Why Is It So Difficult To Develop A Malaria Vaccine?
... merozoite proteins (AMA1 and MSP1) contribute to the acquisition of protective immunity in malaria-endemic areas. Thus, although AMA1 and MSP1 are leading subunit vaccine candidates, their antigenic polymorphism continues to thwart vaccine development. AMA1 is a merozoite protein found in the organe ...
... merozoite proteins (AMA1 and MSP1) contribute to the acquisition of protective immunity in malaria-endemic areas. Thus, although AMA1 and MSP1 are leading subunit vaccine candidates, their antigenic polymorphism continues to thwart vaccine development. AMA1 is a merozoite protein found in the organe ...
2015 Immunology Whitebook - Dalhousie Medical School
... called “growth factors”. These factors belong to the “cytokine” family (see Chapter 6). Growth factors cause the development of progenitor cells in each line from the pluripotent stem cells. A progenitor cell is a committed cell, meaning that it is committed to that line of cell growth. (An eosinoph ...
... called “growth factors”. These factors belong to the “cytokine” family (see Chapter 6). Growth factors cause the development of progenitor cells in each line from the pluripotent stem cells. A progenitor cell is a committed cell, meaning that it is committed to that line of cell growth. (An eosinoph ...
unit-1-5 consise NOTES immunology - E
... The immune system can be thought of as having two “lines of defence”: the first, representing a non-specific (no memory) response to antigen (substance to which the body regards as foreign or potentially harmful) known as the innate immune system; and the second, the adaptive immune system, which di ...
... The immune system can be thought of as having two “lines of defence”: the first, representing a non-specific (no memory) response to antigen (substance to which the body regards as foreign or potentially harmful) known as the innate immune system; and the second, the adaptive immune system, which di ...
Supplementary information for Ronshaugen, McGinnis
... determined for the wild type A1 segments. Identically treated embryos were then stained with a rat monoclonal anti-HA antibody and the mean luminosity with this antibody in the T2 segment was determined. All other transgenic lines were similarly assayed using the anti-HA antibody. These were selecte ...
... determined for the wild type A1 segments. Identically treated embryos were then stained with a rat monoclonal anti-HA antibody and the mean luminosity with this antibody in the T2 segment was determined. All other transgenic lines were similarly assayed using the anti-HA antibody. These were selecte ...
Immunopathogenesis of chronic periapical
... antigens can be proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, or nucleic acids. Further, it is possible that nonspecific activation of the immune system can be brought about by microorganisms. In addition, antigens can be combinations of small foreign molecules (haptens) which combine with host proteins to initi ...
... antigens can be proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, or nucleic acids. Further, it is possible that nonspecific activation of the immune system can be brought about by microorganisms. In addition, antigens can be combinations of small foreign molecules (haptens) which combine with host proteins to initi ...
Prevention of HBV infections: vaccination and its limitations
... • in vivo humoral and in vitro anti-HBs responses are closely correlated • booster responses reveal the immune memory Leroux-Roels et al. Vaccine 1994;12:812-8 ...
... • in vivo humoral and in vitro anti-HBs responses are closely correlated • booster responses reveal the immune memory Leroux-Roels et al. Vaccine 1994;12:812-8 ...
Immune complex formation in IgA nephropathy
... IgA1 is one of the very few serum proteins to posses O-linked sugars. The fact that these O-linked sugars are clustered within a relatively short segment of the IgA1 protein backbone (the so-called hinge region) means they might have a considerable effect on IgA1 function.4 Furthermore, the composit ...
... IgA1 is one of the very few serum proteins to posses O-linked sugars. The fact that these O-linked sugars are clustered within a relatively short segment of the IgA1 protein backbone (the so-called hinge region) means they might have a considerable effect on IgA1 function.4 Furthermore, the composit ...
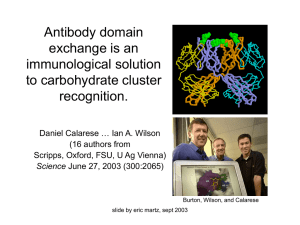
Antibody domain exchange is an immunological solution to
... shielded. • Carbohydrate is made by host (not virus enzymes) hence may be “self” (though the dense cluster of oligomannose residues has not been described on mammalian glycoproteins). ...
