Fractured Fairy Tales
... You are going to rewrite a common fairy tale giving the main character(s) your disorder. 1) Choose a fairy tale you are familiar with (refer to the list provided). Two teams may not use the same story (first come, first serve). 2) Using your book and any other research of the disorder, rewrite the s ...
... You are going to rewrite a common fairy tale giving the main character(s) your disorder. 1) Choose a fairy tale you are familiar with (refer to the list provided). Two teams may not use the same story (first come, first serve). 2) Using your book and any other research of the disorder, rewrite the s ...
Mental Disorders
... Mental Disorder – a behavioral or psychological syndrome or pattern that occurs in an individual and that is associated with distress or disability with a significantly increased risk of suffering, death, pain, disability or an important loss of freedom ...
... Mental Disorder – a behavioral or psychological syndrome or pattern that occurs in an individual and that is associated with distress or disability with a significantly increased risk of suffering, death, pain, disability or an important loss of freedom ...
Neurotic, Psychotic or Just Plain Nuts?
... AXIS II Disorders Axis II is comprised of two categories: mental retardation and personality disorders. The first category is probably familiar to you: it refers to persons whose intelligence falls below a specific level, referred to as an Intelligence Quotient or IQ. A personality disorder is an en ...
... AXIS II Disorders Axis II is comprised of two categories: mental retardation and personality disorders. The first category is probably familiar to you: it refers to persons whose intelligence falls below a specific level, referred to as an Intelligence Quotient or IQ. A personality disorder is an en ...
exploring psychology
... PARAPHILIAS (pp. 173, 174, 188) Exporing Psychology, Ninth Edition with Updates on DSM-5 includes coverage of paraphilias, and the conditions which now must be met for them to be considered a disorder. PERSONALITY DISORDERS (p. 538) The separate categories of personality disorder had been slated for ...
... PARAPHILIAS (pp. 173, 174, 188) Exporing Psychology, Ninth Edition with Updates on DSM-5 includes coverage of paraphilias, and the conditions which now must be met for them to be considered a disorder. PERSONALITY DISORDERS (p. 538) The separate categories of personality disorder had been slated for ...
OL Chapter 12 overview
... Depressed people see life through dark glasses. Social-cognitive theorists point out that biological factors do not operate independently of environmental influences. People who are depressed often have negative beliefs about themselves and their present and future situations (they view life through ...
... Depressed people see life through dark glasses. Social-cognitive theorists point out that biological factors do not operate independently of environmental influences. People who are depressed often have negative beliefs about themselves and their present and future situations (they view life through ...
Paranoid Personality Disorder
... Statistics on the number of people with Personality Disorders: An estimated 36.4 million American adults (14.8 percent) meet standard diagnostic criteria for at least one personality disorder as defined in the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders ( ...
... Statistics on the number of people with Personality Disorders: An estimated 36.4 million American adults (14.8 percent) meet standard diagnostic criteria for at least one personality disorder as defined in the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders ( ...
Dissociative identity disorder.
... A person who has dissociative identity disorder almost always has dissociative amnesia too. (Barlow, Duran,2009) ...
... A person who has dissociative identity disorder almost always has dissociative amnesia too. (Barlow, Duran,2009) ...
Psychological Disorders
... and/or suffer from hallucinations, which are symptoms of psychosis. If this occurs, the condition is called bipolar I with psychotic features. ...
... and/or suffer from hallucinations, which are symptoms of psychosis. If this occurs, the condition is called bipolar I with psychotic features. ...
CLEB-Mental-Health-Issues
... Identify the three most common personality disorders encountered Identify the two most common mood disorders Describe the communicative approach and techniques necessary for dealing with the ...
... Identify the three most common personality disorders encountered Identify the two most common mood disorders Describe the communicative approach and techniques necessary for dealing with the ...
Introduction to Psychology
... Personality Disorders Dependent Personality Disorder Behave in clingy, submissive ways and displays a strong need to have others take care of them Paranoid Personality Disorder Shows deep distrust of other people, which gets in the way of personal relationships Different than paranoid sch ...
... Personality Disorders Dependent Personality Disorder Behave in clingy, submissive ways and displays a strong need to have others take care of them Paranoid Personality Disorder Shows deep distrust of other people, which gets in the way of personal relationships Different than paranoid sch ...
Introduction to Psychology, 7th Edition, Rod Plotnik
... – _____________________________ answer a number of questions • _________________________________________ • ______________________________________________________________ • ___________________________________________________________ • ________________________________ – Diagnostic and Statistical Manu ...
... – _____________________________ answer a number of questions • _________________________________________ • ______________________________________________________________ • ___________________________________________________________ • ________________________________ – Diagnostic and Statistical Manu ...
Abnormal Psychology
... • More likely among rich, nonreligious, If someone confides in you, they single/widowed/divorced are crying out for help • 5x greater risk for those who been depressed • Alcoholics 100x more likely • Teen suicides often linked w/ drug and alcohol abuse • Gay youth & elderly more likely • 33,000 Amer ...
... • More likely among rich, nonreligious, If someone confides in you, they single/widowed/divorced are crying out for help • 5x greater risk for those who been depressed • Alcoholics 100x more likely • Teen suicides often linked w/ drug and alcohol abuse • Gay youth & elderly more likely • 33,000 Amer ...
Chapter 18—Psychological Disorders
... indicate a psychological disorder Culture-Bound Syndromes: Clusters of symptoms that define or describe an illness. ...
... indicate a psychological disorder Culture-Bound Syndromes: Clusters of symptoms that define or describe an illness. ...
