...
Psychological Disorders
... A mood disorder in which a person, for no apparent reason, experiences two or more weeks of depressed moods, feelings of worthlessness, and diminished interest or please in most activities. Manic episode A mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state. Medical model The concept tha ...
... A mood disorder in which a person, for no apparent reason, experiences two or more weeks of depressed moods, feelings of worthlessness, and diminished interest or please in most activities. Manic episode A mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state. Medical model The concept tha ...
Didactic Topic List
... Motivational Interviewing Psychiatric Rehabilitation Capacity to Stand Trial and Insanity Defense Assessment of Malingering Neurology Review PGY-3 Didactic Topics Outpatient Treatment of Neurocognitive Disorders ...
... Motivational Interviewing Psychiatric Rehabilitation Capacity to Stand Trial and Insanity Defense Assessment of Malingering Neurology Review PGY-3 Didactic Topics Outpatient Treatment of Neurocognitive Disorders ...
Check your answers - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
... characterized by mood swings, some of which had been so extreme that they had been psychotic in degree. At one point she became so depressed and asked to return to the hospital where she had been a patient. She then became overactive and exuberant in spirits and visited her friends, to whom she outl ...
... characterized by mood swings, some of which had been so extreme that they had been psychotic in degree. At one point she became so depressed and asked to return to the hospital where she had been a patient. She then became overactive and exuberant in spirits and visited her friends, to whom she outl ...
DSM-IV-TR in Action Powerpoint
... The stressors can be clarified with specifics: • problems with primary support • problems related to social environment • educational problems • occupational problems • housing problems • economic problems • problems with access to health care services • problems related to interaction with the lega ...
... The stressors can be clarified with specifics: • problems with primary support • problems related to social environment • educational problems • occupational problems • housing problems • economic problems • problems with access to health care services • problems related to interaction with the lega ...
Personality Disorders - Psychclerk
... An enduring pattern of inner experience and behavior that deviates markedly from the expectations of individual‘s culture. This pattern is manifested in two (or more) of the following areas: 1) Cognition (i.e., ways of perceiving and interpreting self, other people, and events) 2) Affectivity (i.e., ...
... An enduring pattern of inner experience and behavior that deviates markedly from the expectations of individual‘s culture. This pattern is manifested in two (or more) of the following areas: 1) Cognition (i.e., ways of perceiving and interpreting self, other people, and events) 2) Affectivity (i.e., ...
Schizophrenia & Other Psychotic Disorders
... - According to learning theories, schizophrenic patients learn irrational reactions and ways of thinking by imitating parents who have their own emotional problems. - In family dynamics studies, no well-controlled evidence indicates specific family pattern plays a causative role in the development o ...
... - According to learning theories, schizophrenic patients learn irrational reactions and ways of thinking by imitating parents who have their own emotional problems. - In family dynamics studies, no well-controlled evidence indicates specific family pattern plays a causative role in the development o ...
PERSONALITY DISORDERS and the “difficult patient”
... Perception that innocent remarks or nonthreatening situations are personal insults or attacks. Angry or hostile reaction to perceived slights or insults Schizoid: detached, aloof. Prone to introspection. Indifferent to others. Indifferent to praise/criticism. Inability to pick up normal social cues. ...
... Perception that innocent remarks or nonthreatening situations are personal insults or attacks. Angry or hostile reaction to perceived slights or insults Schizoid: detached, aloof. Prone to introspection. Indifferent to others. Indifferent to praise/criticism. Inability to pick up normal social cues. ...
PS 4251 ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY - The American College of
... Theories of and research in the study of psychopathological development. A scientist-practitioner approach to the study of a variety of psychological disorders, including anxiety, affective and personality disorders. Assessment and treatment approaches. An advanced-level course aimed at familiarizin ...
... Theories of and research in the study of psychopathological development. A scientist-practitioner approach to the study of a variety of psychological disorders, including anxiety, affective and personality disorders. Assessment and treatment approaches. An advanced-level course aimed at familiarizin ...
Psy 120(2). - Highly Derivative
... Even a single strong positive relations can offset this DSM-IV-TR 3 clusters (based on symptom similarities) Cluster A: -odd or eccentric behaviors (social dysfunction) ...
... Even a single strong positive relations can offset this DSM-IV-TR 3 clusters (based on symptom similarities) Cluster A: -odd or eccentric behaviors (social dysfunction) ...
Abnormal Psych
... disorder, social phobia, and schizoid personality disorder. 9. Identify the similarities and differences between obsessive-compulsive disorder and obsessivecompulsive personality disorder. 10. Describe alternative conceptualizations of the personality disorders. ...
... disorder, social phobia, and schizoid personality disorder. 9. Identify the similarities and differences between obsessive-compulsive disorder and obsessivecompulsive personality disorder. 10. Describe alternative conceptualizations of the personality disorders. ...
Pomerantz chapter 7 ppt
... Access treatment Stigma damages self-image Stereotyping by those who know the client Legal consequences ...
... Access treatment Stigma damages self-image Stereotyping by those who know the client Legal consequences ...
Psychological Disorders
... Mental disorders account for 15.4% of the years of life lost due to death or disability, scoring slightly below cardiovascular conditions and slightly about cancer. (Murray & Lopez, 1996). Rates and symptoms of psychological disorders vary by culture, but no known society is free of the two terrible ...
... Mental disorders account for 15.4% of the years of life lost due to death or disability, scoring slightly below cardiovascular conditions and slightly about cancer. (Murray & Lopez, 1996). Rates and symptoms of psychological disorders vary by culture, but no known society is free of the two terrible ...
CHAPTER 18
... functioning in a major part of the body for which there is no medical reason. 2. Hypochondriasis – (hypochondria) a person’s unrealistic preoccupation with the fear of serious illness or disease. ...
... functioning in a major part of the body for which there is no medical reason. 2. Hypochondriasis – (hypochondria) a person’s unrealistic preoccupation with the fear of serious illness or disease. ...
Oppositional Defiant Disorder
... almost 21 % of children ages 9 to 17 in the United States have a diagnosable mental or addictive disorder associated with at least minimum impairment (this chart shows 30.9%) ...
... almost 21 % of children ages 9 to 17 in the United States have a diagnosable mental or addictive disorder associated with at least minimum impairment (this chart shows 30.9%) ...
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual
... – Intellectual, emotional, social and physical disorders that begin at or before adolescence • E.g., separation anxiety disorder, attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder, learning disorders ...
... – Intellectual, emotional, social and physical disorders that begin at or before adolescence • E.g., separation anxiety disorder, attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder, learning disorders ...
Abnormal Psychology
... • An anxiety disorder marked by a persistent, irrational fear and avoidance of a specific object, activity, or situation • Social phobia: intense fear of being scrutinized by others, avoid potentially embarrassing situations (speaking up, going to ...
... • An anxiety disorder marked by a persistent, irrational fear and avoidance of a specific object, activity, or situation • Social phobia: intense fear of being scrutinized by others, avoid potentially embarrassing situations (speaking up, going to ...
Document
... Additional Personality Disorders • Personality disorders in ICD-10 – Dissocial personality disorder – Emotionally unstable personality disorder – Anankastic personality disorder (OCD) – Anxious (avoidant) personality disorder – Eccentric personality disorder – Immature personality disorder – Psycho ...
... Additional Personality Disorders • Personality disorders in ICD-10 – Dissocial personality disorder – Emotionally unstable personality disorder – Anankastic personality disorder (OCD) – Anxious (avoidant) personality disorder – Eccentric personality disorder – Immature personality disorder – Psycho ...