... shielded. • Carbohydrate is made by host (not virus enzymes) hence may be “self” (though the dense cluster of oligomannose residues has not been described on mammalian glycoproteins). ...
Artificial Immune Systems
... fully mature DCs and migrate to lymph nodes where they interact with T-cells. T-cells are of three types; helper T-cells which are essential to the activation of B-cells, killer T-cells which bind to foreign invaders and inject poisonous chemicals into them causing their destruction, and suppressor ...
... fully mature DCs and migrate to lymph nodes where they interact with T-cells. T-cells are of three types; helper T-cells which are essential to the activation of B-cells, killer T-cells which bind to foreign invaders and inject poisonous chemicals into them causing their destruction, and suppressor ...
PROPERTIES OF ANTI-MYCOLIC ACID ANTIBODIES IN HUMAN TUBERCULOSIS PATIENTS Master of Science
... Mycolic acid (MA) is the major lipid cell wall constituent of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the etiological agent of this disease. In this study an antibody response to the MA molecules are investigated as a possible surrogate marker for tuberculosis. In previous studies, IgG antibodies to MA in TB in ...
... Mycolic acid (MA) is the major lipid cell wall constituent of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the etiological agent of this disease. In this study an antibody response to the MA molecules are investigated as a possible surrogate marker for tuberculosis. In previous studies, IgG antibodies to MA in TB in ...
A 205-Nucleotide Deletion in the 3= Untranslated Region of Avian
... Diversification in Hypervaccinated Humans Tine Rugh Poulsen,1 Allan Jensen,2 John S. Haurum,3 and Peter S. Andersen ...
... Diversification in Hypervaccinated Humans Tine Rugh Poulsen,1 Allan Jensen,2 John S. Haurum,3 and Peter S. Andersen ...
immunochemical mechanisms involved in penicillin hypersensitivity
... multivalent conjugates of the BPO, the Dbenzylpenicillenic acid-disulfide or the Dpenicillamine haptenic groups. The antigenic specificities of these skin-sensitizing antibodies have not been determined. Some possibilities are discussed in Siegel and Levine (1964). In addition to these three antigen ...
... multivalent conjugates of the BPO, the Dbenzylpenicillenic acid-disulfide or the Dpenicillamine haptenic groups. The antigenic specificities of these skin-sensitizing antibodies have not been determined. Some possibilities are discussed in Siegel and Levine (1964). In addition to these three antigen ...
Turnover-based in vitro selection and evolution of biocatalysts from
... novel protein catalysts remains largely a basic research goal, albeit one with considerable potential once high turnover numbers are achieved1–4. Antibodies are considered useful candidates for mimicking the process of divergent protein evolution. The versatile immunoglobulin structure combines stab ...
... novel protein catalysts remains largely a basic research goal, albeit one with considerable potential once high turnover numbers are achieved1–4. Antibodies are considered useful candidates for mimicking the process of divergent protein evolution. The versatile immunoglobulin structure combines stab ...
... Effective cancer treatment to prevent the tumor growth as well as to stop its recurrence is the dream of oncologists. Currently available therapeutic measures like, radiotherapy and chemotherapy, often suffer from severe toxicity and lack of specificity of the drug towards tumor cells. Another promi ...
Basic Concepts of Immune Response and Defense Development
... Théry and Amigorena 2001). This process is critically important in defending against intracellular pathogens such as viruses and certain bacteria. The Tc lymphocyte responses are also essential in the immune defense against tumors due to their role in recognizing antigens presented in the context of ...
... Théry and Amigorena 2001). This process is critically important in defending against intracellular pathogens such as viruses and certain bacteria. The Tc lymphocyte responses are also essential in the immune defense against tumors due to their role in recognizing antigens presented in the context of ...
Basic Concepts of Immune Response and Defense Development
... such as DCs through Toll-like receptors (TLRs1) (Diefenbach and Raulet 2003; Gordon 2002; Netea et al. 2004). The critical interaction between the innate and specific parts of the immune system involves the role played by antigen-presenting cells (APCs1), which include monocytes, M⌽s, endothelial ce ...
... such as DCs through Toll-like receptors (TLRs1) (Diefenbach and Raulet 2003; Gordon 2002; Netea et al. 2004). The critical interaction between the innate and specific parts of the immune system involves the role played by antigen-presenting cells (APCs1), which include monocytes, M⌽s, endothelial ce ...