Becoming familiar with the DSM 5
... • 91-100 Superior functioning in a wide range of activities, life’s problems never seem to get out of hand, is sought out by others because of his or her many positive qualities. No symptoms. • 81-90 Absent or minimal symptoms (e.g., mild anxiety before an exam), good functioning in all areas, inter ...
... • 91-100 Superior functioning in a wide range of activities, life’s problems never seem to get out of hand, is sought out by others because of his or her many positive qualities. No symptoms. • 81-90 Absent or minimal symptoms (e.g., mild anxiety before an exam), good functioning in all areas, inter ...
So that explains the voices
... •This is the name of an alter identity that a person may create, in which they create an entirely new identity and experience amnesia of their previous life. ...
... •This is the name of an alter identity that a person may create, in which they create an entirely new identity and experience amnesia of their previous life. ...
DSM-5 and Diagnoses for Children
... an important function in giving feedback on proposed changes and, in some cases, meeting with members of the DSM-5 Work Groups. All revisions to the manual were made to more precisely describe and diagnose the symptoms and behaviors of those seeking clinical help. Parents provided a particularly val ...
... an important function in giving feedback on proposed changes and, in some cases, meeting with members of the DSM-5 Work Groups. All revisions to the manual were made to more precisely describe and diagnose the symptoms and behaviors of those seeking clinical help. Parents provided a particularly val ...
File
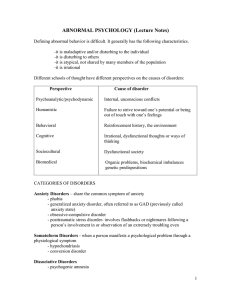
... The psychodynamic approach emphasizes unconscious conflicts as the cause of disabling anxiety. The humanistic approach emphasizes the effects of a faulty self-image. The behaviorists emphasize the effects of previous learning, particularly avoidance learning. Cognitive theories of anxiety fo ...
... The psychodynamic approach emphasizes unconscious conflicts as the cause of disabling anxiety. The humanistic approach emphasizes the effects of a faulty self-image. The behaviorists emphasize the effects of previous learning, particularly avoidance learning. Cognitive theories of anxiety fo ...
Andrew Rosen Early Conceptions of Mental Disorders
... impulsivity, difficulty staying focused on a task, and a range of behavioral problems o Have difficulty keeping attention o Potentially caused by a deficiency in prefrontal brain circuits that protect us from distraction o Stimulants with methylphenidate (Ritalin and Concerta) are used Enhances th ...
... impulsivity, difficulty staying focused on a task, and a range of behavioral problems o Have difficulty keeping attention o Potentially caused by a deficiency in prefrontal brain circuits that protect us from distraction o Stimulants with methylphenidate (Ritalin and Concerta) are used Enhances th ...
Psychology Disorders
... • Write about something in your life that may cause you anxiety and avoidance behaviors that help reduce your anxiety. • I can tell you about not going to “scary movies” ...
... • Write about something in your life that may cause you anxiety and avoidance behaviors that help reduce your anxiety. • I can tell you about not going to “scary movies” ...
mental health sciences library
... The courtship dance of the borderline. Lincoln, NE: iUniverse.com, Inc., 2001. Also published by Rodale as “Siren’s dance”. Aguirre, Blaise A. Depression (biographies of disease). Westport, CT: Greenwood Publishing Group, 2008. Galen, Gillian and Aguirre, Blaise. Mindfulness for borderline personali ...
... The courtship dance of the borderline. Lincoln, NE: iUniverse.com, Inc., 2001. Also published by Rodale as “Siren’s dance”. Aguirre, Blaise A. Depression (biographies of disease). Westport, CT: Greenwood Publishing Group, 2008. Galen, Gillian and Aguirre, Blaise. Mindfulness for borderline personali ...
z2r012162576so2 - American Psychological Association
... symptoms to diagnoses of borderline, avoidant, obsessive–compulsive, narcissistic, antisocial, and schizotypal disorders (Sharp et al., 2015). Interestingly, an exploratory bifactor model found that the large majority of symptoms loaded significantly on a general factor of personality disorder simil ...
... symptoms to diagnoses of borderline, avoidant, obsessive–compulsive, narcissistic, antisocial, and schizotypal disorders (Sharp et al., 2015). Interestingly, an exploratory bifactor model found that the large majority of symptoms loaded significantly on a general factor of personality disorder simil ...
Roadmap for Diagnosis
... P. The best predictor of future behavior is past behavior (p.47) Q. More symptoms of a disorder increase its likelihood as your diagnosis (p.47) R. Typical feature of a disorder increase its likelihood as your diagnosis; in the presence of nontypical features, look for alternatives (p.47) S. Previou ...
... P. The best predictor of future behavior is past behavior (p.47) Q. More symptoms of a disorder increase its likelihood as your diagnosis (p.47) R. Typical feature of a disorder increase its likelihood as your diagnosis; in the presence of nontypical features, look for alternatives (p.47) S. Previou ...
Somatoform Disorders
... – The person will not be able to move their arms, see, feel, etc. but there is no biological cause – The diagnosis of conversion disorder is rare, occurring in only 2% of the population – Usually appears in adolescence or early adulthood (but can occur at any age) – Conversion disorder seems to appe ...
... – The person will not be able to move their arms, see, feel, etc. but there is no biological cause – The diagnosis of conversion disorder is rare, occurring in only 2% of the population – Usually appears in adolescence or early adulthood (but can occur at any age) – Conversion disorder seems to appe ...