Role of complement in health and disease
... reactions • Complement system plays role in type II and type III hypersensitivity reactions. • Type II Reaction: mediated by IgG or IgM to foreign antigens which are bound to cell surfaces or other molecules. • Opsonised antigen stimulates various mechanisms aimed at elimination such as phagocy ...
... reactions • Complement system plays role in type II and type III hypersensitivity reactions. • Type II Reaction: mediated by IgG or IgM to foreign antigens which are bound to cell surfaces or other molecules. • Opsonised antigen stimulates various mechanisms aimed at elimination such as phagocy ...
36.4 How Does the Adaptive Immune System Recognize Invaders?
... – Natural killer cells are another type of leukocyte, which strike primarily at the body’s own cells that have become cancerous or have been invaded by viruses – The surfaces of normal body cells display proteins of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), identifying the cell as “self” – Natural ...
... – Natural killer cells are another type of leukocyte, which strike primarily at the body’s own cells that have become cancerous or have been invaded by viruses – The surfaces of normal body cells display proteins of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), identifying the cell as “self” – Natural ...
Detection of a potent humoral response associated with immune
... approximately one-third of these antigenic targets represent novel genes (http://www.licr.org/SEREX.html; ref. 19). Importantly, many antigens identified previously as T-cell targets have also been shown to be targets of B-cell immunity, and conversely, antigens originally identified because of anti ...
... approximately one-third of these antigenic targets represent novel genes (http://www.licr.org/SEREX.html; ref. 19). Importantly, many antigens identified previously as T-cell targets have also been shown to be targets of B-cell immunity, and conversely, antigens originally identified because of anti ...
Polyclonal Anti-Collagen Type I
... GM-CSF is at 5q21-q32, the chromosome region deleted in the 5q- anomaly. Science 230: 1282-1285, 1985. Grabstein, K. H.; Urdal, D. L.; Tushinski, R. J.; Mochizuki, D. Y.; Price, V. L.; Cantrell, M. A.; Gillis, S.; Conlon, P. J. Induction of macrophage tumoricidal activity by granulocyte-macrophage c ...
... GM-CSF is at 5q21-q32, the chromosome region deleted in the 5q- anomaly. Science 230: 1282-1285, 1985. Grabstein, K. H.; Urdal, D. L.; Tushinski, R. J.; Mochizuki, D. Y.; Price, V. L.; Cantrell, M. A.; Gillis, S.; Conlon, P. J. Induction of macrophage tumoricidal activity by granulocyte-macrophage c ...
Immunology for physicists - Laboratoire de Physique Statistique
... marker called CD4, act through the secretion of lymphokines that promote the growth and differentiation of B cells into an antibody-secreting state. Helper T cells are the cells that are predominantly infected by the human immunodeficiency virus, and their depletion plays a major role in AIDS. Cytot ...
... marker called CD4, act through the secretion of lymphokines that promote the growth and differentiation of B cells into an antibody-secreting state. Helper T cells are the cells that are predominantly infected by the human immunodeficiency virus, and their depletion plays a major role in AIDS. Cytot ...
Thermo Scientific HyClone Super Low IgG Fetal Bovine Serum
... Super Low IgG Fetal Bovine Serum Processed to substantially reduce IgG (via Protein G Chromatography) level, Thermo Scientific HyClone Super Low IgG Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) is suitable for use in more exacting applications. FBS contains natural levels of immunoglobulin (IgG) that may be too high fo ...
... Super Low IgG Fetal Bovine Serum Processed to substantially reduce IgG (via Protein G Chromatography) level, Thermo Scientific HyClone Super Low IgG Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) is suitable for use in more exacting applications. FBS contains natural levels of immunoglobulin (IgG) that may be too high fo ...
Tong, LF, Balakrishan G, Kochan JP, et al. Assessment of
... All antigens initially elicit the production of IgM antibodies against an injected or inhaled allergen. With repeated exposure, the antigen may stimulate an event known as class switching, whereby the constant portion of the antibody will “switch” to another class (i.e., IgG, IgA, or IgE). The new a ...
... All antigens initially elicit the production of IgM antibodies against an injected or inhaled allergen. With repeated exposure, the antigen may stimulate an event known as class switching, whereby the constant portion of the antibody will “switch” to another class (i.e., IgG, IgA, or IgE). The new a ...
Hantavirus (Hantaan)
... Hantaviruses are single-stranded enveloped RNA viruses in the Bunyaviridae family, are widespread and are strictly associated with their serotype-specific reservoir hosts. They cause hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) in Europe and Asia and lead to hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome (HCPS ...
... Hantaviruses are single-stranded enveloped RNA viruses in the Bunyaviridae family, are widespread and are strictly associated with their serotype-specific reservoir hosts. They cause hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) in Europe and Asia and lead to hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome (HCPS ...
Antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shape protein produced by plasma cells that is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the harmful agent, called an antigen, via the variable region. Each tip of the ""Y"" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (similarly analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can tag a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize its target directly (for example, by blocking a part of a microbe that is essential for its invasion and survival). The ability of an antibody to communicate with the other components of the immune system is mediated via its Fc region (located at the base of the ""Y""), which contains a conserved glycosylation site involved in these interactions. The production of antibodies is the main function of the humoral immune system.Antibodies are secreted by cells of the adaptive immune system (B cells), and more specifically, differentiated B cells called plasma cells. Antibodies can occur in two physical forms, a soluble form that is secreted from the cell, and a membrane-bound form that is attached to the surface of a B cell and is referred to as the B cell receptor (BCR). The BCR is found only on the surface of B cells and facilitates the activation of these cells and their subsequent differentiation into either antibody factories called plasma cells or memory B cells that will survive in the body and remember that same antigen so the B cells can respond faster upon future exposure. In most cases, interaction of the B cell with a T helper cell is necessary to produce full activation of the B cell and, therefore, antibody generation following antigen binding. Soluble antibodies are released into the blood and tissue fluids, as well as many secretions to continue to survey for invading microorganisms.Antibodies are glycoproteins belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily; the terms antibody and immunoglobulin are often used interchangeably. Though strictly speaking, an antibody is not the same as an immunoglobulin; B cells can produce two types of immunoglobulins - surface immunoglobulins, which are B cell receptors; and secreted immunoglobulins, which are antibodies. So antibodies are one of two classes of immunoglobulins. Antibodies are typically made of basic structural units—each with two large heavy chains and two small light chains. There are several different types of antibody heavy chains based on five different types of crystallisable fragments (Fc) that may be attached to the antigen-binding fragments. The five different types of Fc regions allow antibodies to be grouped into five isotypes. Each Fc region of a particular antibody isotype is able to bind to its specific Fc Receptor (except for IgD, which is essentially the BCR), thus allowing the antigen-antibody complex to mediate different roles depending on which FcR it binds. The ability of an antibody to bind to its corresponding FcR is further modulated by the structure of the glycan(s) present at conserved sites within its Fc region. The ability of antibodies to bind to FcRs helps to direct the appropriate immune response for each different type of foreign object they encounter. For example, IgE is responsible for an allergic response consisting of mast cell degranulation and histamine release. IgE's Fab paratope binds to allergic antigen, for example house dust mite particles, while its Fc region binds to Fc receptor ε. The allergen-IgE-FcRε interaction mediates allergic signal transduction to induce conditions such as asthma. Though the general structure of all antibodies is very similar, a small region at the tip of the protein is extremely variable, allowing millions of antibodies with slightly different tip structures, or antigen-binding sites, to exist. This region is known as the hypervariable region. Each of these variants can bind to a different antigen. This enormous diversity of antibody paratopes on the antigen-binding fragments allows the immune system to recognize an equally wide variety of antigens. The large and diverse population of antibody paratope is generated by random recombination events of a set of gene segments that encode different antigen-binding sites (or paratopes), followed by random mutations in this area of the antibody gene, which create further diversity. This recombinational process that produces clonal antibody paratope diversity is called V(D)J or VJ recombination. Basically, the antibody paratope is polygenic, made up of three genes, V, D, and J. Each paratope locus is also polymorphic, such that during antibody production, one allele of V, one of D, and one of J is chosen. These gene segments are then joined together using random genetic recombination to produce the paratope. The regions where the genes are randomly recombined together is the hyper variable region used to recognise different antigens on a clonal basis. Antibody genes also re-organize in a process called class switching that changes the one type of heavy chain Fc fragment to another, creating a different isotype of the antibody that retains the antigen-specific variable region. This allows a single antibody to be used by different types of Fc receptors, expressed on different parts of the immune system.